|
Pentazenium Tetraazidoborate
Pentazenium tetraazidoborate is an extremely unstable chemical compound with the formula N5 (N3)4 It is a white solid that violently explodes at room temperature. This compound has a 95.7% nitrogen content which is the second highest known of a chemical compound, exceeding even that of ammonium azide (93.3%) and 1-diazidocarbamoyl-5-azidotetrazole (89.1%), being surpassed only by hydrazoic acid (97.7%). Production and properties The production of N5 (N3)4requires a multi-step synthesis, first, hydrazoic acid and sodium borohydride is reacted in diethyl ether at -78 °C to produce sodium tetraazidoborate (which decomposes at 76 °C): :NaBH4 + 4HN3 → Na (N3)4+ 4H2 The other reactant, pentazenium hexafluoroantimonate, its produced by the reaction of N2F+ and antimony(V) fluoride. Then, two reactants that are produced are mixed at -64 °C under sulfur dioxide: :Na (N3)4+ N5SbF6 → N5 (N3)4+ NaSbF6↓ to produce the pentazenium tetraazidoborate. If heated, it decomposes into nitr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of metals refining and the burning of Sour gas, sulfur-Sour crude oil, bearing fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide is somewhat toxic to humans, although only when inhaled in relatively large quantities for a period of several minutes or more. It was known to medieval alchemy, alchemists as "volatile spirit of sulfur". Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v Point groups in three dimensions, symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance (chemistry), resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken or new bonds formed or both. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at Abundance of the chemical elements, seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element chemical bond, bond to form N2, a colourless and odourless diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant chemical species in air. Because of the volatility of nitrogen compounds, nitrogen is relatively rare in the solid parts of the Earth. It was first discovered and isolated by Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772 and independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Henry Cavendish at about the same time. The name was suggested by French chemist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Azide
Ammonium azide is the chemical compound with the formula , being the salt of ammonia and hydrazoic acid. Like other inorganic azides, this colourless crystalline salt is a powerful explosive, although it has a remarkably low sensitivity. is physiologically active and inhalation of small amounts causes headaches and palpitations. It was first obtained by Theodor Curtius in 1890, along with other azides. Structure Ammonium azide is ionic, meaning it is a salt consisting of ammonium cations and azide anions , therefore its formula is . It is a structural isomer of tetrazene. Ammonium azide contains about 93% nitrogen Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ... by mass. References * * * Further reading * Azides Explosive chemicals Ammonium compounds Nitrogen h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazoic Acid
Hydrazoic acid, also known as hydrogen azide, azic acid or azoimide, This also contains a detailed description of the contemporaneous production process. is a compound with the chemical formula . It is a colorless, volatile, and explosive liquid at room temperature and pressure. It is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen, and is therefore a pnictogen hydride. It was first isolated in 1890 by Theodor Curtius. The acid has few applications, but its conjugate base, the azide ion, is useful in specialized processes. Hydrazoic acid, like its fellow mineral acids, is soluble in water. Undiluted hydrazoic acid is dangerously explosive with a standard enthalpy of formation ΔfHo (l, 298K) = +264 kJ/mol. When dilute, the gas and aqueous solutions (<10%) can be safely prepared but should be used immediately; because of its low boiling point, hydrazoic acid is enriched upon evaporation and condensation such that dilute solutions incapable of explosion can form droplets in the headspace of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Borohydride
Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula (sometimes written as ). It is a white crystalline solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution. Sodium borohydride is a reducing agent that finds application in papermaking and dye industries. It is also used as a reagent in organic synthesis. The compound was discovered in the 1940s by H. I. Schlesinger, who led a team seeking volatile uranium compounds.Hermann I Schlesinger and Herbert C Brown (1945)Preparation of alkali metal compounds. US Patent 2461661. Granted on 1949-02-15; expired on 1966-02-15. Results of this wartime research were declassified and published in 1953. Properties The compound is soluble in alcohols, certain ethers, and water, although it slowly hydrolyzes. Sodium borohydride is an odorless white to gray-white microcrystalline powder that often forms lumps. It can be purified by recrystallization from warm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethyl Ether
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound with the chemical formula , sometimes abbreviated as . It is a colourless, highly Volatility (chemistry), volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), extremely flammable liquid. It belongs to the ether class of organic compounds. It is a common solvent and was formerly used as a general anesthetic. Production Most diethyl ether is produced as a byproduct of the vapor-phase Hydration reaction, hydration of ethylene to make ethanol. This process uses solid-supported phosphoric acid Catalysis, catalysts and can be adjusted to make more ether if the need arises: Vapor-phase Dehydration reaction, dehydration of ethanol over some Aluminium oxide, alumina catalysts can give diethyl ether yields of up to 95%. : Diethyl ether can be prepared both in laboratories and on an industrial scale by the acid ether synthesis. Uses The dominant use of diethyl ether is as a solvent. One particular application is in the production of cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentazenium
In chemistry, the pentazenium cation (also known as pentanitrogen) is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula and structure . Together with solid nitrogen polymers and the azide anion, it is one of only three poly-nitrogen species obtained in bulk quantities. History Within the High Energy Density Matter research program, run by the U.S. Air Force since 1986, systematic attempts to approach polynitrogen compounds began in 1998, when Air Force Research Laboratory at Edwards AFB became interested in researching alternatives to the highly toxic hydrazine-based rocket fuel and simultaneously funded several such proposals. Karl O. Christe, then, a senior investigator at AFRL, chose to attempt building linear out of and , based on the proposed bond structure: : The reaction succeeded, and was created in sufficient quantities to be fully characterized by NMR, IR and Raman spectroscopy in 1999. The salt was highly explosive, but when was replaced by , a stron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimony(V) Fluoride
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb F5. This colorless, viscous liquid is a strong Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed upon mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in 1:1 ratio. It is notable for its strong Lewis acidity and the ability to react with almost all known compounds. Preparation Antimony pentafluoride is prepared by the reaction of antimony pentachloride with anhydrous hydrogen fluoride:Sabina C. Grund, Kunibert Hanusch, Hans J. Breunig, Hans Uwe Wolf "Antimony and Antimony Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim :SbCl5 + 5 HF → SbF5 + 5 HCl It can also be prepared from antimony trifluoride and fluorine. Structure and chemical reactions In the gas phase, SbF5 adopts a trigonal bipyramidal structure of D3h point group symmetry (see picture). The material adopts a more complicated structure in the liquid and solid states. The liquid contains polymers wherein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron Triazide
Boron triazide, also known as triazidoborane, is a thermally unstable compound of boron and nitrogen with a nitrogen content of 92.1 % (by the standard atomic weight). Formally, it is the triazido derivative of borane and is a covalent inorganic azide. The high-energy compound, which has the propensity to undergo spontaneous explosive decomposition, was first described in 1954 by Egon Wiberg and Horst Michaud of the University of Munich. Preparation The first method is by the addition of diborane to a solution of hydrazoic acid in diethyl ether at a temperature range between −20 °C and −10 °C. This synthesis proceeds via the intermediates monoazidoborane, , and diazidoborane, . : The compound can also be obtained by passing boron tribromide vapor over solid silver azide in high vacuum. : A similar gas-phase synthesis uses the spontaneous reaction of boron trichloride with hydrazoic acid. : Properties The compound forms colorless crystals that are only stable at low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
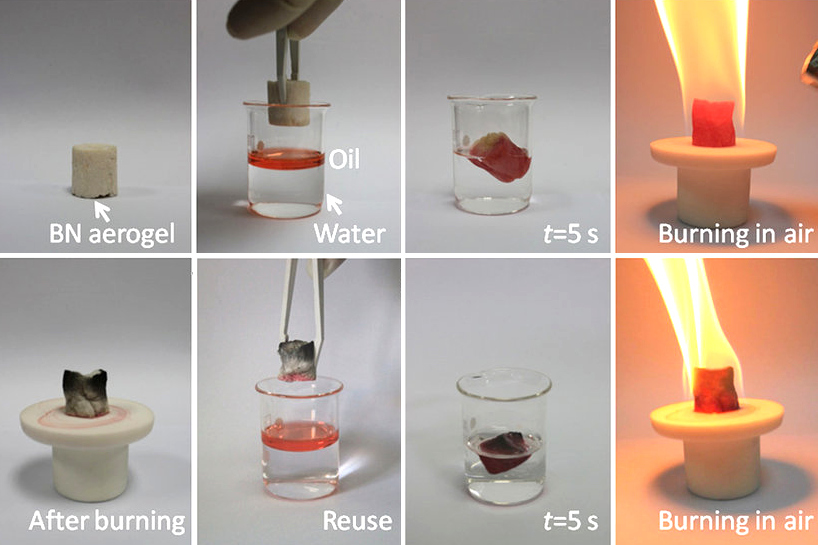
Boron Nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula B N. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal form corresponding to graphite is the most stable and soft among BN polymorphs, and is therefore used as a lubricant and an additive to cosmetic products. The cubic ( zincblende aka sphalerite structure) variety analogous to diamond is called c-BN; it is softer than diamond, but its thermal and chemical stability is superior. The rare wurtzite BN modification is similar to lonsdaleite but slightly softer than the cubic form. Because of excellent thermal and chemical stability, boron nitride ceramics are used in high-temperature equipment and metal casting. Boron nitride has potential use in nanotechnology. History Boron nitride was discovered by chemistry teacher of the Liverpool Institute in 1842 via reduction of boric acid with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |