|
Paracletus Cimiciformis
''Paracletus cimiciformis'' is a species of aphid with a complex life cycle. Its primary host plant is ''Pistacia'' and its secondary host is a grass, where it is present on the roots. Here it is associated with an ant and part of its life cycle is spent in the ant's nest. Hosts The primary host for this species is the terebinth or turpentine tree (''Pistacia terebinthus''). Its secondary hosts include the grasses and cereals bent, wild oat, cock's-foot, fescue, wall barley, barley, rice, meadow-grass, '' Polypogon viridis'', tall fescue, '' Stipellula capensis'', and wheat. Distribution ''Paracletus cimiciformis'' is native to much of Europe and has been recorded in North Africa and Asia. Life cycle The life cycle of ''P. cimiciformis'' is complex. For most of the year, wingless females are produced parthenogenetically, but in the late summer on their secondary hosts (grass), winged males and females are produced which fly to their primary host, the terebinth tree. Here t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects in the Taxonomic rank, family Aphididae. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white Eriosomatinae, woolly aphids. A typical life cycle involves flightless females giving Viviparity, live birth to female Nymph (biology), nymphs—who may also be already Pregnancy, pregnant, an adaptation scientists call telescoping generations—without the involvement of males. Developmental biology, Maturing rapidly, females breed profusely so that the number of these insects multiplies quickly. Alate, Winged females may develop later in the season, allowing the insects to colonize new plants. In Temperate climate, temperate regions, a phase of sexual reproduction occurs in the autumn, with the insects often overwintering as eggs. The life cycle of some species involves an alternation between two species of host plants, for example between an annual crop and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek + ) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which the embryo develops directly from an egg without need for fertilization. In animals, parthenogenesis means the development of an embryo from an unfertilized Gametophyte, egg cell. In plants, parthenogenesis is a component process of apomixis. In algae, parthenogenesis can mean the development of an embryo from either an individual sperm or an individual egg. Parthenogenesis occurs naturally in some plants, algae, invertebrate animal species (including nematodes, some tardigrades, water fleas, some scorpions, aphids, some mites, some bees, some Phasmatodea, and parasitic wasps), and a few vertebrates, such as some fish, amphibians, and reptiles. This type of reproduction has been induced artificially in animal species that naturally reproduce through sex, including fish, amphibians, and mice. Normal egg cells form in the process of meiosis and are haploid, with half as many chromosomes as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insects Described In 1837
Insects (from Latin ') are hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce by laying eggs. Insects breathe air through a system of paired openings along their sides, connected to small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in vessels, and some circulates in an open hemocoel. Insect vision is mainly through their compound eyes, with additional small ocelli. Many insects can hear, using tympanal organs, which may be on the legs or other parts of the body. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphididae
The Aphididae are a very large insect family in the aphid superfamily ( Aphidoidea), of the order Hemiptera. These insects suck the sap from plant leaves. Several thousand species are placed in this family, many of which are considered plant/crop pests. They are the family of insects containing most plant virus vectors (around 200 known) with the green peach aphid ('' Myzus persicae'') being one of the most prevalent and indiscriminate carriers. Evolution Aphids originated in the late Cretaceous about (Mya), but the Aphidinae which comprises about half of the 4700 described species and genera of aphids alive today come from their most recent radiation which occurred in the late Tertiary less than 10 Mya.Von Dohlen CD, Moran NA (2000) Molecular data support a rapid radiation of aphids in the Cretaceous and multiple origins of host alternation. Biol J Linnean Soc 71: 689–717Von Dohlen CD, Rowe CA, Heie OE (2006) A test of morphological hypotheses for tribal and subtribal rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the full set of genes of their single parent and thus the newly created individual is genetically and physically similar to the parent or an exact clone of the parent. Asexual reproduction is the primary form of reproduction for single-celled organisms such as archaea and eubacteria, bacteria. Many Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms including plants, animals, and Fungus, fungi can also reproduce asexually. In Vertebrate, vertebrates, the most common form of asexual reproduction is parthenogenesis, which is typically used as an alternative to sexual reproduction in times when reproductive opportunities are limited. Some Monitor lizard, monitor lizards, including Komodo dragons, can reproduce asexually. While all prokaryotes reproduce without the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
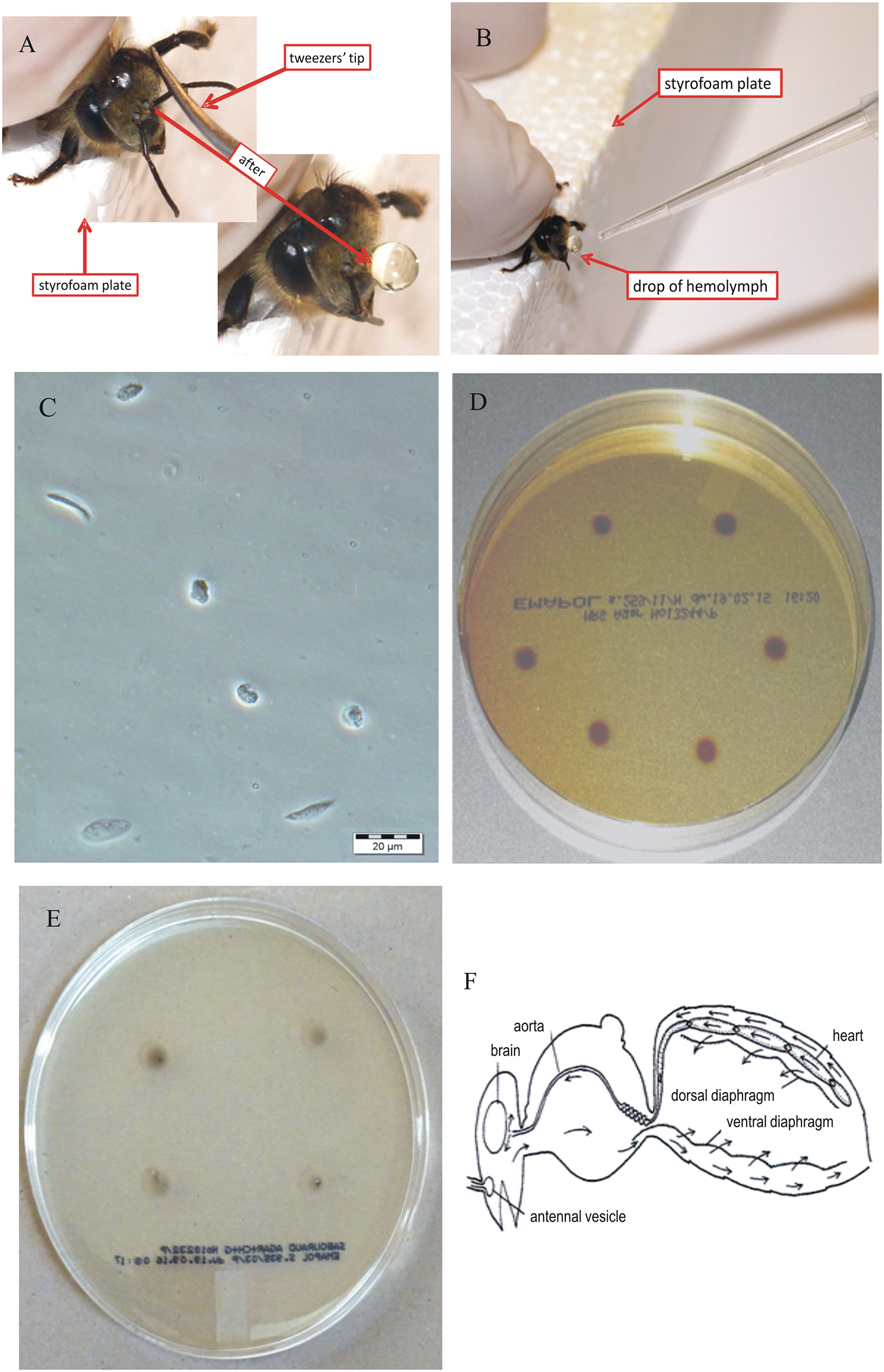
Hemolymph
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, similar to the blood in invertebrates, that circulates in the inside of the arthropod's body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph cells called hemocytes are dispersed. In addition to hemocytes, the plasma also contains many chemicals. It is the major tissue type of the open circulatory system characteristic of arthropods (for example, arachnids, crustaceans and insects). In addition, some non-arthropods such as mollusks possess a hemolymphatic circulatory system. Oxygen-transport systems were long thought unnecessary in insects, but ancestral and functional hemocyanin has been found in the hemolymph. Insect "blood" generally does not carry hemoglobin, although hemoglobin may be present in the tracheal system instead and play some role in respiration. Method of transport In the grasshopper, the closed portion of the system consists of tubular hearts and an ao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offspring
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by sexual reproduction, sexual or asexual reproduction. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny. This can refer to a set of simultaneous offspring, such as the chick (young bird), chicks hatched from one clutch (eggs), clutch of eggs, or to all offspring produced over time, as with the brood (honeybee), honeybee. Offspring can occur after mating, artificial insemination, or as a result of cloning. Human offspring (lineal descendant, descendants) are referred to as children; male children are sons and female children are daughters (see Kinship). Overview Offspring contains many parts and properties that are precise and accurate in what they consist of, and what they define. As the offspring of a new species, also known as a child or f1 generation, consist of genes of the father and the mother, which is also known as the parent generation. Each of these offspring contains numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavior of the receiving individuals. There are ''alarm signal, alarm pheromones'', ''food trail pheromones'', ''sex pheromones'', and many others that affect behavior or physiology. Pheromones are used by many organisms, from basic unicellular prokaryotes to complex multicellular eukaryotes. Their use among insects has been particularly well documented. In addition, some vertebrates, plants and ciliates communicate by using pheromones. The ecological functions and evolution of pheromones are a major topic of research in the field of chemical ecology. Background The portmanteau word "pheromone" was coined by Peter Karlson and Martin Lüscher in 1959, based on the Greek language, Greek () and (). Pheromones are also sometimes classified as ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honeydew (secretion)
Honeydew is a sugar-rich sticky liquid, secreted by aphids, some scale insects, and many other true bugs and some other insects as they feed on plant sap. When their mouthpart penetrates the phloem, the sugary, high-pressure liquid is forced out of the anus of the insects, allowing them to rapidly process the large volume of sap required to extract essential nutrients present at low concentrations. Honeydew is particularly common as a secretion in hemipteran insects and is often the basis for trophobiosis. Some caterpillars of Lycaenidae butterflies and some moths also produce honeydew. In addition to various sugars, honeydew contains small amounts of amino acids, other organic compounds, and inorganic Salt (chemistry), salts with its precise makeup affected by factors such as insect species, host plant species, and whether a symbiotic organism is present. Honeydew-producing insects, like cicadas, pierce phloem ducts to access the sugar rich sap; the excess fluid released by ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetramorium Semilaeve
''Tetramorium'' is a genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae that includes more than 520 species. These ants are also known as pavement ants. Taxonomy and phylogeny ''Tetramorium'' was first described by Gustav Mayr in 1855 in the same publication as ''Monomorium''. Revision within the genus by Wagner et al. in 2017 recognized a complex of 10 cryptic species, 3 of which were raised from subspecies classifications and 2 of which were newly described. This revision also elevated the pavement ant introduced to North America as the species ''T. immigrans'' rather than the previous designation as a subspecies of ''T. caespitum''. These 10 species in the ''T. caespitum'' complex are as follows: * '' Tetramorium alpestre'' Steiner, Schlick-Steiner & Seifert, 2010 * ''Tetramorium breviscapus'' Wagner et al., 2017 * ''Tetramorium caespitum'' (Linnaeus, 1758) * '' Tetramorium caucasicum'' Wagner et al., 2017 * '' Tetramorium fusciclava'' Consani & Zangheri, 1952 * '' Tetramorium hunga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetramorium Caespitum
''Tetramorium caespitum'', also known as the red pavement ant, is a species of Myrmicine ant native to Europe, Morocco, and western Asia, but now found on many other continents as a tramp species. Etymology The species is commonly known as the "pavement ant because workers are commonly found in pavements or roads, usually searching for food. There are also some ''Tetramorium'' species found in North America, although scientists are unsure whether or not ''T. caespitum'' is the species found, so they are often called ''Tetramorium sp. e''. References Tetramorium, caespitum Insects described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus {{Myrmicinae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetramorium
''Tetramorium'' is a genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae that includes more than 520 species. These ants are also known as pavement ants. Taxonomy and phylogeny ''Tetramorium'' was first described by Gustav Mayr in 1855 in the same publication as '' Monomorium''. Revision within the genus by Wagner et al. in 2017 recognized a complex of 10 cryptic species, 3 of which were raised from subspecies classifications and 2 of which were newly described. This revision also elevated the pavement ant introduced to North America as the species ''T. immigrans'' rather than the previous designation as a subspecies of ''T. caespitum''. These 10 species in the ''T. caespitum'' complex are as follows: * '' Tetramorium alpestre'' Steiner, Schlick-Steiner & Seifert, 2010 * '' Tetramorium breviscapus'' Wagner et al., 2017 * ''Tetramorium caespitum'' (Linnaeus, 1758) * '' Tetramorium caucasicum'' Wagner et al., 2017 * '' Tetramorium fusciclava'' Consani & Zangheri, 1952 * '' Tetramorium hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |