|
Permute Instruction
Permute (and Shuffle) instructions, part of bit manipulation as well as vector processing, copy unaltered contents from a source array to a destination array, where the indices are specified by a second source array. The size (bitwidth) of the source elements is not restricted but remains the same as the destination size. There exists two important permute variants, known as gather and scatter, respectively. The gather variant is as follows: for i = 0 to length-1 dest = src ndices[i where the scatter variant is: for i = 0 to length-1 dest ndices[i = src[i] Note that unlike in memory-based Gather-scatter (vector addressing), gather-scatter all three of dest, src, and indices are ''registers'' (or parts of registers in the case of bit-level permute), not memory locations. The scatter variant can be seen to "scatter" the source elements ''across'' (into) to the destination, where the "gather" variant is gathering data ''from'' the indexed source elements. Given th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Bit Manipulation
Bit manipulation is the act of algorithmically manipulating bits or other pieces of data shorter than a word. Computer programming tasks that require bit manipulation include low-level device control, error detection and error correction, correction algorithms, data compression, encryption algorithms, and Optimization (computer science), optimization. For most other tasks, modern programming languages allow the programmer to work directly with Abstraction (computer science), abstractions instead of bits that represent those abstractions. Source code that does bit manipulation makes use of the bitwise operations: AND, OR, XOR, NOT, and possibly other operations analogous to the boolean operators; there are also bitwise operation#Bit shifts, bit shifts and operations to count ones and zeros, find high and low one or zero, set, reset and test bits, extract and insert fields, mask and zero fields, gather and scatter bits to and from specified bit positions or fields. Integer arithm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Cryptographic
Cryptography, or cryptology (from "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or '' -logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security ( data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, computer passwords, and military communications. Cryptography prior to the modern age was effectively synonymous with encryption, convert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
OpenCL
OpenCL (Open Computing Language) is a software framework, framework for writing programs that execute across heterogeneous computing, heterogeneous platforms consisting of central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), digital signal processors (DSPs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) and other processors or hardware accelerators. OpenCL specifies a programming language (based on C99) for programming these devices and application programming interfaces (APIs) to control the platform and execute programs on the OpenCL compute devices, compute devices. OpenCL provides a standard interface for parallel computing using Task parallelism, task- and Data parallelism, data-based parallelism. OpenCL is an open standard maintained by the Khronos Group, a Non-profit organization, non-profit, open standards organisation. Conformant implementations (passed the Conformance Test Suite) are available from a range of companies including AMD, Arm (company), Arm, Caden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
GNU Compiler Collection
The GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) is a collection of compilers from the GNU Project that support various programming languages, Computer architecture, hardware architectures, and operating systems. The Free Software Foundation (FSF) distributes GCC as free software under the GNU General Public License (GNU GPL). GCC is a key component of the GNU toolchain which is used for most projects related to GNU and the Linux kernel. With roughly 15 million lines of code in 2019, GCC is one of the largest free programs in existence. It has played an important role in the growth of free software, as both a tool and an example. When it was first released in 1987 by Richard Stallman, GCC 1.0 was named the GNU C Compiler since it only handled the C (programming language), C programming language. It was extended to compile C++ in December of that year. Compiler#Front end, Front ends were later developed for Objective-C, Objective-C++, Fortran, Ada (programming language), Ada, Go (programming la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
LLVM
LLVM, also called LLVM Core, is a target-independent optimizer and code generator. It can be used to develop a Compiler#Front end, frontend for any programming language and a Compiler#Back end, backend for any instruction set architecture. LLVM is designed around a language-independent specification, language-independent intermediate representation (IR) that serves as a Software portability, portable, high-level assembly language that can be optimizing compiler, optimized with a variety of transformations over multiple passes. The name ''LLVM'' originally stood for ''Low Level Virtual Machine.'' However, the project has since expanded, and the name is no longer an acronym but an orphan initialism. LLVM is written in C++ and is designed for compile-time, Linker (computing), link-time, runtime (program lifecycle phase), runtime, and "idle-time" optimization. Originally implemented for C (programming language), C and C++, the language-agnostic design of LLVM has since spawned a wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Scalable Vector Extension
AArch64, also known as ARM64, is a 64-bit version of the ARM architecture family, a widely used set of computer processor designs. It was introduced in 2011 with the ARMv8 architecture and later became part of the ARMv9 series. AArch64 allows processors to handle more memory and perform faster calculations than earlier 32-bit versions. It is designed to work alongside the older 32-bit mode, known as AArch32, allowing compatibility with a wide range of software. Devices that use AArch64 include smartphones, tablets, personal computers, and servers. The AArch64 architecture has continued to evolve through updates that improve performance, security, and support for advanced computing tasks. AArch64 Execution state In ARMv8-A, ARMv8-R, and ARMv9-A, an "Execution state" defines key characteristics of the processor’s environment. This includes the number of bits used in the primary processor registers, the supported instruction sets, and other aspects of the processor's execution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
PowerPC G4
PowerPC G4 is a designation formerly used by Apple Inc., Apple to describe a ''fourth generation'' of 32-bit PowerPC microprocessors. Apple has applied this name to various (though closely related) processor models from Freescale Semiconductor, Freescale, a former part of Motorola. Motorola and Freescale's internal name of this family of processors is PowerPC 74xx. Macintosh computers such as the PowerBook G4 and iBook, iBook G4 laptops and the Power Mac G4 and Power Mac G4 Cube desktops all took their name from the processor. PowerPC G4 microprocessors were also used in the eMac, first-generation Xserves, first-generation Mac Minis, and the iMac G4 before the introduction of the PowerPC 970. Apple completely phased out the G4 series for desktop models after it selected the 64-bit IBM-produced PowerPC 970 processor as the basis for its PowerPC G5 series. The last desktop model that used the G4 was the Mac Mini. The last portable to use the G4 was the iBook G4, which was replaced b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
AVX-512
AVX-512 are 512-bit extensions to the 256-bit Advanced Vector Extensions SIMD instructions for x86 instruction set architecture (ISA) proposed by Intel in July 2013, and first implemented in the 2016 Intel Xeon Phi x200 (Knights Landing), and then later in a number of AMD and other Intel CPUs ( see list below). AVX-512 consists of multiple extensions that may be implemented independently. This policy is a departure from the historical requirement of implementing the entire instruction block. Only the core extension AVX-512F (AVX-512 Foundation) is required by all AVX-512 implementations. Besides widening most 256-bit instructions, the extensions introduce various new operations, such as new data conversions, scatter operations, and permutations. The number of AVX registers is increased from 16 to 32, and eight new "mask registers" are added, which allow for variable selection and blending of the results of instructions. In CPUs with the vector length (VL) extension—included in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Power ISA
Power ISA is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) currently developed by the OpenPOWER Foundation, led by IBM. It was originally developed by IBM and the now-defunct Power.org industry group. Power ISA is an evolution of the PowerPC ISA, created by the mergers of the core PowerPC ISA and the optional Book E for embedded applications. The merger of these two components in 2006 was led by Power.org founders IBM and Freescale Semiconductor. Prior to version 3.0, the ISA is divided into several categories. Processors implement a set of these categories as required for their task. Different classes of processors are required to implement certain categories, for example a server-class processor includes the categories: ''Base'', ''Server'', ''Floating-Point'', ''64-Bit'', etc. All processors implement the Base category. Power ISA is a RISC load/store architecture. It has multiple sets of registers: * ''32'' × 32-bit or 64-bit general- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel computer, parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneously. SIMD can be internal (part of the hardware design) and it can be directly accessible through an instruction set architecture (ISA), but it should not be confused with an ISA. Such machines exploit Data parallelism, data level parallelism, but not Concurrent computing, concurrency: there are simultaneous (parallel) computations, but each unit performs exactly the same instruction at any given moment (just with different data). A simple example is to add many pairs of numbers together, all of the SIMD units are performing an addition, but each one has different pairs of values to add. SIMD is particularly applicable to common tasks such as adjusting the contrast in a digital image or adjusting the volume of digital audio. Most modern Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
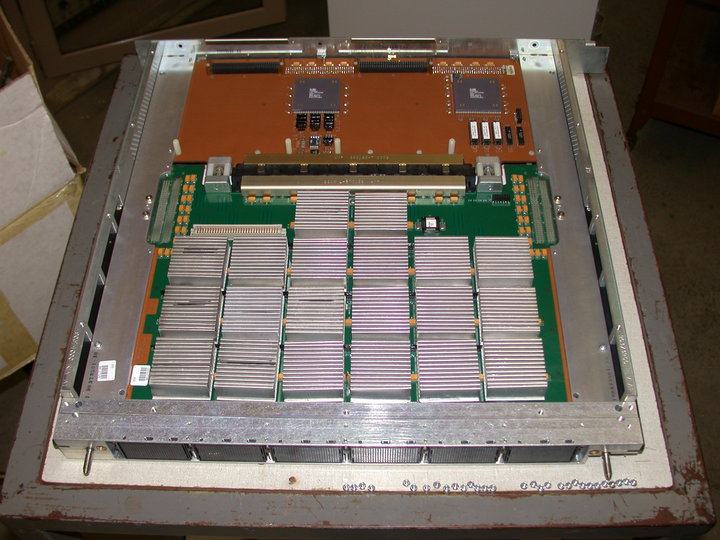 |
Vector Processing
In computing, a vector processor or array processor is a central processing unit (CPU) that implements an instruction set where its Instruction (computer science), instructions are designed to operate efficiently and effectively on large Array data structure, one-dimensional arrays of data called ''vectors''. This is in contrast to scalar processors, whose instructions operate on single data items only, and in contrast to some of those same scalar processors having additional single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) or SIMD within a register (SWAR) Arithmetic Units. Vector processors can greatly improve performance on certain workloads, notably numerical simulation, Data compression, compression and similar tasks. Vector processing techniques also operate in video game console, video-game console hardware and in graphics accelerators. Vector machines appeared in the early 1970s and dominated supercomputer design through the 1970s into the 1990s, notably the various Cray platforms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |