|
Panzer Army Africa
The Panzer Army Africa (German language, German: ''Panzerarmee Afrika''; Italian language, Italian: ''Gruppo Corazzato Africa'') was a joint German-Italian field army that fought in the North African campaign during World War II. It consisted of one German corps and three Italian corps. On 1943, during the Tunisian campaign, the ''Panzerarmee Afrika'' was changed to as the ''Army Group Africa'', and was consisted of the newly-formed German 5th Panzer Army, 5th Army and the Italian Italian 1st Army, 1st Army. During the campaigns in North Africa, the ''Panzerarmee Afrika'' was subordinated to the Italian command, as well as to German command headquarters in the Mediterranean. History Panzer Group Africa When the ''Afrikakorps'' was formed on 11 January 1941 it was subordinated to the Italian chain of command in Africa. In the middle of 1941 the Oberkommando der Wehrmacht (OKW, Armed Forces High Command) created a larger command structure in Africa, forming a new headquarters, Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Army
A field army (also known as numbered army or simply army) is a military formation in many armed forces, composed of two or more corps. It may be subordinate to an army group. Air army, Air armies are the equivalent formations in air forces, and Naval fleet, fleets in navy, navies. A field army is composed of 80,000 to 300,000 soldiers. History Specific field armies are usually named or numbered to distinguish them from "army" in the sense of an entire national defence force or land force. In English language, English, the typical orthography, orthographic style for writing out the names field armies is Numeral (linguistics), word numbers, such as "First Army"; whereas corps are usually distinguished by Roman numerals (e.g. I Corps) and subordinate formations with ordinal number (linguistics), ordinal numbers (e.g. 1st Division). A field army may be given a geographical name in addition to or as an alternative to a numerical name, such as the British Army of the Rhine, Army of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Close-quarters Battle
Close-quarters battle (CQB), also called close-quarters combat (CQC), is a close combat situation between multiple combatants involving ranged (typically firearm-based) or melee combat. It can occur between military units, law enforcement and criminal elements, and in other similar situations. CQB is typically defined as a short duration, high intensity conflict characterized by sudden violence at close range. History Close-quarters battle has occurred since the beginning of warfare, in the form of melee combat, the use of ranged weaponry (such as slings, bows, and muskets) at close range, and the necessity of bayonets. During World War I, CQB was a significant part of trench warfare, where enemy soldiers would fight in close and narrow quarters in attempts to capture trenches. The origins of modern close-quarters battle lie in the combat methods pioneered by Assistant Commissioner William E. Fairbairn of the Shanghai Municipal Police, the police force of the Shanghai Interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raid (military)
Raiding, also known as depredation, is a military tactics, military tactic or operational warfare "smash and grab" mission which has a specific purpose. Raiders do not capture and hold a location, but quickly retreat to a previous defended position before enemy forces can respond in a coordinated manner or formulate a counter-attack. Raiders must travel swiftly and are generally too lightly equipped and supported to be able to hold ground. A raiding group may consist of combatants specially trained in this tactic, such as commandos, or as a special mission assigned to any Regular army, regular troops. Raids are often a standard tactic in irregular warfare, employed by warriors, guerrilla warfare, guerrilla fighters or other irregular military forces. Some raids are large, for example the Sullivan Expedition. The purposes of a raid may include: * to demoralization (warfare), demoralize, confuse, or exhaust the enemy; * to destroy specific goods or installations of military or econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrolling
Patrolling is a military tactic. Small groups or individual units are deployed from a larger formation to achieve a specific objective and then return. The tactic of patrolling may be applied to ground troops, armored units, naval units, and combat aircraft. The duration of a patrol will vary from a few hours to several weeks depending on the nature of the objective and the type of units involved. There are several different types of patrol each with a different objective. The most common is to collect information by carrying out a reconnaissance patrol. Such a patrol may try to remain clandestine and observe an enemy without themselves being detected. Other reconnaissance patrols are overt, especially those that interact with the civilian population. Ground patrol types A combat patrol is a group with sufficient size (usually platoon or company) and resources to raid or ambush a specific enemy. It primarily differs from an attack in that the aim is not to ''hold ground''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Engineering
Military engineering is loosely defined as the art, science, and practice of designing and building military works and maintaining lines of military transport and military communications. Military engineers are also responsible for logistics behind military tactics. Modern military engineering differs from civil engineering. In the 20th and 21st centuries, military engineering also includes CBRN defense and other engineering disciplines such as mechanical and electrical engineering techniques. According to NATO, "military engineering is that engineer activity undertaken, regardless of component or service, to shape the physical operating environment. Military engineering incorporates support to maneuver and to the force as a whole, including military engineering functions such as engineer support to force protection, counter improvised explosive devices, environmental protection, engineer intelligence and military search. Military engineering does not encompass the activities u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Communications
Military communications or military signals involve all aspects of communications, or conveyance of information, by armed forces. Examples from '' Jane's Military Communications'' include text, audio, facsimile, tactical ground-based communications, naval signalling, terrestrial microwave, tropospheric scatter, satellite communications systems and equipment, surveillance and signal analysis, security, direction finding and jamming. IHS Jane'sbr>Military Communications Retrieved 2012-01-23. The most urgent purposes are to communicate information to commanders and orders from them. Military communications span from pre-history to the present. The earliest military communications were delivered by runners. Later, communications progressed to visual signals. For example, Naval ships would use flag signaling to communicate from ship to ship. These flags are a uniform set of easily identifiable nautical codes that would convey visual messages and codes between ships and fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maneuver Warfare
Maneuver warfare, or manoeuvre warfare, is a military strategy which emphasizes movement, initiative and surprise to achieve a position of advantage. Maneuver seeks to inflict losses indirectly by envelopment, encirclement and disruption, while minimizing the need to engage in frontal combat. In contrast to attrition warfare where strength tends to be applied against strength, maneuver warfare attempts to apply strength against weakness in order to accomplish the mission. Maneuver warfare, the use of initiative, originality and the unexpected, combined with a ruthless determination to succeed, seeks to avoid opponents' strengths while exploiting their weaknesses and attacking their critical vulnerabilities and is the conceptual opposite of attrition warfare. Rather than seeking victory by applying superior force and mass to achieve physical destruction, maneuver uses preemption, deception, dislocation, and disruption to destroy the enemy's will and ability to fight. Historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
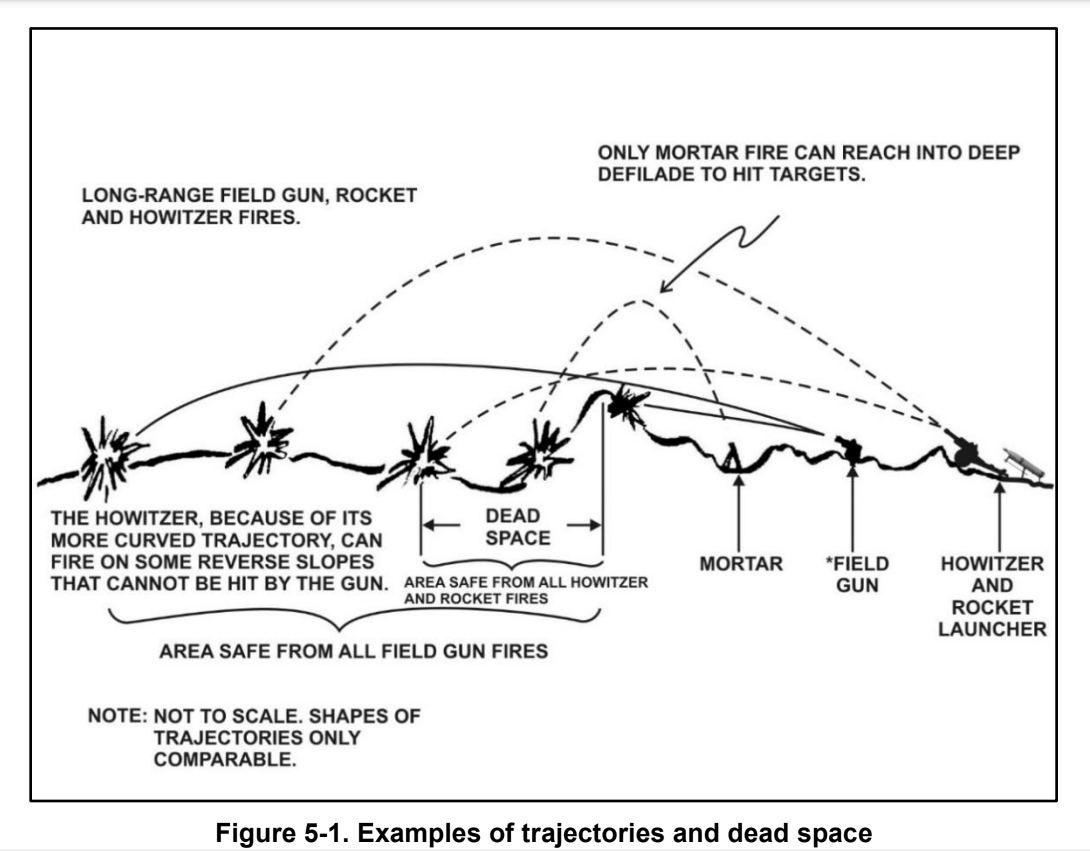
Indirect Fire
Indirect fire is aiming and firing a projectile without relying on a direct line of sight between the gun and its target, as in the case of direct fire. Aiming is performed by calculating azimuth and inclination, and may include correcting aim by observing the fall of shot and calculating new angles. Description Indirect fire is most commonly used by field artillery and mortars (although field artillery was originally and until after World War I a direct fire weapon, hence the bullet-shields fitted to the carriages of guns such as the famous M1897 75 mm). It is also used with missiles, howitzers, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, naval guns against shore targets, sometimes with machine guns, and has been used with tank and anti-tank guns and by anti-aircraft guns against surface targets. There are two dimensions in aiming a weapon: * In the horizontal plane (azimuth); and * In the vertical plane (elevation), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HUMINT
Human intelligence (HUMINT, pronounced ) is intelligence-gathering by means of human sources and interpersonal communication. It is distinct from more technical intelligence-gathering disciplines, such as signals intelligence (SIGINT), imagery intelligence (IMINT), and measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT). HUMINT can be conducted in a variety of ways, including via espionage, reconnaissance, interrogation, witness interviews, or torture. Although associated with military and intelligence agencies, HUMINT can also apply in various civilian sectors such as law enforcement. Overview NATO defines HUMINT as "a category of intelligence derived from information collected and provided by human sources." A typical HUMINT activity consists of interrogations and conversations with persons having access to information. As the name suggests, human intelligence is mostly collected by people and is commonly provided via espionage or some other form of covert surveillance. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Support
Fire support is a military tactics term used to describe weapons fire used to support friendly forces by engaging, suppressing, or destroying enemy forces, facilities, or materiel in combat. It is often provided through indirect fire, though the term may also be used for some forms of supporting direct fire. The United States Department of Defense defines fire support as " fires that directly support land, maritime, amphibious, and special operations forces to engage enemy forces, combat formations, and facilities in pursuit of tactical and operational objectives." Overview Fire support generally consists of fire from heavy or crew-served weaponry with high firepower, including strikes and barrages from artillery, mortars, rocket artillery, and missiles; naval gunfire support from naval artillery; airstrikes, strafes, and close air support from military aircraft; and drone strikes from unmanned combat aerial vehicles; among various other forms. Fire support i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expeditionary Warfare
Expeditionary warfare is a military invasion of a foreign territory, especially away from established bases. Expeditionary forces were in part the antecedent of the modern concept of rapid deployment forces. Traditionally, expeditionary forces were essentially self-sustaining with an Organic unit, organic Military logistics, logistics capability and with a full array of supporting arms. In the ancient world The earliest examples of expeditionary warfare come from the Sea Peoples, a term used for a confederation of seafaring Raid (military), raiders of the second millennium BC who sailed into the eastern shores of the Mediterranean, caused political unrest, and attempted to enter or control Egyptian territory during the late Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, 19th dynasty, and especially during Year 8 of Ramesses III of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt, 20th dynasty. The raiding tactics were expanded into the more complex expeditionary warfare operations by Alexander the Great who used C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Fire
Direct fire or line-of-sight fire refers to firing of a ranged weapon whose projectile is launched directly at a target within the line-of-sight of the user. The firing weapon must have a sighting device and an unobstructed view to the target, which means no obstacles or friendly units can be between it and the target. A weapon engaged in direct fire conversely exposes itself to direct return fire from the target.p.49, Bailey This is in contrast to indirect fire, which refers to firing a projectile on a curved ballistic trajectory or delivering self-accelerated munitions capable of long range and various degrees of homing abilities to alter the flight path. Indirect fire does not need a direct line-of-sight to the target because the shots are normally directed by a forward observer. As such, indirect-fire weapons can shoot over obstacles or friendly units and the weapons can be concealed from counter-battery fire. Description Examples of direct-fire weapons include most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |