|
Phage Therapy
Phage therapy, viral phage therapy, or phagotherapy is the therapeutic use of bacteriophages for the treatment of pathogenic bacterial infections. This therapeutic approach emerged at the beginning of the 20th century but was progressively replaced by the use of antibiotics in most parts of the world after the Second World War. Bacteriophages, known as phages, are a form of virus that attach to bacterial cells and inject their genome into the cell. The bacteria's production of the viral genome interferes with its ability to function, halting the bacterial infection. The bacterial cell causing the infection is unable to reproduce and instead produces additional phages. Phages are very selective in the strains of bacteria they are effective against. Advantages include reduced side effects and reduced risk of the bacterium developing resistance, since bacteriophages are much more specific than antibiotics. They are typically harmless not only to the host organism but also to ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phage Injecting Its Genome Into Bacteria
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a phage (), is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria. The term is derived . Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biomass after prokaryotes, where up to 9x108 virions per millilitre have been found in microbial mats at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
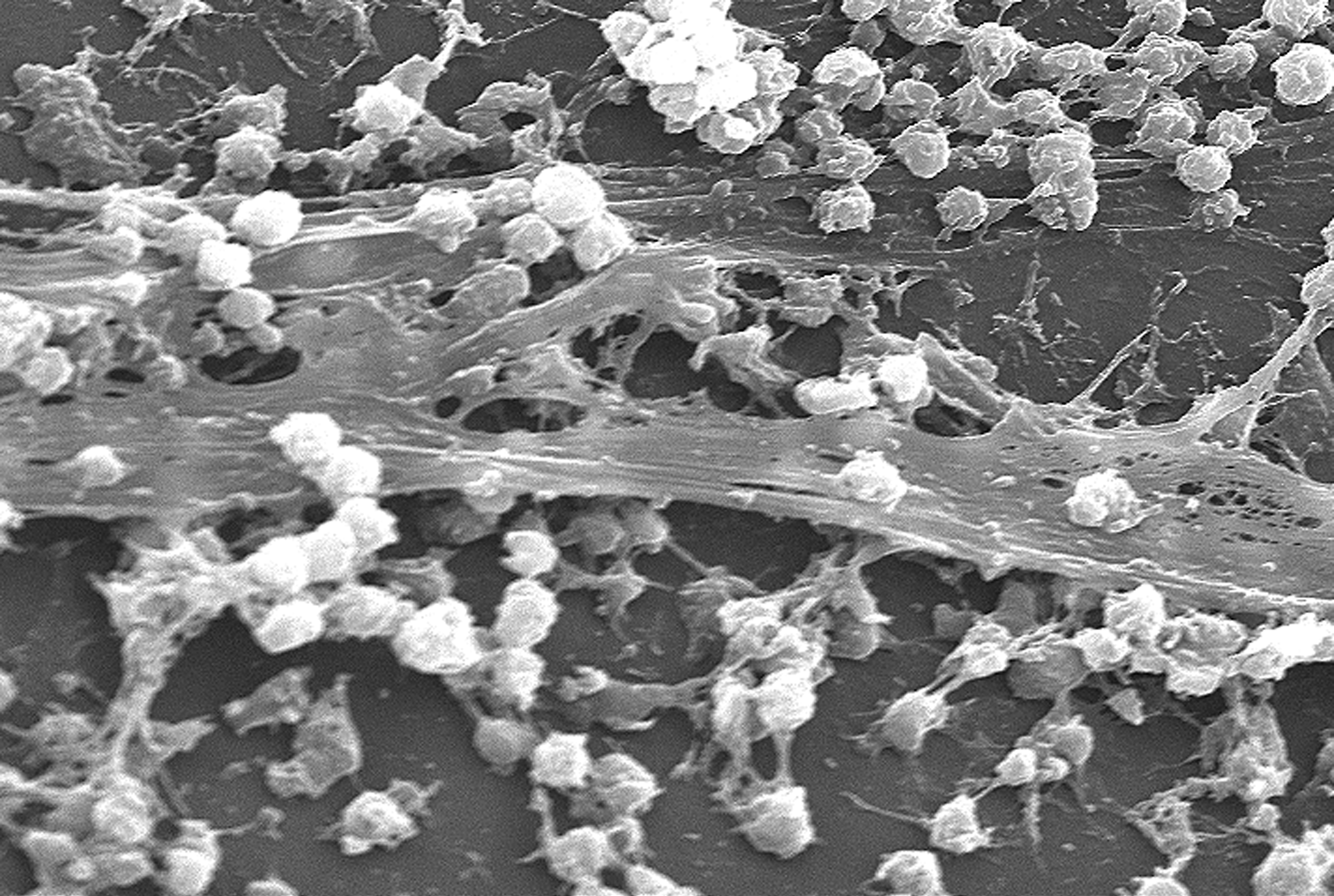
Biofilm
A biofilm is a Syntrophy, syntrophic Microbial consortium, community of microorganisms in which cell (biology), cells cell adhesion, stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric combination of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have a three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living (biotic) or non-living (abiotic) surfaces and can be common in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiology, physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Eliava
George Eliava ( Georgian — გიორგი ელიავა; January 13, 1892 – July 10, 1937) was a Georgian-Soviet microbiologist who worked with bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria). Eliava was born in Sachkhere. From 1909 to 1912 he studied medicine, at Novorossiysk University, continued his studies in Geneva until 1914, and graduated at Moscow University in 1916. The same year, he became head of the bacteriological laboratory in Trabzon, in 1917 he headed the bacteriological laboratory in Tbilisi. In 1918–1921, and again in 1926–1927, he worked at the Pasteur Institute in Paris, where he met Félix d'Hérelle, the co-discoverer of bacteriophages. Eliava got excited about the potential of bacteriophages in medical applications, and brought the research (and, eventually, d'Hérelle), to Tbilisi. In 1923, Eliava founded a bacteriological institute in Tbilisi on the basis of the laboratory he headed since 1921, to research and promote phage therapy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shigella
''Shigella'' is a genus of bacteria that is Gram negative, facultatively anaerobic, non–spore-forming, nonmotile, rod shaped, and is genetically nested within ''Escherichia''. The genus is named after Kiyoshi Shiga, who discovered it in 1897. ''Shigella'' causes disease in primates, but not in other mammals; it is the causative agent of human shigellosis. It is only naturally found in humans and gorillas. During infection, it typically causes dysentery. ''Shigella'' is a leading cause of bacterial diarrhea worldwide, with 80–165 million annual cases (estimated) and 74,000 to 600,000 deaths. It is one of the top four pathogens that cause moderate-to-severe diarrhea in African and South Asian children. Classification ''Shigella'' species are classified by three serogroups and one serotype: * Serogroup ''A'': '' S. dysenteriae'' (15 serotypes) * Serogroup ''B'': '' S. flexneri'' (9 serotypes) * Serogroup ''C'': '' S. boydii'' (19 serotypes) * Serogroup ''D'': '' S. so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix D'Hérelle
Felix may refer to: * Felix (name), people and fictional characters with the name Places * Arabia Felix is the ancient Latin name of Yemen * Felix, Spain, a municipality of the province Almería, in the autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain * St. Felix, Prince Edward Island, a rural community in Prince County, Prince Edward Island, Canada. * Felix, Ontario, an unincorporated place and railway point in Northeastern Ontario, Canada * St. Felix, South Tyrol, a village in South Tyrol, in northern Italy. * Felix, California, an unincorporated community in Calaveras County * Felix Township, Grundy County, Illinois * Felix Township, Grundy County, Iowa Music * Felix (band), a British band * Felix (musician), British DJ * Felix (rapper) (born 2000), Australian rapper and member of the K-pop boy band Stray Kids * Félix Award, a Quebec music award named after Félix Leclerc Business * Felix (pet food), a brand of cat food sold in most European countries * AB Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
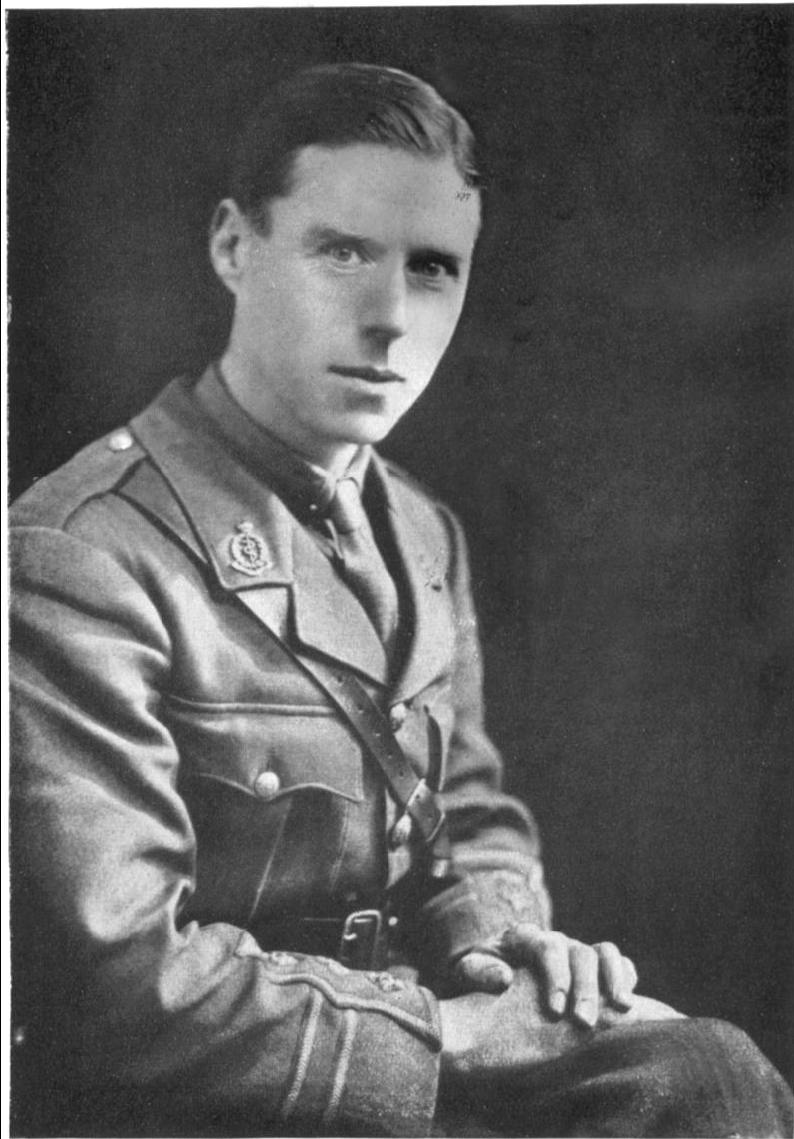
Frederick Twort
Frederick William Twort FRS (22 October 1877 – 20 March 1950) was an English bacteriologist and was the original discoverer in 1915 of bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria). He studied medicine at St Thomas's Hospital, London, was superintendent of the Brown Institute for Animals (a pathology research centre), and was a professor of bacteriology at the University of London. He researched into Johne's disease, a chronic intestinal infection of cattle, and also discovered that vitamin K is needed by growing leprosy bacteria. Early life and scientific training The eldest of the eleven children of Dr. William Henry Twort, Frederick Twort was born in Camberley, Surrey on 22 October 1877. The three eldest sons went to Tomlinson's Modern School in Woking. From 1894 Frederick studied medicine at St Thomas's Hospital, London. After qualifying in medicine (Membership of the Royal College of Surgeons, Licentiate of the Royal College of Physicians) in 1900, Twort took the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Anthracis Lyse
''Bacillus'', from Latin "bacillus", meaning "little staff, wand", is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum ''Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural ''Bacilli'' is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus belongs. ''Bacillus'' species can be either obligate aerobes which are dependent on oxygen, or facultative anaerobes which can survive in the absence of oxygen. Cultured ''Bacillus'' species test positive for the enzyme catalase if oxygen has been used or is present. ''Bacillus'' can reduce themselves to oval endospores and can remain in this dormant state for years. The endospore of one species from Morocco is reported to have survived being heated to 420 °C. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients: the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. They are not true spores (i.e., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Félix D'Hérelle
Félix d'Hérelle (25 April 1873 – 22 February 1949) was a French microbiologist. He was co-discoverer of bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) and experimented with the possibility of phage therapy. D'Hérelle has also been credited for his contributions to the larger concept of applied microbiology. d'Hérelle was a self-taught microbiologist. In 1917 he discovered that "an invisible antagonist", when added to bacteria on agar, would produce areas of dead bacteria. The antagonist, now known to be a bacteriophage, could pass through a Chamberland filter. He accurately diluted a suspension of these viruses and discovered that the highest dilutions (lowest virus concentrations), rather than killing all the bacteria, formed discrete areas of dead organisms. Counting these areas and multiplying by the dilution factor allowed him to calculate the number of viruses in the original suspension. He realised that he had discovered a new form of virus and later coined the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twort
Twort is an English surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Frederick Twort Frederick William Twort FRS (22 October 1877 – 20 March 1950) was an English bacteriologist and was the original discoverer in 1915 of bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria). He studied medicine at St Thomas's Hospital, London, was sup ... (1877–1950), English bacteriologist * Flora Twort (1893–1985), English artist and bookshop proprietor {{Surname English-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biocontrol
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of pest control, controlling pests, whether pest animals such as insects and mites, weeds, or pathogens affecting animals or phytopathology, plants by bioeffector, using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also involves an active human management role. It can be an important component of integrated pest management (IPM) programs. There are three basic strategies for biological control: classical (importation), where a natural enemy of a pest is introduced in the hope of achieving control; inductive (augmentation), in which a large population of natural enemies are administered for quick pest control; and inoculative (conservation), in which measures are taken to maintain natural enemies through regular reestablishment. Natural enemies of insects play an important part in limiting the densities of potential pests. Biological control agents such as these include Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host (biology)
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasite, parasitic, a mutualism (biology), mutualistic, or a commensalism, commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cell (biology), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, or a Fabaceae, bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) Rhizobia, nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies nutrient, food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C). However, the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |