|
Pierre-Joseph Van Beneden
Pierre-Joseph Van Beneden FRS FRSE FGS FZS (19 December 1809 – 8 January 1894) was a Belgian zoologist and paleontologist. He has been credited with introducing the terms " mutualism" and "commensalism" into biology in 1875 and 1876 respectively. Life Born in Mechelen, First French Empire, he studied medicine at the State University of Leuven and studied zoology in Paris under Georges Cuvier (1769–1832). In 1831, he became curator at the natural history museum in Leuven, and from 1836 until 1894, was a professor of zoology at the Catholic University of Leuven. In 1842, he became a member of the ''Académie des sciences de Belgique'', becoming its President in 1881. In 1875, he became a foreign member of the Royal Society of London, and in 1884, an Honorary Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. In 1843, he established one of the world's first marine laboratories and aquariums. He was the father of biologist Edouard van Beneden (1846–1910). Pierre-Joseph van Beneden died ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechelen
Mechelen (; ; historically known as ''Mechlin'' in EnglishMechelen has been known in English as ''Mechlin'', from where the adjective ''Mechlinian'' is derived. This name may still be used, especially in a traditional or historical context. The city's French name, ', had also been used in English in the past (in the 19th and 20th centuries); however, this has largely been abandoned. Meanwhile, the Dutch-derived ' began to be used in English increasingly from the late 20th century onwards, even while ''Mechlin'' remained still in use (for example, a ''Mechlinian'' is an inhabitant of this city or someone seen as born-and-raised there; the term is also the name of the city dialect; as an adjective ''Mechlinian'' may refer to the city or to its dialect.) is a city and municipality in the province of Antwerp in the Flemish Region of Belgium. The municipality comprises the city of Mechelen proper, some quarters at its outskirts, the hamlets of Nekkerspoel (adjacent) and Battel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of London
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, education and public engagement and fostering international and global co-operation. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by King Charles II and is the oldest continuously existing scientific academy in the world. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the society's president, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. The members of Council and the president are elected from and by its Fellows, the basic members of the society, who are themselves elected by existing Fellows. , there are about 1,700 fellows, allowed to use the postnominal title FRS (Fellow of the Royal Society) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after Tournai and Couvin. With a population of 565,039, it is the List of most populous municipalities in Belgium, most populous municipality in Belgium, and with a metropolitan population of over 1.2 million people, the country's Metropolitan areas in Belgium, second-largest metropolitan area after Brussels. Definitions of metropolitan areas in Belgium. Flowing through Antwerp is the river Scheldt. Antwerp is linked to the North Sea by the river's Western Scheldt, Westerschelde estuary. It is about north of Brussels, and about south of the Netherlands, Dutch border. The Port of Antwerp is one of the biggest in the world, ranking second in Europe after Rotterdam and List of world's busiest container ports, within the top 20 globally. The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetacean
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla that includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel themselves through the water with powerful up-and-down movements of their tail, which ends in a paddle-like fluke, using their flipper-shaped forelimbs to steer. While the majority of cetaceans live in marine environments, a small number reside solely in brackish water, brackish or fresh water. Having a cosmopolitan distribution, they can be found in some rivers and all of Earth's oceans, and many species migrate throughout vast ranges with the changing of the seasons. Cetaceans are famous for cetacean intelligence, their high intelligence, complex social behaviour, and the enormous size of some of the group's members. For example, the blue whale reaches a maximum confirmed length of and a weight of 173 tonne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Gervais
Paul Gervais (full name: François Louis Paul Gervais) (26 September 1816 – 10 February 1879) was a French palaeontologist and entomologist. Biography Gervais was born in Paris, where he obtained the diplomas of doctor of science and of medicine, and in 1835 he began palaeontological research as assistant in the laboratory of comparative anatomy at the ''Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle''. In 1841 he obtained the chair of zoology and comparative anatomy at the Faculty of Sciences in Montpellier, of which he was in 1856 appointed dean. In 1848–1852 appeared his important work ''Zoologie et paléontologie françaises'', supplementary to the palaeontological publications of Georges Cuvier and Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville; of this a second and greatly improved edition was issued in 1859. In 1865 he accepted the professorship of zoology at the Sorbonne, vacant through the death of Louis Pierre Gratiolet; this post he left in 1868 for the chair of comparative anatomy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostend
Ostend ( ; ; ; ) is a coastal city and municipality in the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It comprises the boroughs of Mariakerke, Raversijde, Stene and Zandvoorde, and the city of Ostend proper – the largest on the Belgian coast. History Middle Ages In the Early Middle Ages, Ostend was a small village built on the east-end () of an island (originally called Testerep) between the North Sea and a beach lake. Although small, the village rose to the status of "town" around 1265, when the inhabitants were allowed to hold a market and to build a market hall. The major source of income for the inhabitants was fishing. The North Sea coastline has always been rather unstable due to the power of the water. In 1395 the inhabitants decided to build a new Ostend behind large dikes and further away from the always-threatening sea. 15th–18th centuries The strategic position on the North Sea coast had major advantages for Ostend as a harbour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquarium
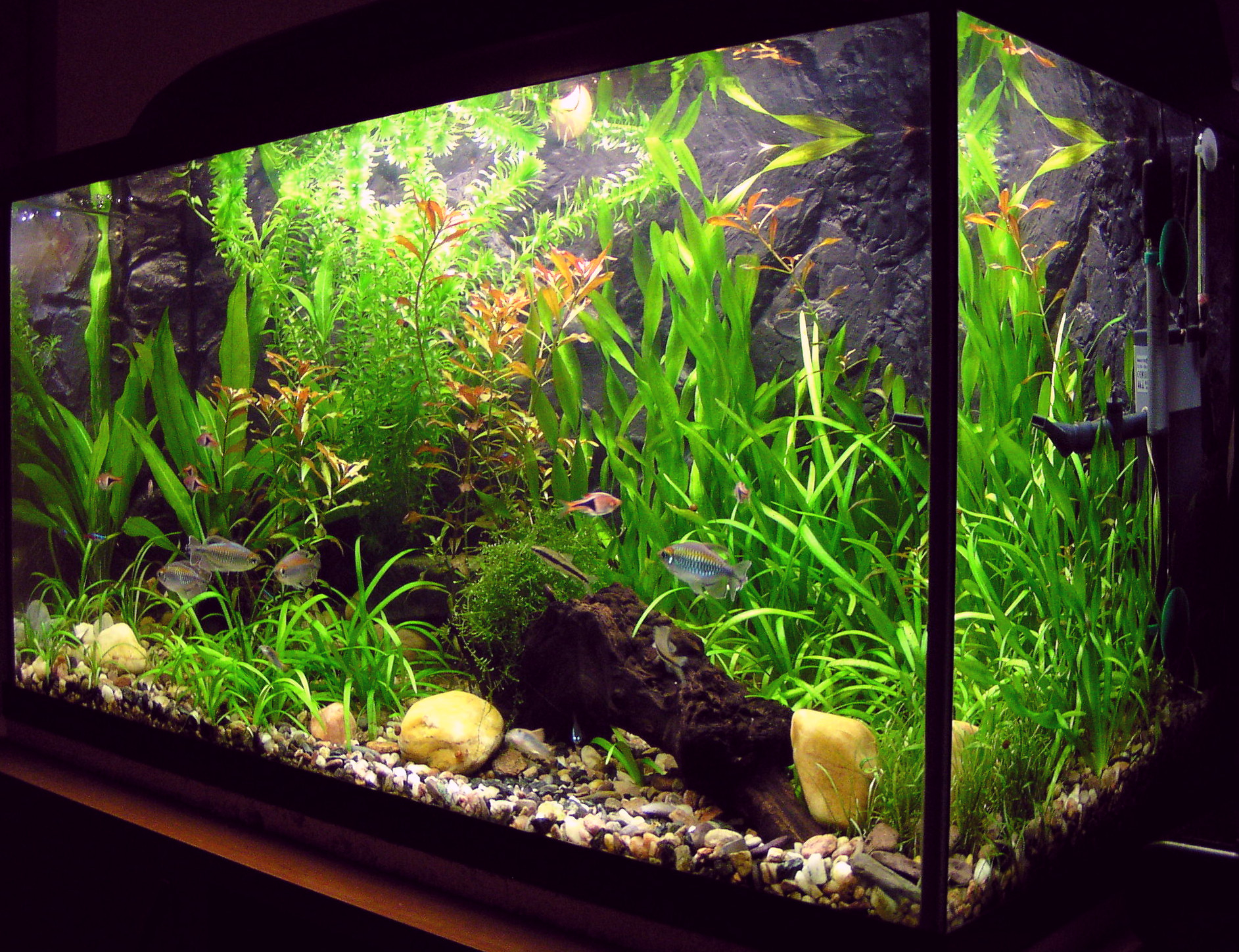
An aquarium (: aquariums or aquaria) is a vivarium of any size having at least one transparent side in which aquatic plants or animals are kept and displayed. fishkeeping, Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, aquatic reptiles, such as turtles, and aquatic plants. The term ''aquarium'', coined by English naturalist Philip Henry Gosse, combines the Latin root , meaning 'water', with the suffix , meaning 'a place for relating to'. The aquarium principle was fully developed in 1850 by the chemist Robert Warington, who explained that plants added to water in a container would give off enough oxygen to support animals, so long as the numbers of animals did not grow too large. The aquarium craze was launched in early Victorian era, Victorian England by Gosse, who created and stocked the first public aquarium at the London Zoo in 1853, and published the first manual, ''The Aquarium: An Unveiling of the Wonders of the Deep Sea'' in 1854. Small aquariums are k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Biology
Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life, organisms that inhabit the sea. Given that in biology many scientific classification, phyla, family (biology), families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment (biophysical), environment rather than on taxonomy (biology), taxonomy. A large proportion of all life, life on Earth lives in the ocean. The exact size of this "large proportion" is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world, covering approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institut De France
The ; ) is a French learned society, grouping five , including the . It was established in 1795 at the direction of the National Convention. Located on the Quai de Conti in the 6th arrondissement of Paris, the institute manages approximately 1,000 foundations, as well as museums and châteaux open for visit. It also awards prizes and subsidies, which amounted to a total of over €27 million per year in 2017. Most of these prizes are awarded by the institute on the recommendation of the . History The building was originally constructed as the Collège des Quatre-Nations by Cardinal Mazarin, as a school for students from new provinces attached to France under Louis XIV. The inscription over the façade reads "JUL. MAZARIN S.R.E. CARD BASILICAM ET GYMNAS F.C.A M.D.C.LXI", attesting that Mazarin ordered its construction in 1661. The was established on 25 October 1795, by the National Convention. On 1 January 2018, Xavier Darcos took office as the 's chancellor. Elected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
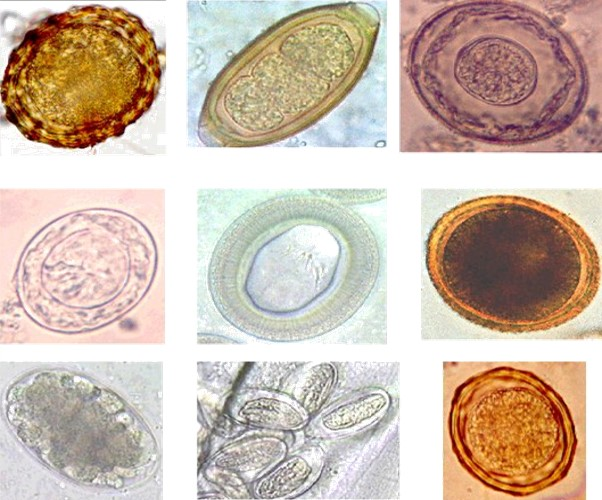
Parasitic Worms
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in their mammalian hosts for many years due to their ability to manipulate the host's immune response ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitology
Parasitology is the study of parasites, their host (biology), hosts, and the relationship between them. As a List of biology disciplines, biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question but by their way of life. This means it forms a synthesis of other disciplines, and draws on techniques from fields such as cell biology, bioinformatics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, genetics, evolution and ecology. Fields The study of these diverse organisms means that the subject is often broken up into simpler, more focused units, which use common techniques, even if they are not studying the same organisms or diseases. Much research in parasitology falls somewhere between two or more of these definitions. In general, the study of prokaryotes falls under the field of bacteriology rather than parasitology. Medical The parasitologist F. E. G. Cox noted that "Humans are hosts to nearly 300 species of parasitic worms a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leuven, Belgium
Leuven (, , ), also called Louvain (, , ), is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the sub-municipalities of Heverlee, Kessel-Lo, Leuven proper, Wilsele, Wijgmaal and part of Haasrode and Korbeek-Lo. It is the eighth largest city in Belgium, with more than 100,244 inhabitants. Leuven has been a university city since 1425. This makes it the oldest university city in the Low Countries. KU Leuven, the largest Dutch-speaking university in the world and the largest university in the Low Countries (and thus also Belgium's largest university), has its flagship campus in Leuven. The city is home of the headquarters of Anheuser-Busch InBev, the world's largest beer brewer and sixth-largest fast-moving consumer goods company. History Middle Ages The earliest mention of Leuven (''Loven'') dates from 891, when a Viking army was defeated by the Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |