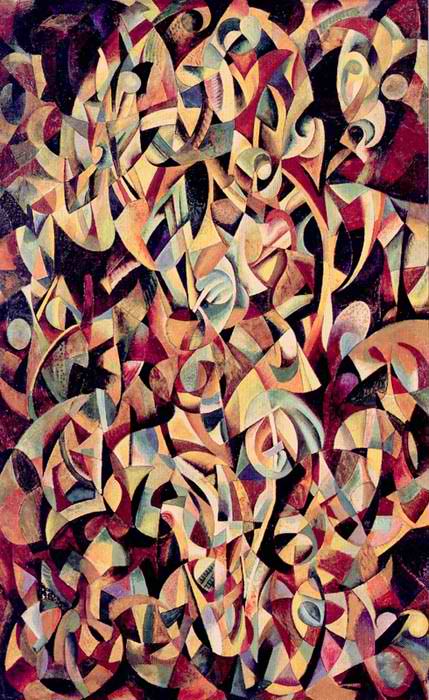|
People's Commissariat For Education
The People's Commissariat for Education (or Narkompros; , directly translated as the "People's Commissariat for Enlightenment") was the Soviet agency charged with the administration of public education and most other issues related to culture. In 1946, it was transformed into the Ministry of Education. Its first head was Anatoly Lunacharsky. However he described Nadezhda Krupskaya as the "soul of Narkompros". Mikhail Pokrovsky, Dmitry Leshchenko and Evgraf Litkens also played important roles. Lunacharsky protected most of the avant-garde artists such as Vladimir Mayakovsky, Kazimir Malevich, Vladimir Tatlin and Vsevolod Meyerhold. Despite his efforts, the official policy after Joseph Stalin put him in disgrace. Narkompros had seventeen sections, in addition to the main ones related to general education, e.g., * Likbez, a section for liquidation of illiteracy, * " Profobr", a section for professional education, * Glavlit, a section for literature and publishing (also in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Commissariat
A People's Commissariat (; Narkomat) was a structure in the Soviet state (in the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, in other union and autonomous republics, in the Soviet Union) from 1917–1946 which functioned as the central executive body in charge of managing a particular field of state activity or a separate sector of the national economy; analogue of the ministry. As a rule, a People's Commissariat was headed by a People's Commissar (; Narkom), which is part of the government – the Council of People's Commissars of the appropriate level. Commissariats were created as central organs of state administration when Soviet power was established in the republics in the territory of the former Russian Empire. The number of People's Commissariats changed in accordance with the requirements of the current moment; overall it increased due to the separation of existing ones and the formation of new ones. First People's Commissariats The first People's Commissariats were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Academy Of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation; and additional scientific and social units such as libraries, publishing units, and hospitals. Peter the Great established the academy (then the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences) in 1724 with guidance from Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Gottfried Leibniz. From its establishment, the academy benefitted from a slate of foreign scholars as professors; the academy then gained its first clear set of goals from the 1747 Charter. The academy functioned as a university and research center throughout the mid-18th century until the university was dissolved, leaving research as the main pillar of the institution. The rest of the 18th century continuing on through the 19th century consisted of many published academic works from Academy scholars and a few Academy name changes, ending as The Imperial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
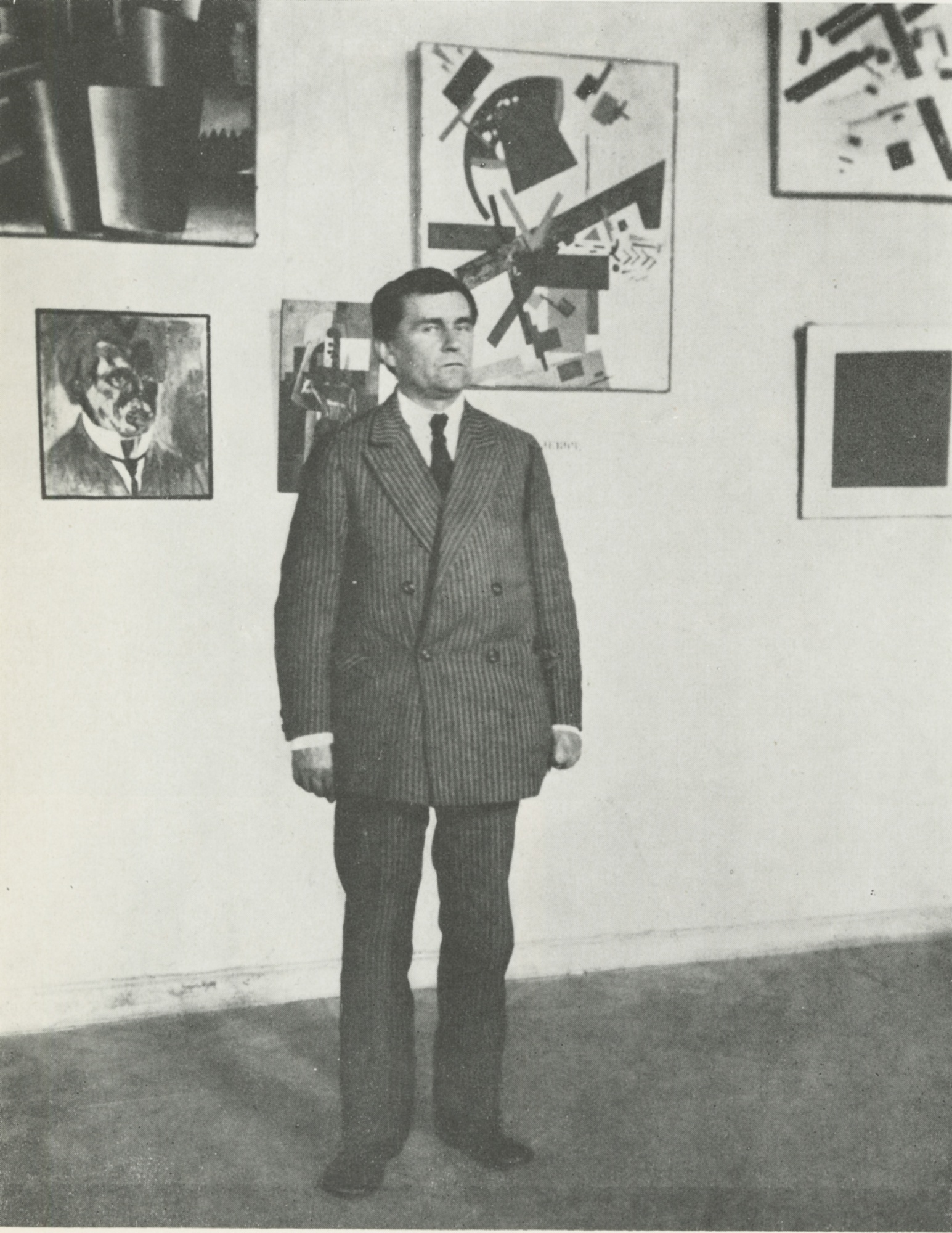
Natan Altman
Nathan Isaevich Altman (; ; – 12 December 1970) was a Russian avant-garde artist, stage designer and book illustrator. Born in Vinnytsia (now Ukraine), he worked in Russia, France, and the Soviet Union. His works combine elements of Cubo-Futurism and Suprematism. Early life Altman was born in Vinnytsia, in the Podolia Governorate of the Russian Empire (now Ukraine) to a family of Jewish merchants. He studied in a religious Jewish school (cheder), then in a public elementary school in Vinnytsia. Career From 1902 to 1907, he studied painting and sculpture at the Odessa Art School. In 1906, he had his first exhibition in Odessa. In 1910, he went to Paris, where he stayed for one year. He studied at the Free Russian Academy in Paris, working in the studio of Wladimir Baranoff-Rossine, and had contact with Marc Chagall, Alexander Archipenko, and David Shterenberg. In 1910, he became a member of the group ''Soyuz Molodyozhi'' (Union of Youth). He also befriended Jewish intellectuals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Shterenberg
David Petrovich Shterenberg (; Zhitomir – May 1, 1948 Moscow) was a Ukrainian-born Russian Soviet painter and graphic artist. Life Born to a Jewish family in Zhitomir, Ukraine, Shterenberg studied art in Odessa and then from 1906 to 1912 based himself in Paris where he studied with, amongst others, Kees van Dongen. He studied at the Académie Vitti in Paris. He was influenced by the works of Paul Cézanne and by Cubism. He made return visits to Russia but did not settle there until after the Revolution of 1917, when he was supported by his acquaintance Lunacharsky, who was the People's Commissar responsible for culture. He attended the ''Conference of Authors, Artists and Directors'' on cooperation with the Soviet Government at the Smolny Palace in Petrograd (St.Petersburg) with Nathan Altman and others . In 1917 -1918 he was a Commissar for Artistic Matters. In 1918 he had an exhibition with the group ''Jewish Society for the Furthering of the Arts'' together with Baranoff- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wassily Kandinsky
Wassily Wassilyevich Kandinsky ( – 13 December 1944) was a Russian painter and art theorist. Kandinsky is generally credited as one of the pioneers of abstract art, abstraction in western art. Born in Moscow, he spent his childhood in Odessa, where he graduated from Grekov Odesa Art School, Odessa Art School. He enrolled at the University of Moscow, studying law and economics. Successful in his profession, he was offered a professorship (chair of Roman Law) at the University of Tartu, University of Dorpat (today Tartu, Estonia). Kandinsky began painting studies (life-drawing, sketching and anatomy) at the age of 30. In 1896, Kandinsky settled in Munich, studying first at Anton Ažbe's private school and then at the Academy of Fine Arts, Munich, Academy of Fine Arts. During this time, he was first the teacher and then the partner of German artist Gabriele Münter. He returned to Moscow in 1914 after the outbreak of World War I. Following the Russian Revolution, Kand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Rodchenko
Aleksander Mikhailovich Rodchenko (; – 3 December 1956) was a Russian and Soviet artist, sculptor, photographer, and graphic designer. He was one of the founders of constructivism and Russian design; he was married to the artist Varvara Stepanova. Rodchenko was one of the most versatile constructivist and productivist artists to emerge after the Russian Revolution. He worked as a painter and graphic designer before turning to photomontage and photography. His photography was socially engaged, formally innovative, and opposed to a painterly aesthetic. Concerned with the need for analytical-documentary photo series, he often shot his subjects from odd angles—usually high above or down below—to shock the viewer and to postpone recognition. He wrote: "One has to take several different shots of a subject, from different points of view and in different situations, as if one examined it in the round rather than looked through the same key-hole again and again." He is also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olga Rozanova
Olga Vladimirovna Rozanova (also spelled Rosanova, Russian: Ольга Владимировна Розанова) (22 June 1886 – 7 November 1918, Moscow) was a Russian avant-garde artist painting in the styles of Suprematism, Neo-Primitivism, and Cubo-Futurism. Biography Early life Olga Rozanova was born in Melenki, a small town near Vladimir. Her father, Vladimir Rozanov, was a district police officer and her mother, Elizaveta Rozanova, was the daughter of an Orthodox priest. She was the family's fifth child; she had two sisters, Anna and Alevtina, and two brothers, Anatolii and Vladimir. Rozanova's father died in 1903, and her mother became the head of the household. She graduated from the Vladimir Women's Gymnasium in 1904. Due to her interest in the avant-garde movement, she moved to Moscow to study painting. Artistic career After arriving in Moscow, she attended the Bolshakov Art School, where she worked under Nikolai Ulyanov and sculptor Andrey Matveev. She aud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nadezhda Udaltsova
Nadezhda Andreevna Udaltsova (, 29 December 1885 – 25 January 1961) was a Russian avant-garde artist ( Cubist, Suprematist), painter and teacher. Early life and education Nadezhda Udaltsova was born in the city of Orel, Russia, on 29 December 1885. When she was six, her family moved to Moscow, where she graduated from high school and began her artistic career. In September 1905 Udaltsova enrolled in the art school run by Konstantin Yuon and Ivan Dudin, where she studied for two years and met fellow-students Vera Mukhina, Liubov Popova, and Aleksander Vesnin. In the spring of 1908 she traveled to Berlin and Dresden, and upon her return to Russia, she unsuccessfully applied for admission to the Moscow Institute of Painting, Sculpture, and Architecture. She also married Alexander Udaltsov, her first husband, in 1908. In 1910–11, Udaltsova studied at several private studios, among them Vladimir Tatlin's. In 1912–13 she and Popova traveled to Paris to continue their studi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilya Mashkov
Ilya Ivanovich Mashkov (; – 20 March 1944) was a Russian artist, one of the most significant and at the same time most characteristic painters of the circle of " Jack of Diamonds" (). Biography He was born in the cossack village Mikhailovskaya-on-Don (near Volgograd) in a peasant family. After arriving at Moscow in 1900 he attended the Moscow School of Painting, Sculpture and Architecture, whose teachers included Konstantin Korovin and Valentin Serov. In 1909 he was expelled from the school because of his artistic free thinking. He traveled much as a student, visiting a number of the countries of West Europe, and also Turkey and Egypt. He was the member of associations "Mir iskusstva" (Russian: Мир иску́сства) and " Jack of Diamonds". He lived in Moscow, sometimes visiting his village. His creative work reflected the colour revolution of the 20th century. The artistic innovations of Paul Cézanne and Henri Matisse were evident in his paintings which contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Arts
The visual arts are art forms such as painting, drawing, printmaking, sculpture, ceramics (art), ceramics, photography, video, image, filmmaking, design, crafts, and architecture. Many artistic disciplines such as performing arts, conceptual art, and textile arts, also involve aspects of the visual arts, as well as arts of other types. Within the visual arts, the applied arts, such as industrial design, graphic design, fashion design, interior design, and decorative art are also included. Current usage of the term "visual arts" includes fine art as well as applied art, applied or decorative arts and crafts, but this was not always the case. Before the Arts and Crafts Movement in Britain and elsewhere at the turn of the 20th century, the term 'artist' had for some centuries often been restricted to a person working in the fine arts (such as painting, sculpture, or printmaking) and not the decorative arts, crafts, or applied visual arts media. The distinction was emphasized by ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proletkult
Proletkult ( rus, Пролетку́льт, p=prəlʲɪtˈkulʲt), a portmanteau of the Russian words "proletarskaya kultura" ( proletarian culture), was an experimental Soviet artistic institution that arose in conjunction with the Russian Revolution of 1917. This organization, a federation of local cultural societies and avant-garde artists, was most prominent in the visual, literary, and dramatic fields. Proletkult aspired to radically modify existing artistic forms by creating a new, revolutionary working-class aesthetic, which drew its inspiration from the construction of modern industrial society in backward, agrarian Russia. Although funded by the People's Commissariat for Education of Soviet Russia, the Proletkult organization sought autonomy from state control, a demand which brought it into conflict with the Communist Party hierarchy and the Soviet state bureaucracy. Some top party leaders, such as Lenin, sought to concentrate state funding and retain it from such arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |