|
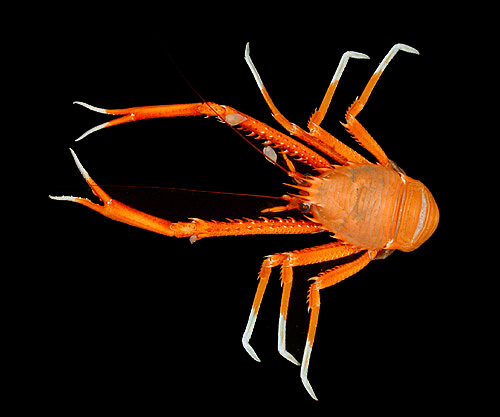
Paralomis Serrata
''Paralomis serrata'' is a species of king crab known from the Caribbean Sea. Description ''Paralomis serrata'' has a pyriform carapace which is covered dorsally in rounded granules. From the center outward, the front edge of the carapace has a short, trifid Rostrum (anatomy), rostrum whose median spine is horizontal; a pair of orbital spines whose extent is just short of the cornea; and a smaller pair of lateral spines. Behind the rostrum, the gastric region is highly pronounced, and the triangular cardiac region behind that is smaller than the gastric and branchial regions. Like the dorsal carapace, the abdomen is covered in granules. The male holotype's carapace measures long and wide. The walking legs are long and slender, with the third pair being the shortest at 2.7 times the carapace length. The anterior and posterior edges of the merus, carpus, and propodus feature a row of spines – referenced in ''P. serrata''s name – and the slightly curved anterior edge of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Description
A species description is a formal scientific description of a newly encountered species, typically articulated through a scientific publication. Its purpose is to provide a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been previously described or related species. For a species to be considered valid, a species description must follow established guidelines and naming conventions dictated by relevant nomenclature codes. These include the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) for animals, the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) for plants, and the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) for viruses. A species description often includes photographs or other illustrations of type material and information regarding where this material is deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomura Of The Atlantic Ocean
Anomura (sometimes Anomala) is a group of decapod crustaceans, including hermit crabs and others. Although the names of many anomurans include the word ''crab'', all true crabs are in the sister group to the Anomura, the Brachyura (the two groups together form the clade Meiura). Description The name Anomura derives from an old classification in which reptant decapods were divided into Macrura (long-tailed), Brachyura (short-tailed) and Anomura (differently-tailed). The alternative name Anomala reflects the unusual variety of forms in this group; whereas all crabs share some obvious similarities, the various groups of anomurans are quite dissimilar. The group has been moulded by several instances of carcinisation – the development of a crab-like body form. Thus, the king crabs (Lithodidae), porcelain crabs (Porcellanidae) and hairy stone crab (Lomisidae) are all separate instances of carcinisation. As decapods (meaning ''ten-legged''), anomurans have ten pereiopods, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Crabs
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by fixed laws. Kings are hereditary monarchs when they inherit power by birthright and elective monarchs when chosen to ascend the throne. *In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the title may refer to tribal kingship. Germanic kingship is cognate with Indo-European traditions of tribal rulership (cf. Indic ''rājan'', Gothic ''reiks'', and Old Irish ''rí'', etc.). *In the context of classical antiquity, king may translate in Latin as '' rex'' and in Greek as ''archon'' or ''basileus''. *In classical European feudalism, the title of ''king'' as the ruler of a ''kingdom'' is understood to be the highest rank in the feudal order, potentially subject, at least nominally, only to an emperor (harking back to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Museum Of Los Angeles County
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the laws, elements and phenomena of the physical world, including life. Although humans are part of nature, human activity or humans as a whole are often described as at times at odds, or outright separate and even superior to nature. During the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries, nature became the passive reality, organized and moved by divine laws. With the Industrial Revolution, nature increasingly became seen as the part of reality deprived from intentional intervention: it was hence considered as sacred by some traditions ( Rousseau, American transcendentalism) or a mere decorum for divine providence or human history ( Hegel, Marx). However, a vitalist vision of nature, closer to the pre-Socratic one, got reborn at the same time, especially after Charles Darwin. Within the various uses of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralomis Verrilli
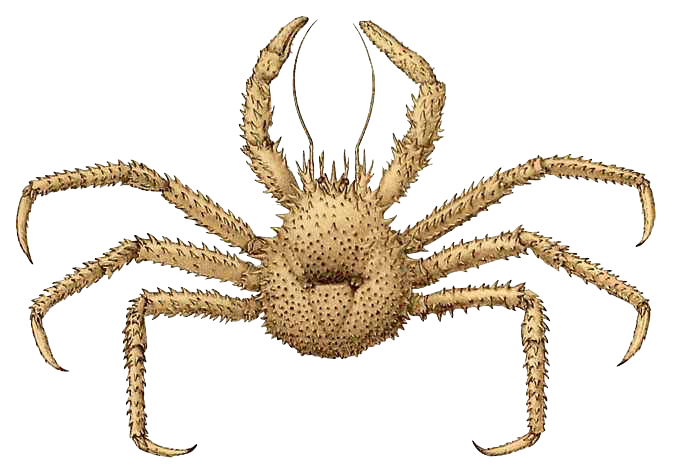
''Paralomis'' is a widely distributed, highly speciose, and morphologically diverse genus of king crabs in the subfamily Lithodinae. Description Like all king crabs, ''Paralomis'' has evolved a crab-like appearance through a process called carcinisation. ''Paralomis'' has either a pentagonal or pyriform carapace. At the very front, its rostrum consists of one short, conical spine projecting forward in the middle and one or more pairs of spines angled upward around the base. Like all king crabs, the gastric region, directly behind the rostrum, is elevated above the others. Like ''Lithodes'' and ''Neolithodes'', the cardiac region – directly behind the gastric region, separated by a deep groove – is triangular. Its three pairs of walking legs – morphologically similar, with the middle pair typically being the longest – are not covered at their bases by the carapace. In adults, the undersides of the dactyli feature horn-like spines. The abdomen is more calcified than in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
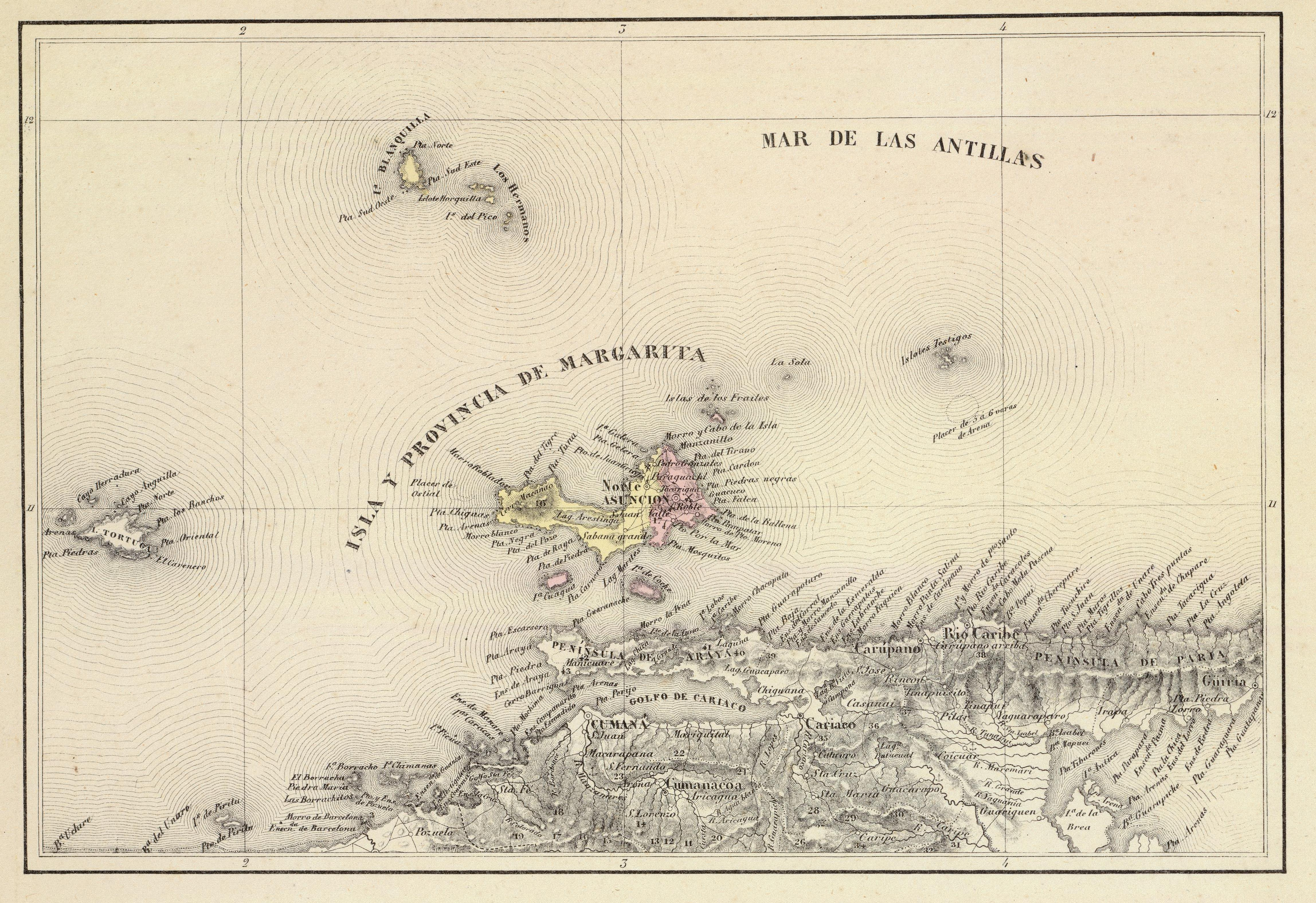
Margarita Island
Margarita Island (, ) is the largest island in the States of Venezuela, Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated off the north west coast of the country, in the Caribbean Sea. The capital city of Nueva Esparta, La Asunción, is located on the island. History Age of Exploration Christopher Columbus was the first European to arrive on Margarita Island in 1498. The local natives were the Guaiqueries people. The coast of the island was abundant in pearls, which represented almost a third of all New World tribute to the Spanish Crown. Margarita Island was fortified against the increasing threat of pirate attacks, and some fortifications remain today. It was the center of Spanish colonial Margarita Province, established in 1525. In 1561, the island was seized by Lope de Aguirre, a notoriously violent and rebellious conquistador who killed the governor Juan Villadrando. Around 1675, the island was captured again, this time by Red Legs Greaves, a pirate known for his humanity and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralomis Pectinata
''Paralomis'' is a widely distributed, highly speciose, and morphologically diverse genus of king crabs in the subfamily Lithodinae. Description Like all king crabs, ''Paralomis'' has evolved a crab-like appearance through a process called carcinisation. ''Paralomis'' has either a pentagonal or pyriform carapace. At the very front, its rostrum consists of one short, conical spine projecting forward in the middle and one or more pairs of spines angled upward around the base. Like all king crabs, the gastric region, directly behind the rostrum, is elevated above the others. Like ''Lithodes'' and ''Neolithodes'', the cardiac region – directly behind the gastric region, separated by a deep groove – is triangular. Its three pairs of walking legs – morphologically similar, with the middle pair typically being the longest – are not covered at their bases by the carapace. In adults, the undersides of the dactyli feature horn-like spines. The abdomen is more calcified than in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name , the second part (the species epithet) of the name of an animal species
{{Set index article ...
Specific name may refer to: * in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules: * Specific name (botany), the two-part (binomial) name of a plant species. Hoevever, the species epithet refers to the second part of the name. * Specific name (zoology) In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet, species epithet, or epitheton) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east and northeast, Brazil to the southeast, Peru and Ecuador to the south and southwest, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Panama to the northwest. Colombia is divided into 32 Departments of Colombia, departments. The Capital District of Bogotá is also the List of cities in Colombia by population, country's largest city hosting the main financial and cultural hub. Other major urban areas include Medellín, Cali, Barranquilla, Cartagena, Colombia, Cartagena, Santa Marta, Cúcuta, Ibagué, Villavicencio and Bucaramanga. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi) and has a population of around 52 million. Its rich cultural heritage—including language, religion, cuisine, and art—reflects its history as a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba to Puerto Rico, the Lesser Antilles to the east from the Virgin Islands to Trinidad and Tobago, South America to the south from the Venezuela, Venezuelan coastline to the Colombia, Colombian coastline, and Central America and the Yucatán Peninsula to the west from Panama to Mexico. The Geopolitics, geopolitical region around the Caribbean Sea, including the numerous islands of the West Indies and adjacent coastal areas in the mainland of the Americas, is known as the Caribbean. The Caribbean Sea is one of the largest seas on Earth and has an area of about . The sea's deepest point is the Cayman Trough, between the Cayman Islands and Jamaica, at below sea level. The Caribbean coastline has many gulfs and bays: the Gulf of Gonâve, the Gul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelae
A chela ()also called a claw, nipper, or pinceris a pincer-shaped organ at the end of certain limbs of some arthropods. The name comes from Ancient Greek , through Neo-Latin '. The plural form is chelae. Legs bearing a chela are called chelipeds. Another name is ''claw'' because most chelae are curved and have a sharp point like a claw. Chelae can be present at the tips of arthropod legs as well as their pedipalps. Chelae are distinct from spider chelicerae in that they do not contain venomous glands and cannot distribute venom. Uses Chelae have a wide variety of uses, but most commonly they are used for handling their prey and for defense. These uses are often reflected in the morphology of the chelae. For instance, some species, such as the members of the families Ocypodidae and Alpheidae show asymmetry between their paired claws. Possessing one enlarged chela used for defensive and courtship purposes and a smaller chela for shearing and feeding. For some species, this asymm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |