|
Phon Sung People
The phon is a logarithmic unit of loudness level for tones and complex sounds. Loudness is measured in sones, a linear unit. Human sensitivity to sound is variable across different frequencies; therefore, although two different tones may present an identical sound pressure to a human ear, they may be psychoacoustically perceived as differing in loudness. The purpose of the phon is to provide a logarithmic measurement (like decibels) for perceived sound magnitude, while the primary loudness standard methods result in a linear representation. A sound with a loudness of 1 sone is judged equally loud as a 1 kHz tone with a sound pressure level of 40 decibels above 20 micropascals. The phon is psychophysically matched to a reference frequency of 1 kHz. In other words, the phon matches the sound pressure level ( SPL) in decibels of a similarly perceived 1kHz pure tone. For instance, if a sound is perceived to be equal in intensity to a 1kHz tone with an SPL of 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pure Tone
In psychoacoustics, a pure tone is a sound with a sinusoidal waveform; that is, a sine wave of constant frequency, phase-shift, and amplitude. By extension, in signal processing a single-frequency tone or pure tone is a purely sinusoidal signal (e.g., a voltage). A pure tone has the property – unique among real-valued wave shapes – that its wave shape is unchanged by linear time-invariant systems; that is, only the phase and amplitude change between such a system's pure-tone input and its output. Sine and cosine waves can be used as basic building blocks of more complex waves. As additional sine waves having different frequencies are combined, the waveform transforms from a sinusoidal shape into a more complex shape. When considered as part of a whole spectrum, a pure tone may also be called a ''spectral component''. In clinical audiology, pure tones are used for pure-tone audiometry to characterize hearing thresholds at different frequencies. Sound localization is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Units Of Sound
Unit may refer to: General measurement * Unit of measurement, a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law **International System of Units (SI), modern form of the metric system **English units, historical units of measurement used in England up to 1824 **Unit of length Science and technology Physical sciences * Natural unit, a physical unit of measurement * Geological unit or rock unit, a volume of identifiable rock or ice * Astronomical unit, a unit of length roughly between the Earth and the Sun Chemistry and medicine * Equivalent (chemistry), a unit of measurement used in chemistry and biology * Unit, a vessel or section of a chemical plant * Blood unit, a measurement in blood transfusion * Enzyme unit, a measurement of active enzyme in a sample * International unit, a unit of measurement for nutrients and drugs Mathematics * Unit number, the number 1 * Unit, identity element * Unit (ring theory), an element that is invertib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
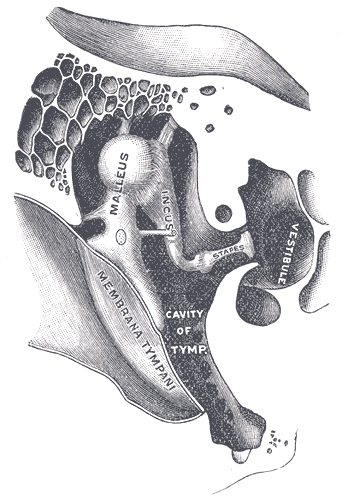
Hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduction (physiology), transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity to the movement of molecules in the world outside the organism. Both hearing and touch are types of mechanosensation. Hearing mechanism There are three main components of the human auditory system: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Outer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-weighting
A-weighting is a form of frequency weighting and the most commonly used of a family of curves defined in the International standard IEC 61672:2003 and various national standards relating to the measurement of sound pressure level. A-weighting is applied to instrument-measured sound levels in an effort to account for the relative loudness perceived by the human ear, as the ear is less sensitive to low audio frequencies. It is employed by arithmetically adding a table of values, listed by octave or third-octave bands, to the measured sound pressure levels in dB. The resulting octave band measurements are usually added (logarithmic method) to provide a single A-weighted value describing the sound; the units are written as dB(A). Other weighting sets of values – B, C, D and now Z – are discussed below. The curves were originally defined for use at different average sound levels, but A-weighting, though originally intended only for the measurement of low-level sounds (aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equal-loudness Contour
An equal-loudness contour is a measure of sound pressure level, over the frequency spectrum, for which a listener perceives a constant loudness when presented with pure steady tones. The unit of measurement for loudness levels is the phon and is arrived at by reference to equal-loudness contours. By definition, two sine waves of differing frequencies are said to have equal-loudness level measured in phons if they are perceived as equally loud by the average young person without significant hearing impairment. The Fletcher–Munson curves are one of many sets of equal-loudness contours for the human ear, determined experimentally by Harvey Fletcher and Wilden A. Munson, and reported in a 1933 paper entitled "Loudness, its definition, measurement and calculation" in the ''Journal of the Acoustical Society of America''. Fletcher–Munson curves have been superseded and incorporated into newer standards. The definitive curves are those defined in ISO 226 from the International O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international standards so that American products can be used worldwide. ANSI accredits standards that are developed by representatives of other standards organizations, government agencies, consumer groups, companies, and others. These standards ensure that the characteristics and performance of products are consistent, that people use the same definitions and terms, and that products are tested the same way. ANSI also accredits organizations that carry out product or personnel certification in accordance with requirements defined in international standards. The organization's headquarters are in Washington, D.C. ANSI's operations office is located in New York City. The ANSI annual operating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SI Unit
The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI (from French ), is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of units of measurement, system of measurement. It is the only system of measurement with official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI system is coordinated by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, which is abbreviated BIPM from . The SI comprises a coherence (units of measurement), coherent system of unit of measurement, units of measurement starting with seven SI base unit, base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (unit), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DB SPL
Sound pressure or acoustic pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient (average or equilibrium) atmospheric pressure, caused by a sound wave. In air, sound pressure can be measured using a microphone, and in water with a hydrophone. The SI unit of sound pressure is the pascal (Pa). Mathematical definition A sound wave in a transmission medium causes a deviation (sound pressure, a ''dynamic'' pressure) in the local ambient pressure, a ''static'' pressure. Sound pressure, denoted ''p'', is defined by p_\text = p_\text + p, where * ''p''total is the total pressure, * ''p''stat is the static pressure. Sound measurements Sound intensity In a sound wave, the complementary variable to sound pressure is the particle velocity. Together, they determine the sound intensity of the wave. ''Sound intensity'', denoted I and measured in W· m−2 in SI units, is defined by \mathbf I = p \mathbf v, where * ''p'' is the sound pressure, * v is the particle velocity. Acousti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Unit
A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement. For example, a length is a physical quantity. The metre (symbol m) is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. For instance, when referencing "10 metres" (or 10 m), what is actually meant is 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". The definition, agreement, and practical use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in human endeavour from early ages up to the present. A multitude of systems of units used to be very common. Now there is a global standard, the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system. In trade, weights and measures are often a subject of governmental regulation, to ensure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |