|
People's Guard (1942–1944)
The People's Guard (GL; ; ) was a communist partisan force of the Polish Workers' Party (PPR) active in Occupied Poland during World War II from 1942 to 1944. The ''Gwardia Ludowa'' was established with sponsorship from the Soviet Union to support the Red Army and Polish communists against Nazi Germany. It became the largest partisan force in Poland which refused to join the structures of the Polish Underground State loyal to the London-based Polish government-in-exile. The ''Gwardia Ludowa'' was incorporated into the larger ''Armia Ludowa'' in January 1944. Background The ''Gwardia Ludowa'' was created on 6 January 1942 with military aid from the Red Army, with the availability of firearms led to it swiftly reaching a strength of 3,000 fighters. It was connected to the NKVD, the intelligence services of the Soviet Union, to the point that some of its military actions were commanded by NKVD colonels. It was tasked with fighting against Nazi Germany by means of partisan warfare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armia Ludowa
The People's Army (AL; ; ) was a communist partisan force of the Polish Workers' Party (PPR) active in Occupied Poland during World War II from January to July 1944. It was created on the order of the Soviet-backed State National Council to fight against Nazi Germany and support the Red Army against the German forces in Poland. The ''Armia Ludowa'' was formed from the '' Gwardia Ludowa'' ("People's Guard") to aid the creation of a pro-Soviet communist government in Poland and, along with the National Armed Forces, refused to join the structures of the Polish Underground State and Home Army. It participated in a number of uprisings and supported Red Army offensives through Poland. The ''Armia Ludowa'' became part of the new Polish People's Army of the Soviet Polish Armed Forces in the East after seven months of existence. The ''Armia Ludowa'' was heroized in the Polish People's Republic with its size and actions being exaggerated in propaganda in communist Poland. Since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
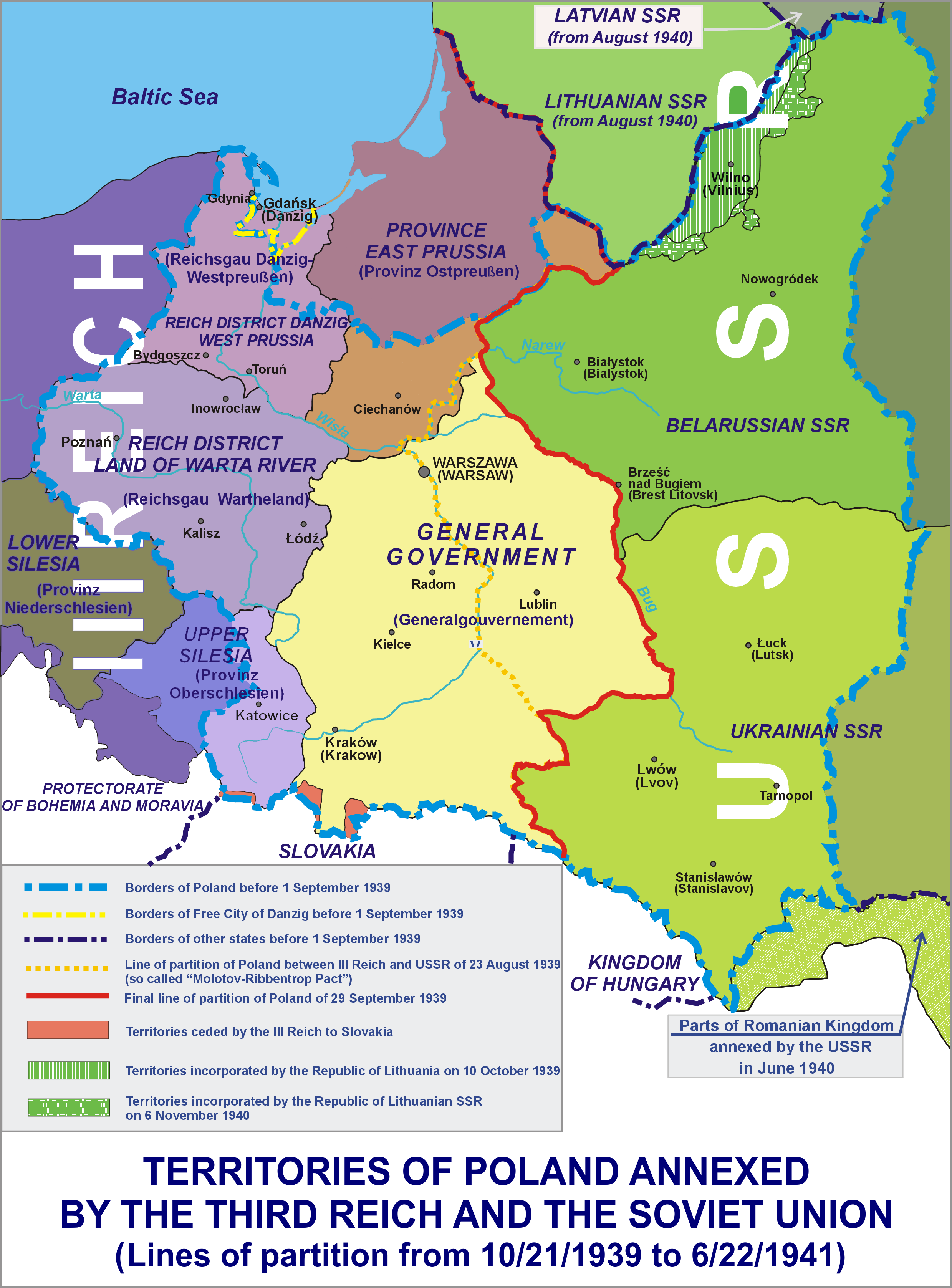
Occupation Of Poland (1939–1945)
During World War II, Poland was occupied by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union following the invasion in September 1939, and it was formally concluded with the defeat of Germany by the Allies in May 1945. Throughout the entire course of the occupation, the territory of Poland was divided between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union (USSR), both of which intended to eradicate Poland's culture and subjugate its people. In the summer-autumn of 1941, the lands which were annexed by the Soviets were overrun by Germany in the course of the initially successful German attack on the USSR. After a few years of fighting, the Red Army drove the German forces out of the USSR and crossed into Poland from the rest of Central and Eastern Europe. Sociologist Tadeusz Piotrowski argues that both occupying powers were hostile to the existence of Poland's sovereignty, people, and the culture and aimed to destroy them. Before Operation Barbarossa, Germany and the Soviet Union coordinated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a Warsaw metropolitan area, greater metropolitan area of 3.27 million residents, which makes Warsaw the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 6th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises List of districts and neighbourhoods of Warsaw, 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is classified as an Globalization and World Cities Research Network#Alpha 2, alpha global city, a major political, economic and cultural hub, and the country's seat of government. It is also the capital of the Masovian Voivodeship. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radom
Radom is a city in east-central Poland, located approximately south of the capital, Warsaw. It is situated on the Mleczna River in the Masovian Voivodeship. Radom is the fifteenth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest in its province with a population of 196,918 (30.06.2023) Radom was a significant center of administration, having served as seat of the Polish Crown Council which ratified the Pact of Vilnius and Radom between Lithuania and Poland in 1401. The Nihil novi and Łaski's Statute were adopted by the Sejm at Radom's Royal Castle in 1505. In 1976, it was a center of the June 1976 protests. Despite being part of the Masovian Voivodeship, the city historically belongs to Lesser Poland. The city is home to the biennial Radom Air Show, the largest air show in the country, held during the last weekend of August. "Radom" is also the popular unofficial name for a semiautomatic FB Vis pistol, which was produced from 1935 to 1944 by Radom's Łucznik Arms Factory. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piotrków Trybunalski
Piotrków Trybunalski (; also known by #Etymology, alternative names), often simplified to Piotrków, is a city in central Poland with 71,252 inhabitants (2021). It is the capital of Piotrków County and the second-largest city in the Łódź Voivodeship. Founded in the late Middle Ages, Piotrków was once a Royal city in Poland, royal city and holds an important place in Polish history; the first Sejm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, parliament sitting was held here in the 15th century. It then became the seat of a Crown Tribunal, the highest court of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The city also hosted one of Poland's oldest History of Jews in Poland, Jewish communities, which was entirely destroyed by the Holocaust. The old town in Piotrków features many historical and architectural monuments, including tenements, churches, synagogues and the medieval Piotrków Trybunalski Castle, Royal Castle. Etymology and other names According to tradition, but not confirmed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonel
Colonel ( ; abbreviated as Col., Col, or COL) is a senior military Officer (armed forces), officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations. In the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of a regiment in an army. Modern usage varies greatly, and in some cases, the term is used as an Colonel (title), honorific title that may have no direct relationship to military. In some smaller military forces, such as those of Monaco or the Holy See, Vatican, colonel is the highest Military rank, rank. Equivalent naval ranks may be called Captain (naval), captain or ship-of-the-line captain. In the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth's air force ranking system, the equivalent rank is group captain. History and origins By the end of the late medieval period, a group of "companies" was referred to as a "column" of an army. According to Raymond Oliver, , the Spanish began explicitly reorganizing part of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence Service
An intelligence agency is a government agency responsible for the collection, analysis, and exploitation of information in support of law enforcement, national security, military, public safety, and foreign policy objectives. Means of information gathering are both overt and covert and may include espionage, communication interception, cryptanalysis, cooperation with other institutions, and evaluation of public sources. The assembly and propagation of this information is known as intelligence analysis or intelligence assessment. Objectives Intelligence agencies can provide the following services for their national governments. * Give early warning of impending crisis; * Serve national and international crisis management by helping to discern the intentions of current or potential opponents; * Inform national defense planning and military operations, known as military intelligence; * Protect sensitive information secrets, both of their own sources and activities, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (, ), abbreviated as NKVD (; ), was the interior ministry and secret police of the Soviet Union from 1934 to 1946. The agency was formed to succeed the Joint State Political Directorate (OGPU) secret police organization, and thus had a monopoly on intelligence and state security functions. The NKVD is known for carrying out political repression and the Great Purge under Joseph Stalin, as well as counterintelligence and other operations on the Eastern Front of World War II. The head of the NKVD was Genrikh Yagoda from 1934 to 1936, Nikolai Yezhov from 1936 to 1938, Lavrentiy Beria from 1938 to 1946, and Sergei Kruglov in 1946. First established in 1917 as the NKVD of the Russian SFSR, the ministry was tasked with regular police work and overseeing the country's prisons and labor camps. It was disbanded in 1930, and its functions dispersed among other agencies before being reinstated as a commissariat of the Soviet Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firearm
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions). The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes containing gunpowder and pellet projectiles were mounted on spears to make the portable fire lance, operable by a single person, which was later used effectively as a shock weapon in the siege of De'an in 1132. In the 13th century, fire lance barrels were replaced with metal tubes and transformed into the metal-barreled hand cannon. The technology gradually spread throughout Eurasia during the 14th century. Older firearms typically used black powder as a propellant, but modern firearms use smokeless powder or other explosive propellants. Most modern firearms (with the notable exception of smoothbore shotguns) have rifled barrels to impart spin to the projectile for improved flight stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Government-in-exile
The Polish government-in-exile, officially known as the Government of the Republic of Poland in exile (), was the government in exile of Poland formed in the aftermath of the Invasion of Poland of September 1939, and the subsequent Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), occupation of Poland by Nazi Germany, Germany, the Soviet Union, and the Slovak Republic (1939-1945), Slovak Republic, which brought to an end the Second Polish Republic. Despite the occupation of Poland by hostile powers, the government-in-exile exerted considerable influence in Poland during World War II through the structures of the Polish Underground State and its military arm, the Armia Krajowa (Home Army) resistance. Abroad, under the authority of the government-in-exile, Polish military units that had escaped the occupation fought under their own commanders as part of Allies of World War II, Allied forces in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. After the war, as the Polish territory came under the control o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Western Europe, with a population of 14.9 million. London stands on the River Thames in southeast England, at the head of a tidal estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for nearly 2,000 years. Its ancient core and financial centre, the City of London, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as Londinium and has retained its medieval boundaries. The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has been the centuries-long host of Government of the United Kingdom, the national government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. London grew rapidly 19th-century London, in the 19th century, becoming the world's List of largest cities throughout history, largest city at the time. Since the 19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Underground State
The Polish Underground State (, also known as the Polish Secret State) was a single political and military entity formed by the union of resistance organizations in occupied Poland that were loyal to the Government of the Republic of Poland in exile in London. The first elements of the Underground State were established in the final days of the German and Soviet invasion of Poland, in late September 1939. The Underground State was perceived by supporters as a legal continuation of the pre-war Republic of Poland (and its institutions) that waged an armed struggle against the country's occupying powers: Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. The Underground State encompassed not only military resistance, one of the largest in the world, but also civilian structures, such as justice, education, culture and social services. Although the Underground State enjoyed broad support throughout much of the war, it was not supported or recognized by the communists and some of the right-w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |