|
Pelopia (daughter Of Thyestes)
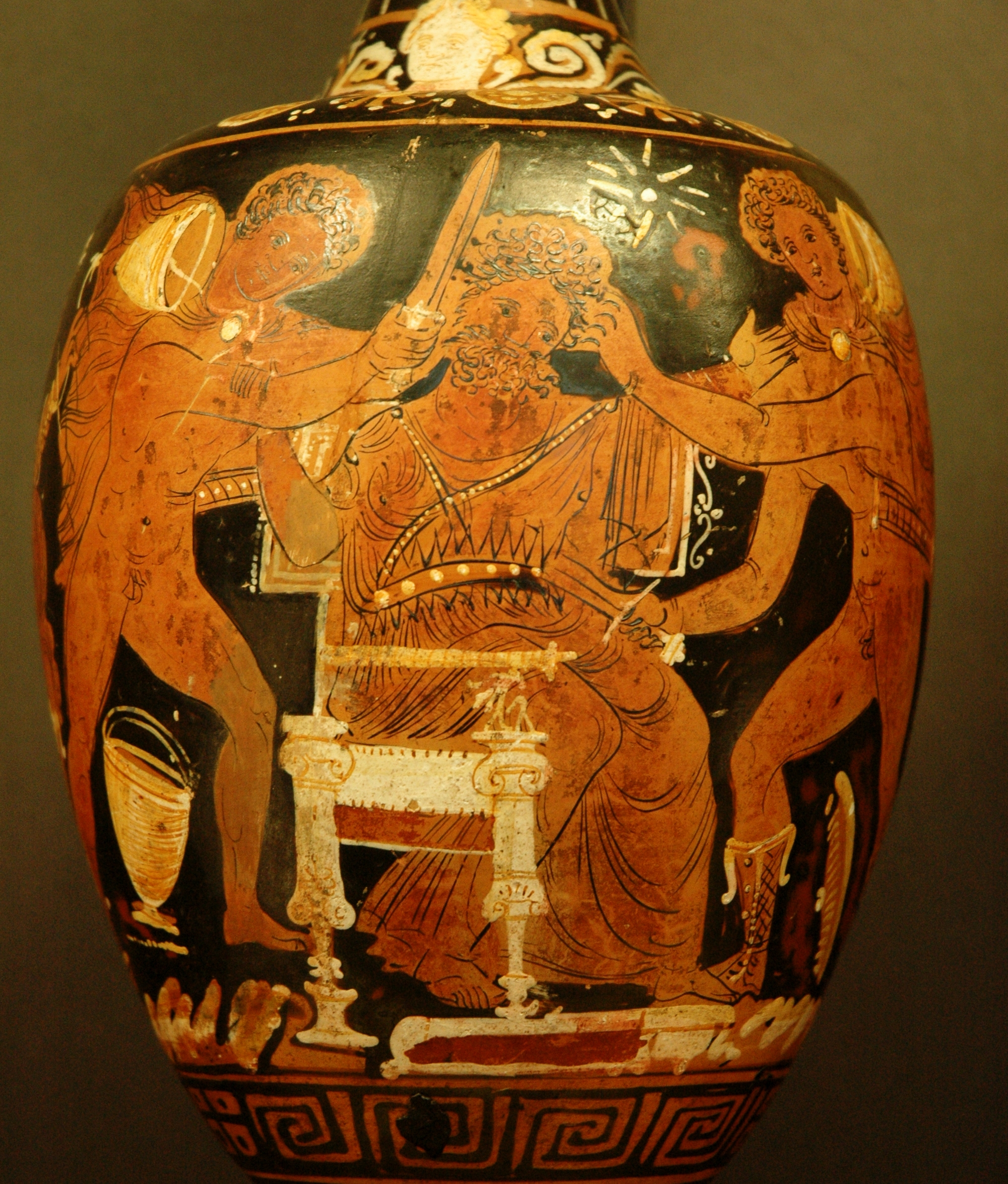
In Greek mythology, Pelopia, Pelopea or Pelopeia (Ancient Greek: Πελόπεια), less commonly known as Mnesiphane, was the daughter of Thyestes. Mythology Thyestes had been fighting with his brother, Atreus, for the throne of Mycenae for some time, as well as having an affair with Atreus' wife, Aerope. In vengeance for the affair, Atreus killed Thyestes' sons and served them to him at a banquet. Thyestes swore vengeance. An oracle then advised Thyestes that, if he had a son with his own daughter, Pelopia, that son would kill Atreus. So when Pelopia, who at the time stayed in Sicyon at the court of king Thesprotus, came to the bank of a river to wash her clothes that had been stained with blood during a sacrificial rite, Thyestes, covering his face, attacked and raped her. She managed to pull out his sword and kept it so she could recognize her offender. Soon after that, Atreus came to Thesprotus in search of his brother and, taking Pelopia for a daughter of Thesprotus, ask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories concern the ancient Greek religion's view of the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical cosmology, nature of the world; the lives and activities of List of Greek deities, deities, Greek hero cult, heroes, and List of Greek mythological creatures, mythological creatures; and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' cult (religious practice), cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of mythmaking itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral tradition, oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agamemnon
In Greek mythology, Agamemnon (; ''Agamémnōn'') was a king of Mycenae who commanded the Achaeans (Homer), Achaeans during the Trojan War. He was the son (or grandson) of King Atreus and Queen Aerope, the brother of Menelaus, the husband of Clytemnestra, and the father of Iphigenia, Iphianassa (daughter of Agamemnon), Iphianassa, Electra, Laodice (Greek myth), Laodike, Orestes and Chrysothemis. Legends make him the king of Mycenae or Argos, Peloponnese, Argos, thought to be different names for the same area. Agamemnon was killed upon his Returns from Troy, return from Troy by Clytemnestra, or in an older version of the story, by Clytemnestra's lover Aegisthus. Etymology Different etymologies have been proposed for the name ''Agamemnon'' (). According to one view, the name means 'very steadfast', 'unbowed' or 'resolute'. This is based on the interpretation of the name as a compound word comprising the elements 'very much' and 'to stay, wait; stand fast'. According to anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suicides In Greek Mythology
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or academic difficulties), relationship problems (such as breakups or divorces), or harassment and bullying. Those who have previously attempted suicide are at a higher risk for future attempts. Effective suicide prevention efforts include limiting access to methods of suicide such as firearms, drugs, and poisons; treating mental disorders and substance abuse; careful media reporting about suicide; improving economic conditions; and dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT). Although crisis hotlines, like 988 in North America and 13 11 14 in Australia, are common resources, their effectiveness has not been well studied. Suicide is the 10th leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for approximately 1.5% of total deaths. In a given year, this is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Characters In Greek Mythology
Character or Characters may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Literature * ''Character'' (novel), a 1936 Dutch novel by Ferdinand Bordewijk * ''Characters'' (Theophrastus), a classical Greek set of character sketches attributed to Theophrastus Music * ''Character'' (Dark Tranquillity album), 2005 * ''Character'' (Julia Kent album), 2013 * ''Character'', an album by Rachael Sage, 2020 * ''Characters'' (John Abercrombie album), 1977 * ''Characters'' (Stevie Wonder album), 1987 * "Character", a song by Ryokuoushoku Shakai, 2022 Types of entity * Character (arts), an agent within a work of art, including literature, drama, cinema, opera, etc. ** Character actor, an actor known for playing unusual, eccentric or interesting characters in supporting roles ** Character sketch or character, a literary description of a character type * Game character (other), various types of characters in a video game or role playing game ** Player character, as above but who is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women In Greek Mythology
A woman is an adult female human. Before adulthood, a female child or adolescent is referred to as a girl. Typically, women are of the female sex and inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and women with functional uteruses are capable of pregnancy and giving birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, '' SRY'' gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. An adult woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. These characteristics facilitate childbirth and breastfeeding. Women typically have less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscular than men. Throughout human history, traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Julius Hyginus
Gaius Julius Hyginus (; 64 BC – AD 17) was a Latin author, a pupil of the scholar Alexander Polyhistor, and a freedman of Augustus, and reputed author of the '' Fabulae'' and the '' De astronomia'', although this is disputed. Life and works Hyginus may have originated either from Spain, or from the Egyptian city of Alexandria. He was elected superintendent of the Palatine library by Augustus according to Suetonius' ''De Grammaticis'', 20. Suetonius remarks that Hyginus fell into great poverty in his old age and was supported by the historian Clodius Licinus. Hyginus was a voluminous author: his works included topographical and biographical treatises, commentaries on Helvius Cinna and the poems of Virgil, and disquisitions on agriculture and bee-keeping. All these are lost. Attributed works Two Latin works which have survived under the name of Hyginus are a mythological handbook, known as the ''Genealogiae'' or the '' Fabulae'', and an astronomical work, entitled '' D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks considered the centre of the world to be in Delphi, marked by the stone monument known as the Omphalos of Delphi (navel). According to the Suda, Delphi took its name from the Delphyne, the she-serpent (''Drakaina (mythology), drakaina'') who lived there and was killed by the god Apollo (in other accounts the serpent was the male serpent (''drakon'') Python (mythology), Python). The sacred precinct occupies a delineated region on the south-western slope of Mount Parnassus. It is now an extensive archaeological site, and since 1938 a part of Mount Parnassus, Parnassos National Park. The precinct is recognized by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site in having had a great influence in the ancient world, as evidenced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menelaus
In Greek mythology, Menelaus (; ) was a Greek king of Mycenaean (pre- Dorian) Sparta. According to the ''Iliad'', the Trojan war began as a result of Menelaus's wife, Helen, fleeing to Troy with the Trojan prince Paris. Menelaus was a central figure in the Trojan War, leading the Spartan contingent of the Greek army, under his elder brother Agamemnon, king of Mycenae. Prominent in both the ''Iliad'' and ''Odyssey'', Menelaus was also popular in Greek vase painting and Greek tragedy, the latter more as a hero of the Trojan War than as a member of the doomed House of Atreus. Description In the account of Dares the Phrygian, Menelaus was described as "of moderate stature, auburn-haired, and handsome. He had a pleasing personality." Family Menelaus was a descendant of Pelops son of Tantalus. He was the younger brother of Agamemnon, and the husband of Helen of Troy. According to the usual version of the story, followed by the ''Iliad'' and ''Odyssey'' of Homer, Agamemno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegisthus
Aegisthus (; ; also transliterated as Aigisthos, ) was a figure in Greek mythology. Aegisthus is known from two primary sources: the first is Homer's ''Odyssey'', believed to have been first written down by Homer at the end of the 8th century BC, and the second from Aeschylus's '' Oresteia'', written in the 5th century BC. Aegisthus also features heavily in the action of Euripides's '' ''Electra'''' ( 420 BC), although his character remains offstage. Family Aegisthus was the son of Thyestes and Thyestes's own daughter Pelopia, an incestuous union motivated by his father's rivalry with the house of Atreus for the throne of Mycenae. Aegisthus murdered Atreus in order to restore his father to power, ruling jointly with him, only to be driven from power by Atreus's son Agamemnon. In another version, Aegisthus was the sole surviving son of Thyestes after Atreus killed his brother's children and served them to Thyestes in a meal. While Agamemnon laid siege to Troy, his estrange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicyon
Sicyon (; ; ''gen''.: Σικυῶνος) or Sikyōn was an ancient Greek city state situated in the northern Peloponnesus between Corinth and Achaea on the territory of the present-day regional unit of Corinthia. The ruins lie just west of the modern village of Sikyona (previously Vasiliko). An ancient monarchy at the times of the Trojan War, the city was ruled by a number of tyrants during the Archaic and Classical period and became a democracy in the 3rd century BC. Sicyon was celebrated for its contributions to ancient Greek art, producing many famous painters and sculptors. In Hellenistic times it was also the home of Aratus of Sicyon, the leader of the Achaean League. Ancient history Sicyon was built on a low triangular plateau about 3 kilometres (two miles) from the Corinthian Gulf. Between the city and its port lay a fertile plain with olive groves and orchards. In Mycenean times, according to Eusebius, Sicyon had been ruled by a line of twenty-six mythical king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle
An oracle is a person or thing considered to provide insight, wise counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. If done through occultic means, it is a form of divination. Description The word ''oracle'' comes from the Latin verb ''ōrāre'', "to speak" and properly refers to the priest or priestess uttering the prediction. In extended use, ''oracle'' may also refer to the ''site of the oracle'', and the oracular utterances themselves, are called ''khrēsmoí'' (χρησμοί) in Greek. Oracles were thought to be portals through which the gods spoke directly to people. In this sense, they were different from seers (''manteis'', μάντεις) who interpreted signs sent by the gods through bird signs, animal entrails, and other various methods.Flower, Michael Attyah. ''The Seer in Ancient Greece.'' Berkeley: University of California Press, 2008. The most important oracles of Greek antiquity were Pythia (priestes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |