|
Photobacterium Damselae Subsp. Piscicida
''Photobacterium damselae'' subsp. ''piscicida'' (previously known as ''Pasteurella piscicida'') is a gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium that causes disease in fish. Hosts Hosts of ''Photobacterium damselae'' subsp. ''piscicida'' include: * Barramundi/Asian sea bass (''Lates calcarifer'')Trung Hieu Pham, Shreesha Rao, Ta-Chih Cheng, Pei-Chi Wang, Shih-Chu Chen, The moonlighting protein fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase as a potential vaccine candidate against Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida in Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer), Developmental & Comparative Immunology,Volume 124,2021,104187,ISSN 0145-305X,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2021.104187. Disease Pasteurellosis is also described as photobacteriosis (due to the change in the taxonomic position), caused by this halophilic bacterium. It was first isolated in mortalities occurring in natural populations of white perch (''Morone americana'') and striped bass (''M. saxatilis'') in 1963 in Chesapeake Bay, USA (''S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. This self-protection method can be contrasted with that employed by Natural killer cell, Natural Killer cells. This process of engulfment and digestion is called phagocytosis; it acts to defend the host against infection and injury. Macrophages are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adapti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocyte
Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek ', "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek ''kutos,'' "hollow vessel". They are essential for fighting infections and for subsequent immunity. Phagocytes are important throughout the animal kingdom and are highly developed within vertebrates. One litre of human blood contains about six billion phagocytes. They were discovered in 1882 by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov while he was studying starfish larvae.Ilya Mechnikov retrieved on November 28, 2008. Fro ''Physiology or Medicine 1901–192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Capsule
The bacterial capsule is a large structure common to many bacteria. It is a polysaccharide layer that lies outside the cell envelope, and is thus deemed part of the outer envelope of a bacterial cell. It is a well-organized layer, not easily washed off, and it can be the cause of various diseases. The capsule—which can be found in both gram negative and gram-positive bacteria—is different from the second lipid membrane – bacterial outer membrane, which contains lipopolysaccharides and lipoproteins and is found only in gram-negative bacteria. When the amorphous viscid secretion (that makes up the capsule) diffuses into the surrounding medium and remains as a loose undemarcated secretion, it is known as a slime layer. Capsule and slime layer are sometimes summarized under the term glycocalyx. Composition Most bacterial capsules are composed of polysaccharide, but some species use other materials, such as poly-D- glutamic acid in '' Bacillus anthracis''. Because most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
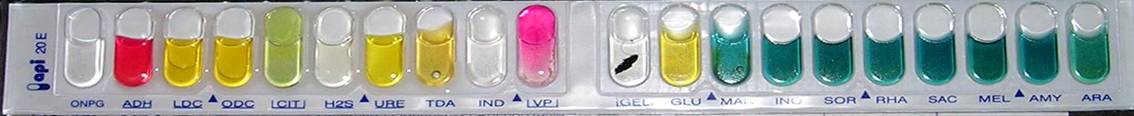
Analytical Profile Index
The analytical profile index, or API, is a classification system for bacteria based on biochemical tests. The system was developed to accelerate the speed of identifying clinically relevant bacteria. It can only be used to identify known species from an index. The data obtained are phenotypic traits. DNA sequence-based methods, including multi-locus sequence typing and even whole-genome sequencing, are increasingly used in the identification of bacterial species and strains. These newer methods can be used to complement or even replace the use of API testing in clinical settings. History The analytical profile index (API) was invented in the 1970s in the United States by Pierre Janin of Analytab Products Inc. The API test system is currently manufactured by bioMérieux. The API range introduced a standardized and miniaturized version of existing techniques, which were considered complicated to perform and difficult to read. Description Identification is only possible with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram Negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner (cytoplasmic) membrane and an outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and '' Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the antimicrobial enzyme lysozyme produced by animals as part of their innate immune system. Furthermore, the outer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently using metabolism, metabolic energy. This biological concept encompasses movement at various levels, from whole organisms to cells and subcellular components. Motility is observed in animals, microorganisms, and even some plant structures, playing crucial roles in activities such as foraging, reproduction, and cellular functions. It is genetically determined but can be influenced by environmental factors. In multicellular organisms, motility is facilitated by systems like the Nervous system, nervous and Human musculoskeletal system, musculoskeletal systems, while at the cellular level, it involves mechanisms such as amoeboid movement and flagellar propulsion. These cellular movements can be directed by external stimuli, a phenomenon known as taxis. Examples include chemotaxis (movement along chemical gradients) and phototaxis (movement in response to light). Motility also includes physiological processes like gastroi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
API Phdp
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build such a connection or interface is called an ''API specification''. A computer system that meets this standard is said to ''implement'' or ''expose'' an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation. In contrast to a user interface, which connects a computer to a person, an application programming interface connects computers or pieces of software to each other. It is not intended to be used directly by a person (the end user) other than a computer programmer who is incorporating it into software. An API is often made up of different parts which act as tools or services that are available to the programmer. A program or a programmer that uses one of these parts is said to ''call'' that portion of the API. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anorexia
Anorexia nervosa (AN), often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by Calorie restriction, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin. Individuals with anorexia nervosa have a fear of being overweight or being seen as such, despite the fact that they are typically underweight. The DSM-5 describes this perceptual symptom as "disturbance in the way in which one's body weight or shape is experienced". In research and clinical settings, this symptom is called "body image disturbance" or Body dysmorphic disorder, body dysmorphia. Individuals with anorexia nervosa also often deny that they have a problem with low weight due to their altered perception of appearance. They may weigh themselves frequently, eat small amounts, and only eat certain foods. Some patients with anorexia nervosa Binge eating, binge eat and Purging disorder, purge to influence their weight or shape. Purging can manifest a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled cell nucleus, nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Inactive fibroblasts, called 'fibrocytes', are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have less RER. Although disjointed and scattered when covering large spaces, fibroblasts often locally align in parallel clusters when crowded together. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a polarizing attachment to a basal lamina on one side, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |