|
Peace–industrial Complex
In political science, political economy, political economics, and peace and conflict studies, referring to the military–industrial complex, the peace–industrial complex defines the industry and economy derived from international development, development, peacemaking, peacebuilding, and conflict resolution at both the domestic and foreign levels. While some scholars (Seiberling 1972) argue that the peace–industrial complex must oppose the military-industrial complex, others (Aberkane 2012) argue it is destined to become its natural, peaceful evolution, and further call it the "military-industrial complex 2.0". The latter argue the peace-industrial complex more precisely consists of turning military research and development into civilian technology as systematically as possible. Although it has been discussed in more recent times the concept was introduced as early as in 1969 by the U.S. Senate Committee on Government Operations. In relation to the War Against War Origin of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and Power (social and political), power, and the analysis of political activities, political philosophy, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and laws. Specialists in the field are political scientists. History Origin Political science is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political institutions, political thought and behavior, and associated constitutions and laws. As a social science, contemporary political science started to take shape in the latter half of the 19th century and began to separate itself from political philosophy and history. Into the late 19th century, it was still uncommon for political science to be considered a distinct field from history. The term "political science" was not always distinguished from political philosophy, and the modern dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
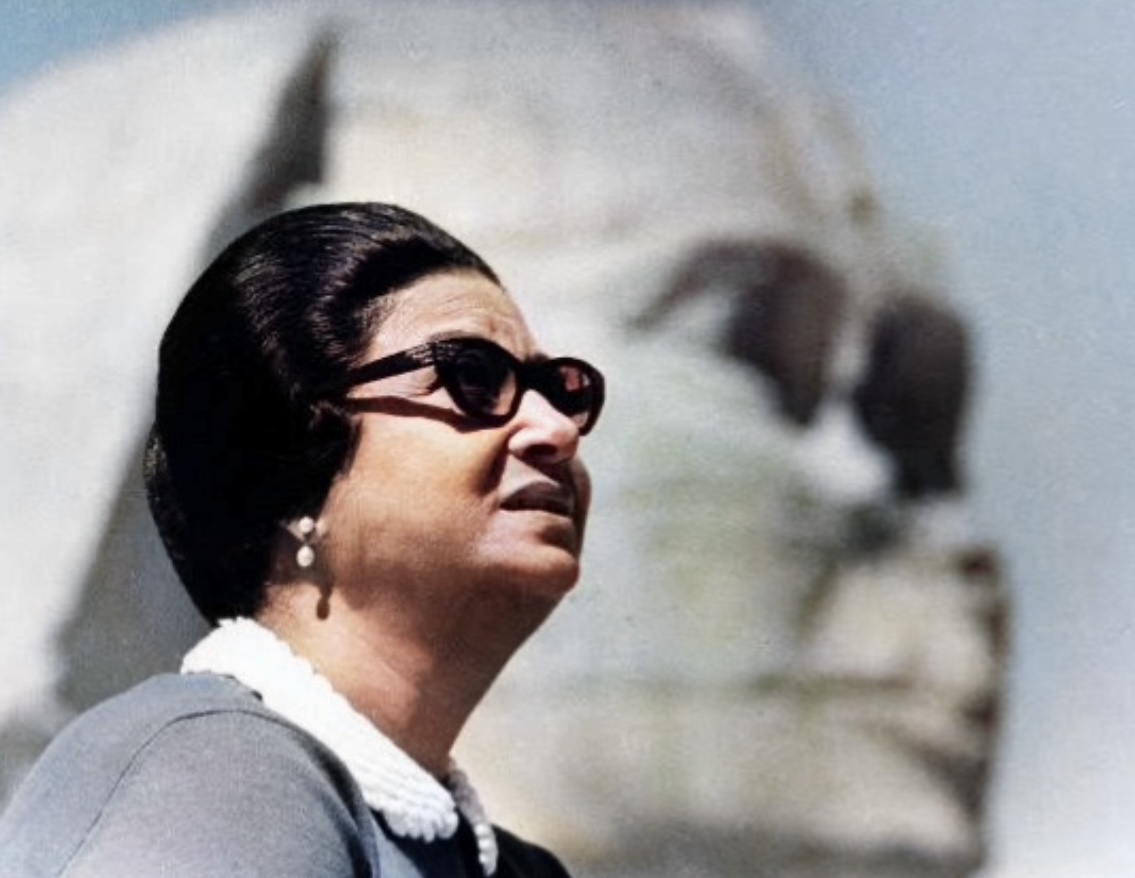
Martin Luther King, Jr
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American Baptist minister, civil rights activist and political philosopher who was a leader of the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination in 1968. He advanced civil rights for people of color in the United States through the use of nonviolent resistance and nonviolent civil disobedience against Jim Crow laws and other forms of legalized discrimination. A Black church leader, King participated in and led marches for the right to vote, desegregation, labor rights, and other civil rights. He oversaw the 1955 Montgomery bus boycott and became the first president of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC). As president of the SCLC, he led the unsuccessful Albany Movement in Albany, Georgia, and helped organize nonviolent 1963 protests in Birmingham, Alabama. King was one of the leaders of the 1963 March on Washington, where he delivered his "I H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expenditures In The United States Federal Budget
The United States federal budget consists of mandatory expenditures (which includes Medicare and Social Security), discretionary spending for defense, Cabinet departments (e.g., United States Department of Justice, Justice Department) and agencies (e.g., Securities & Exchange Commission), and interest payments on debt. This is currently over half of Government spending in the United States, U.S. government spending, the remainder coming from state and local governments. During FY2022, the federal government spent $6.3 trillion. Spending as % of GDP is 25.1%, almost 2 percentage points greater than the average over the past 50 years. Major categories of FY 2022 spending included: Medicare and Medicaid ($1.339T or 5.4% of GDP), Social Security ($1.2T or 4.8% of GDP), non-defense discretionary spending used to run federal Departments and Agencies ($910B or 3.6% of GDP), Defense Department ($751B or 3.0% of GDP), and net interest ($475B or 1.9% of GDP). Expenditures are classified a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
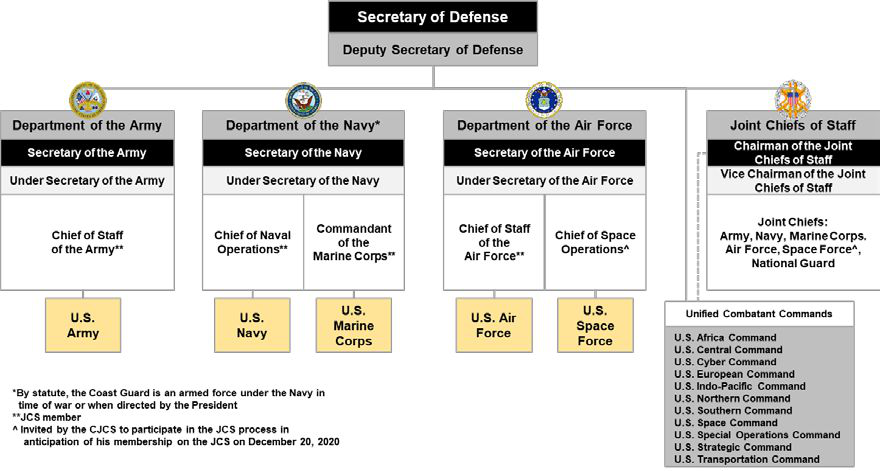
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marines, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard (United States), National Guard and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Budget Of The United States
The military budget of the United States is the largest portion of the discretionary United States federal budget, federal budget allocated to the United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense (DoD), or more broadly, the portion of the budget that goes to any military-related expenditures. The military budget pays the salaries, training, and health care of uniformed and civilian personnel, maintains arms, equipment and facilities, funds operations, and develops and buys new items. The budget funds six branches of the US military: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard, United States Air Force, Air Force, and United States Space Force, Space Force. Budget for FY2025 As of 11 March 2024 the US Department of Defense fiscal year 2025 (FY2025) budget request was $849.8billion. On 20 December 2024 the House approved a Continuing Resolution to fund DoD and DoE operations at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Pentagon
The Pentagon is the headquarters building of the United States Department of Defense, in Arlington County, Virginia, across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C. The building was constructed on an accelerated schedule during World War II. As a symbol of the United States Armed Forces, U.S. military, the phrase ''The Pentagon'' is often used as a metonym for the Department of Defense and its leadership. The building was designed by American architect George Bergstrom and built by contractor John McShain. Ground was broken on 11 September 1941, and the building was dedicated on 15 January 1943. General Brehon Somervell provided the major impetus to gain Congressional approval for the project. Colonel Leslie Groves was responsible for overseeing the project for the United States Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, which supervised it. The Pentagon is List of largest office buildings, the world's second-largest office building, with about of floor space, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weapon Of Mass Destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a biological, chemical, radiological, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill or significantly harm many people or cause great damage to artificial structures (e.g., buildings), natural structures (e.g., mountains), or the biosphere. The scope and usage of the term has evolved and been disputed, often signifying more politically than technically. Originally coined in reference to aerial bombing with chemical explosives during World War II, it has later come to refer to large-scale weaponry of warfare-related technologies, such as biological, chemical, radiological, or nuclear warfare. Early usage The first use of the term "weapon of mass destruction" on record is by Cosmo Gordon Lang, Archbishop of Canterbury, in 1937 in reference to the bombing of Guernica, Spain: At the time, nuclear weapons had not been developed fully. Japan conducted research on biological weapons, and chemical weapons had seen wide battlefield use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superpower
Superpower describes a sovereign state or supranational union that holds a dominant position characterized by the ability to Sphere of influence, exert influence and Power projection, project power on a global scale. This is done through the combined means of economic, military, technological, political, and cultural strength as well as International relations, diplomatic and soft power influence. Traditionally, superpowers are preeminent among the great powers. While a great power state is capable of exerting its influence globally, superpowers are states so influential that no significant action can be taken by the global community without first considering the positions of the superpowers on the issue. In 1944, during World War II, the term was first applied to the British Empire, the Soviet Union, and the United States. During the Cold War, the British Empire dissolved, leaving the United States and the Soviet Union to dominate world affairs. At the end of the Cold War and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Power
In politics (and particularly in international politics), soft power is the ability to co-option, co-opt rather than coerce (in contrast with hard power). It involves shaping the preferences of others through appeal and attraction. Soft power is non-coercive, using culture, political Value (ethics), values, and foreign policies to enact change. In 2012, Joseph Nye of Harvard University explained that with soft power, "the best propaganda is not propaganda", further explaining that during the Information Age, "credibility is the scarcest resource". Nye popularised the term in his 1990 book, ''Bound to Lead: The Changing Nature of American Power''. In this book he wrote: "when one country gets other countries to want what it wants might be called co-optive or soft power in contrast with the hard or command power of ordering others to do what it wants". He further developed the concept in his 2004 book, ''Soft Power: The Means to Success in World Politics''. Explanation of concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idriss Aberkane
Idriss Jamil Aberkane (; born May 23, 1986) is a French public speaker and essayist. Known for his writings and lectures on personal development, he published a particularly successful essay in 2016, titled ''Free up your mind!''. However, he has been accused of artificially inflating his resume, plagiarizing portions of one of this theses, and of using his three doctoral diplomas ( Ph.Ds) to talk about sciences that are not in his areas of expertise, including claiming to be a "doctor of neuroscience" and "teacher-researcher". The scientific accuracy of some of his statements and publications was questioned by other researchers. His support for embattled French epidemiologist Didier Raoult, and his questioning of the reliability of COVID-19 vaccines, in particular Pfizer's, has caused him to be classified as an anti-vax conspiracist. Early life and education Aberkane's parents taught mathematics at a teachers' college, and as a boy he participated in the Muslim Scouts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Times
''Nuclear Times'' was a magazine devoted to nuclear disarmament that was published from 1982 to 1992. "Devoted to education between and communication among peace activists," contributors to the magazine included "journalists, scholars, and activists." The magazine was noted for its practice of listing "organizational resources keyed to each issue's articles." ''Nuclear Times'' was characterized by ''The New York Times'' as "the peace movement's most popular magazine." The magazine is not related to a later e-newsletter published by the United Steelworkers to "share the latest news and information for atomic workers in the United States and Canada." Publication history Launch ''Nuclear Times'' was launched in October 1982, with Greg Mitchell serving as the publication's first editor. Set up as a nonprofit, members of the magazine's board of directors included Hodding Carter III, Adam Hochschild, Anne Mollegen Smith, and Thomas Powers. In a United Press International artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States House Committee On Science, Space And Technology
The Committee on Science, Space, and Technology is a standing committee, committee of the United States House of Representatives. It has jurisdiction over non-defense federal scientific research and development. More specifically, the committee has complete jurisdiction over the following federal agencies: NASA, National Science Foundation, NSF, National Institute of Standards and Technology, NIST, and the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy, OSTP. The committee also has authority over R&D activities at the United States Department of Energy, Department of Energy, the United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA, Federal Aviation Administration, FAA, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, NOAA, the United States Department of Transportation, DOT, the National Weather Service, NWS, the Department of Homeland Security, DHS and the U.S. Fire Administration. History In the wake of the Soviet Union, Soviet Sputnik program in the late 1950s, Congress cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |