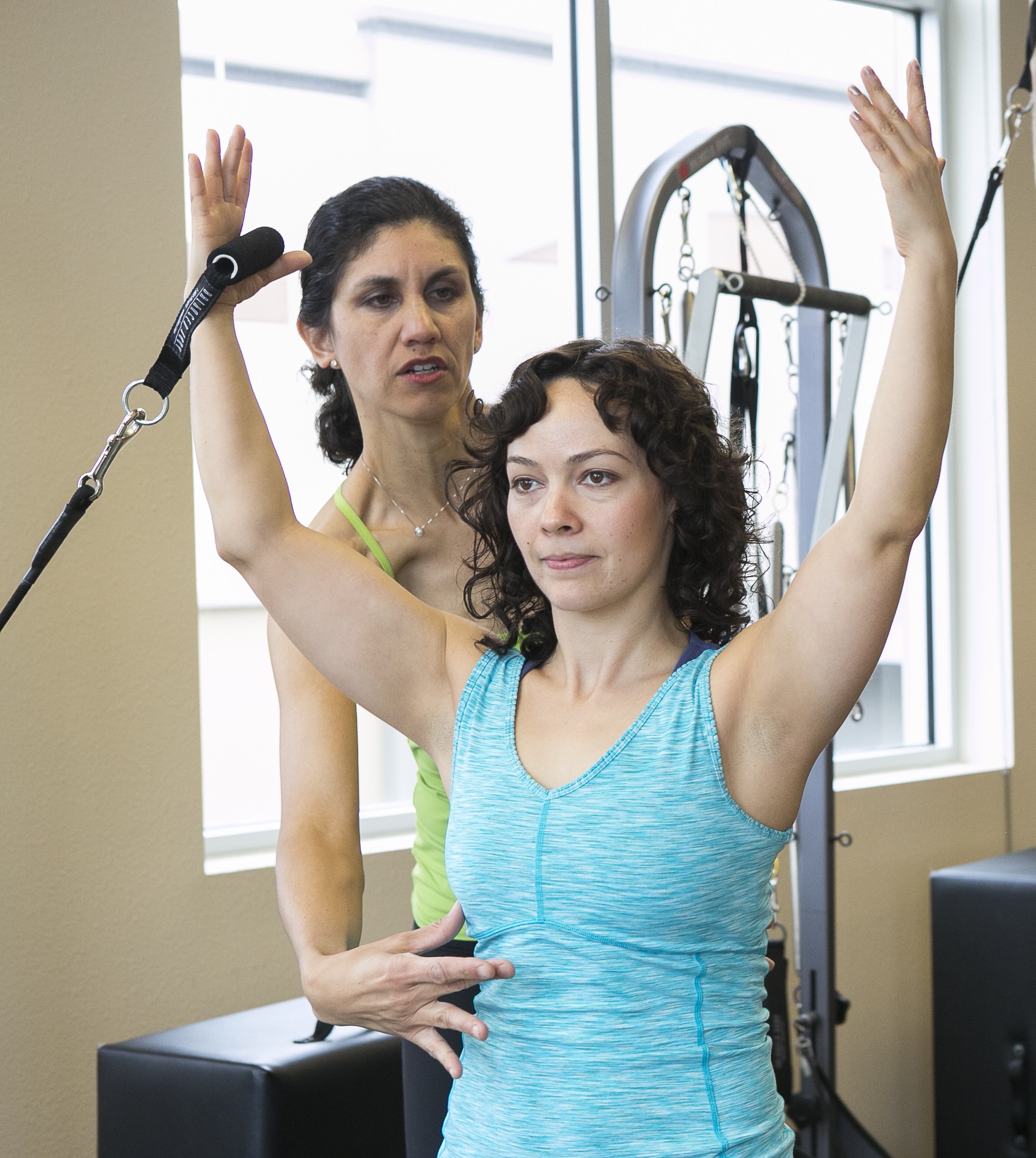|
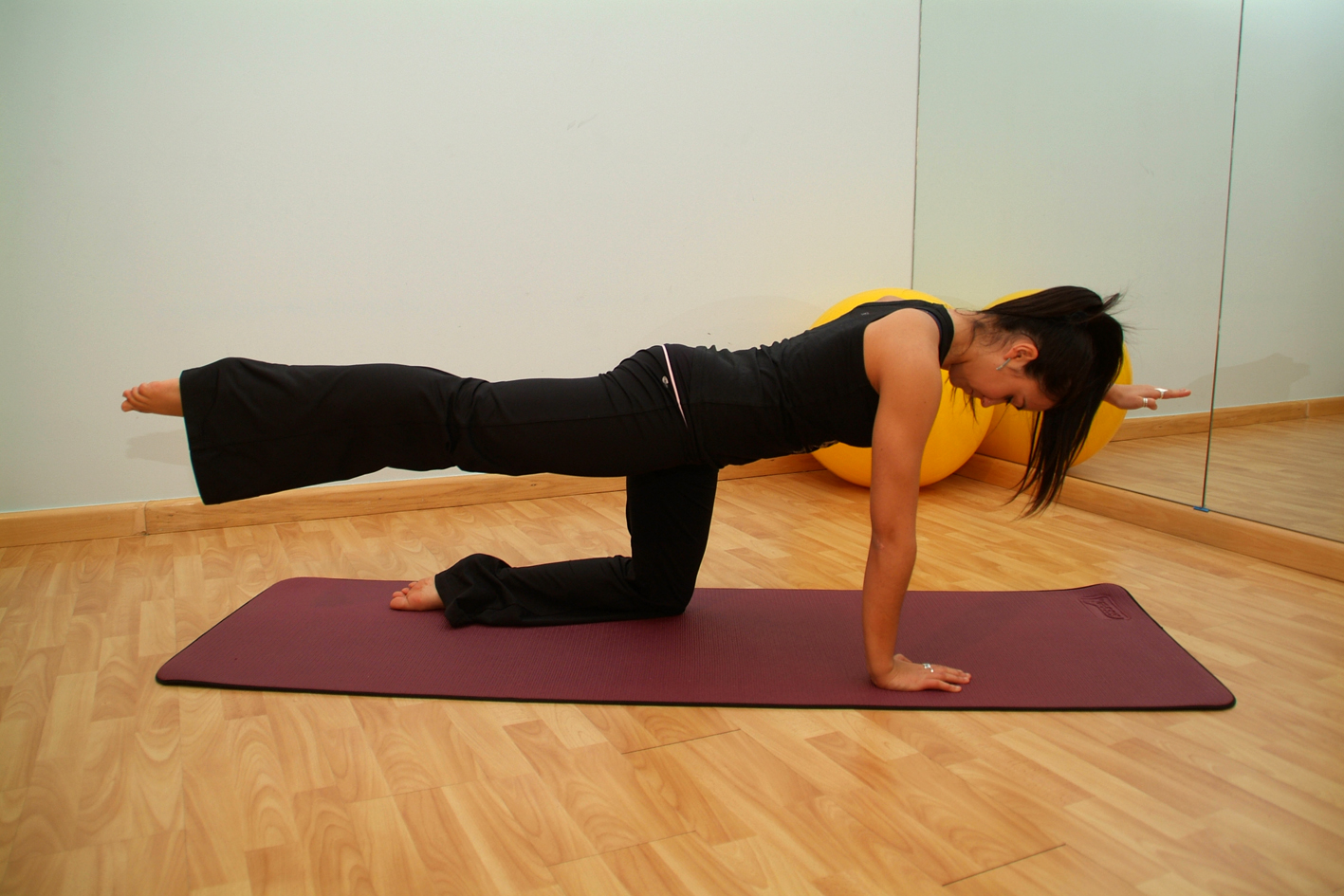
Pilates Reformer
Pilates (; ) is a type of mind-body exercise developed in the early 20th century by German physical trainer Joseph Pilates, after whom it was named. Pilates called his method "Contrology". Pilates uses a combination of around 50 repetitive exercises to spur muscle exertion. Each exercise flows from the "five essentials": breath, cervical alignment, rib and scapular stabilization, pelvic mobility, and utilization of the transversus abdominis. Each exercise is typically repeated three to five times. As of 2023, over 12 million people practice Pilates. Pilates developed in the aftermath of the late nineteenth century physical culture of exercising to alleviate ill health. There is, however, only limited evidence to support the use of Pilates to alleviate problems such as lower back pain. While studies have found that regular sessions improve balance, and can help muscle conditioning in healthy adults (compared to doing no exercise), it has not been shown to be an effective trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilates 01
Pilates (; ) is a type of mind–body intervention, mind-body exercise developed in the early 20th century by German physical trainer Joseph Pilates, after whom it was named. Pilates called his method "Contrology". Pilates uses a combination of around 50 repetitive exercises to spur muscle exertion. Each exercise flows from the "five essentials": breath, cervical alignment, rib and scapular stabilization, pelvic mobility, and utilization of the transversus abdominis. Each exercise is typically repeated three to five times. As of 2023, over 12 million people practice Pilates. Pilates developed in the aftermath of the late nineteenth century physical culture of exercising to alleviate ill health. There is, however, only limited evidence to support the use of Pilates to alleviate problems such as lower back pain. While studies have found that regular sessions improve balance, and can help muscle conditioning in healthy adults (compared to doing no exercise), it has not been shown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strengthening
Chinese food therapy (, also called nutrition therapy and dietary therapy) is a mode of dieting rooted in Chinese beliefs concerning the effects of food on the human organism, and centered on concepts such as seasonal eating and in moderation. Its basic precepts are a mix of Taoist Wuxing and eight principle theory that are concepts drawn from the modern representation of traditional Chinese medicine. Food that conform to the mode are called ''yaoshan'' (). Food therapy has long been a common approach to health among Chinese people both in China and overseas, and was popularized for western readers in the 1990s with the publication of books like ''The Tao of Healthy Eating'' () and ''The Wisdom of the Chinese Kitchen'' (). Origins A number of ancient Chinese cookbooks and treatises on food (now lost) display an early Chinese interest in food, but no known focus on its medical value. The literature on "nourishing life" () integrated advice on food within broader advice on ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halasana
Halasana (; ) or Plough pose is an inverted asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. Its variations include Karnapidasana with the knees by the ears, and Supta Konasana with the feet wide apart. Etymology and origins The name Halasana comes from Sanskrit , "plough" and , "posture" or "seat". The pose is described and illustrated in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi'' as ''Lāṇgalāsana'', which also means plough pose in Sanskrit. Karnapidasana is not found in the medieval hatha yoga texts. It is described independently in Swami Vishnudevananda's 1960 ''Complete Illustrated Book of Yoga'' in the Sivananda Yoga tradition, and by B. K. S. Iyengar in his 1966 ''Light on Yoga'', implying that it may have older origins. The name comes from the Sanskrit words () meaning "ears", () meaning "to squeeze", and () meaning "posture" or "seat". File:Arair champige a reil.png, The completed pose resembles a traditional plough. File:Sritattvanidhi Lalangasana.jpg, ''Lāṇgal� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navasana
Navasana (; ), Naukasana, Boat Pose, or Paripurna Navasana (; "Full Boat Pose") is a seated asana in modern yoga as exercise Yoga as exercise is a physical activity consisting mainly of asana, postures, often connected by vinyasa, flowing sequences, sometimes accompanied by pranayama, breathing exercises, and frequently ending with savasana, relaxation lying down or .... Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit words meaning "full", meaning "boat" and meaning "posture" or "seat". The pose was illustrated in the 19th century '' Sritattvanidhi'' under the name ''Naukāsana'', also meaning boat pose. Description To enter the pose from sitting, the knees are bent, and the body's weight is shifted back until the soles of the feet lift off the ground. In the pose, the body is balanced on the sitting bones, not leaning right back on to the tailbone. The spine is lengthened to broaden and lift the chest. Preparatory poses for Navasana include the stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Yoga
Modern yoga is a wide range of yoga practices with differing purposes, encompassing in its various forms yoga philosophy derived from the Vedas, asana, physical postures derived from Hatha yoga, Bhaktiyoga, devotional and tantra-based practices, and Hindu nationalism, Hindu nation-building approaches. The scholar Elizabeth de Michelis proposed a 4-part typology of modern yoga in 2004, separating modern psychosomatic, denominational, yoga as exercise, postural, and meditational yogas. Other scholars have noted that her work stimulated research into the history, sociology, and anthropology of modern yoga, but have not all accepted her typology. They have variously emphasised modern yoga's international nature with its intercultural exchanges; its variety of beliefs and practices; its degree of continuity with older traditions, such as ancient Indian philosophy and medieval Hatha yoga; its relationship to Hinduism; its claims to provide health and fitness; and its tensions between th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Motion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformer Apparatus Pilates London
A reformer is someone who works for reform. Reformer may also refer to: *Catalytic reformer, in an oil refinery *Methane reformer, producing hydrogen * Steam reformer *Hydrogen reformer, extracting hydrogen *Methanol reformer, producing hydrogen from methanol *Kim reformer, producing syngas * Protestant Reformers *Reformers Bookshop, Australia *Reformer (Enneagram), a personality type *Pilates reformer, an exercise machine * ''The Reformers'' (film), 1916 *Reform movement Reformism is a type of social movement that aims to bring a social system, social or also a political system closer to the community's ideal. A reform movement is distinguished from more Radicalism (politics), radical social movements such as re ... *'' The Reformer'', a short-lived American newspaper published in 1837 *'' Rutherglen Reformer'', a Scottish newspaper first published in 1875 {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among many individuals. By estimating the overall risk of health risk and health system expenses over the risk pool, an insurer can develop a routine finance structure, such as a monthly premium or payroll tax, to provide the money to pay for the health care benefits specified in the insurance agreement. The benefit is administered by a central organization, such as a government agency, private business, or not-for-profit entity. According to the Health Insurance Association of America, health insurance is defined as "coverage that provides for the payments of benefits as a result of sickness or injury. It includes insurance for losses from accident, medical expense, disability, or accidental death and dismemberment". A health insurance policy i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Health (Australia)
Department may refer to: * Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility Government and military * Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, for example: **Departments of Colombia, a grouping of municipalities **Departments of France, administrative divisions three levels below the national government ** Departments of Honduras ** Departments of Peru, name given to the subdivisions of Peru until 2002 ** Departments of Uruguay * Department (United States Army), corps areas of the U.S. Army prior to World War I * Fire department, a public or private organization that provides emergency firefighting and rescue services *Ministry (government department), a specialized division of a government *Police department, a body empowered by the state to enforce the law * Department (naval) administrative/functional sub-unit of a ship's company. Other uses * ''Department'' (film), a 2012 Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core (anatomy)
The core or trunk is the axial skeleton, axial (central) part of an organism's body (biology), body. In common parlance, the term is broadly considered to be synonymous with the torso, but academically it also includes the head and neck. Functional movements are highly dependent on this part of the body, and lack of core muscular development can result in a predisposition to injury. The major muscles of the core reside in the area of the belly and the mid- and lower back (not the shoulders), and peripherally include the hips, the shoulders and the neck. Muscles Major muscles included are the pelvic floor muscles, transversus abdominis, multifidus, internal oblique, internal and external obliques, rectus abdominis, erector spinae (sacrospinalis) especially the longissimus thoracis, and the diaphragm (anatomy), diaphragm. The lumbar muscles, quadratus Lumborum (deep portion), deep rotators, as well as cervical muscles, rectus capitus anterior and lateralis, longus coli may also b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breathwork (New Age)
Breathwork is a term for various breathing practices in which the conscious control of breathing is said to influence a person's mental, emotional, or physical state, with a therapeutic effect. Background and rationale Edzard Ernst writes that breathwork (or 'rebirthing') is a form of alternative medicine first devised by Leonard Orr in the 1970s. Breathwork is the use of breathing techniques to achieve altered states of consciousness and to have a variety of effects on physical and mental well-being. Breathwork has been seen as derived from multiple spiritual and pre-scientific traditions from around the world. According to Jack Raso, ''breathwork'' is described by proponents as a multiform "healing modality" characterized by stylized breathing. Its purported design is to effect physical, emotional, and spiritual change. Such a process can allegedly "dissolve limiting programs" that are "stored" in the mind and body, and increases one's ability to handle more "energy". Breathw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systematic Review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on the topic (in the scientific literature), then analyzes, describes, critically appraises and summarizes interpretations into a refined evidence-based conclusion. For example, a systematic review of randomized controlled trials is a way of summarizing and implementing evidence-based medicine. Systematic reviews, sometimes along with meta-analyses, are generally considered the highest level of evidence in medical research. While a systematic review may be applied in the biomedical or health care context, it may also be used where an assessment of a precisely defined subject can advance understanding in a field of research. A systematic review may examine clinical tests, public health interventions, environmental interventions, social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |