|
Pannonian Island Mountains
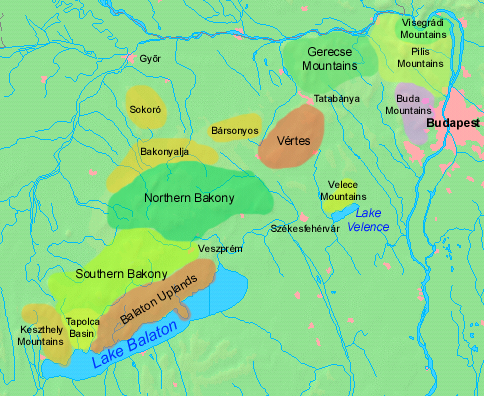
The Pannonian island mountains (, ) is a term for isolated mountains scattered across the Pannonian Plain, chiefly its western and southern parts, in Hungary, Serbia and Croatia. In prehistoric times, these mountains were islands of the ancient Pannonian Sea that disappeared about 600,000 years ago. The island mountains include: ;Croatia *Central Slavonian Mountains: ** Dilj **Krndija **Papuk ** Psunj **Požeška Gora *Medvednica in western Croatia ;Hungary * Transdanubian Mountains of western Hungary: **Bakony **Buda Hills **Gerecse **Pilis Mountains ** Vértes Hills ** Velence Mountains *Mecsek, in south Hungary * Kőszeg Mountains (Geschriebenstein), on Hungary–Austria border * Baranya Hills ;Serbia (autonomous province of Vojvodina)Dragan Rodić, Geografija za I ili III razred srednje škole, Zavod za udžbenike i nastavna sredstva, Beograd, 1995. *Fruška Gora *Vršac Mountains The Vršac Mountains (, sr-Cyrl, Вршачке планине, ), also known as Vrš ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerecse
Gerecse is a mountain range in northwestern Hungary that belongs to the Transdanubian Mountains. Geography The range lies in the Central Transdanubian region and connects Vértes Hills with Pilis Mountains in Komárom-Esztergom County, between the town of Tatabánya and the Danube River. Gerecse occupies an area of 850 km2 (20,300 ha). The highest point is ''Nagy-Gerecse'' at 634 m. The main rock is limestone and chalk. Biology Deciduous oak forests cover the lower slopes, with submontane species of Quercus, Carpinus, Fagus, and at higher altitudes karst scrub. The area is 70% forest, 5% scrubland, 10% grassland, and 15% artificial landscapes. Yearly sunshine duration is around 1,980 hours. The average annual temperature above the height of 350 meters is 9.5 C (in January -2,8 C). The average annual precipitation In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of Serbia
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonian Island Mountains
The Pannonian island mountains (, ) is a term for isolated mountains scattered across the Pannonian Plain, chiefly its western and southern parts, in Hungary, Serbia and Croatia. In prehistoric times, these mountains were islands of the ancient Pannonian Sea that disappeared about 600,000 years ago. The island mountains include: ;Croatia *Central Slavonian Mountains: ** Dilj **Krndija **Papuk ** Psunj **Požeška Gora *Medvednica in western Croatia ;Hungary * Transdanubian Mountains of western Hungary: **Bakony **Buda Hills **Gerecse **Pilis Mountains ** Vértes Hills ** Velence Mountains *Mecsek, in south Hungary * Kőszeg Mountains (Geschriebenstein), on Hungary–Austria border * Baranya Hills ;Serbia (autonomous province of Vojvodina)Dragan Rodić, Geografija za I ili III razred srednje škole, Zavod za udžbenike i nastavna sredstva, Beograd, 1995. *Fruška Gora *Vršac Mountains The Vršac Mountains (, sr-Cyrl, Вршачке планине, ), also known as Vrš ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danubian Hills
The Danubian Hills (Slovak: ''Podunajská pahorkatina''), also translated as Danubian Upland, is the north-eastern part of the Danubian Lowland in Slovakia, often appearing as low rolling hills of prevalently eolic origin. Location It lies between the Danubian Flat and the Danube in the south, the Little Carpathians in the west and all the other Western Carpathians in the north and east. The border with the Danubian Flat runs approximately along the line Bratislava – Senec – Sereď – Nové Zámky – Patince. Geology The area has varied rocks (clay, gravel, sands), which are covered by Quaternary sediments (loess) and very fertile soils (black and brown earths). Towns Major towns of the area are Trnava, Topoľčany, Nitra, Levice, Dudince and Štúrovo. Parts The Váh, Nitra, Žitava, Hron and Ipeľ rivers divide the area into the following 11 geomorphological parts (from the west to the east): *Trnavská pahorkatina (Trnava Hills) *Dolnovážska niv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vršac Mountains
The Vršac Mountains (, sr-Cyrl, Вршачке планине, ), also known as Vršac Hill (, sr-Cyrl, Вршачки брег, ), are located in the Banat region near the city of Vršac, Serbia, and partially also in Romania. They represent an independent and distinct massif, long and spreading across an area of , of which belong to Serbia and to Romania. Geography The Vršac mountains have a shape of an arch, where the basic mountain mass takes the central position, while the hills extend to the south and north. The mountains are built of Paleozoic rocks (which date back over 260 million years) which are surrounded by Neogene sediments (about 60 mya), including those of the ancient Pannonian sea (about 25 mya). Contrary to some literature data, the Vršac Mountains are not part of the Carpathians but are a Pannonian island mountain according to their geotectonic position and geological structure. Specific forms of geomorphological diversity, naturally sculpted – mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
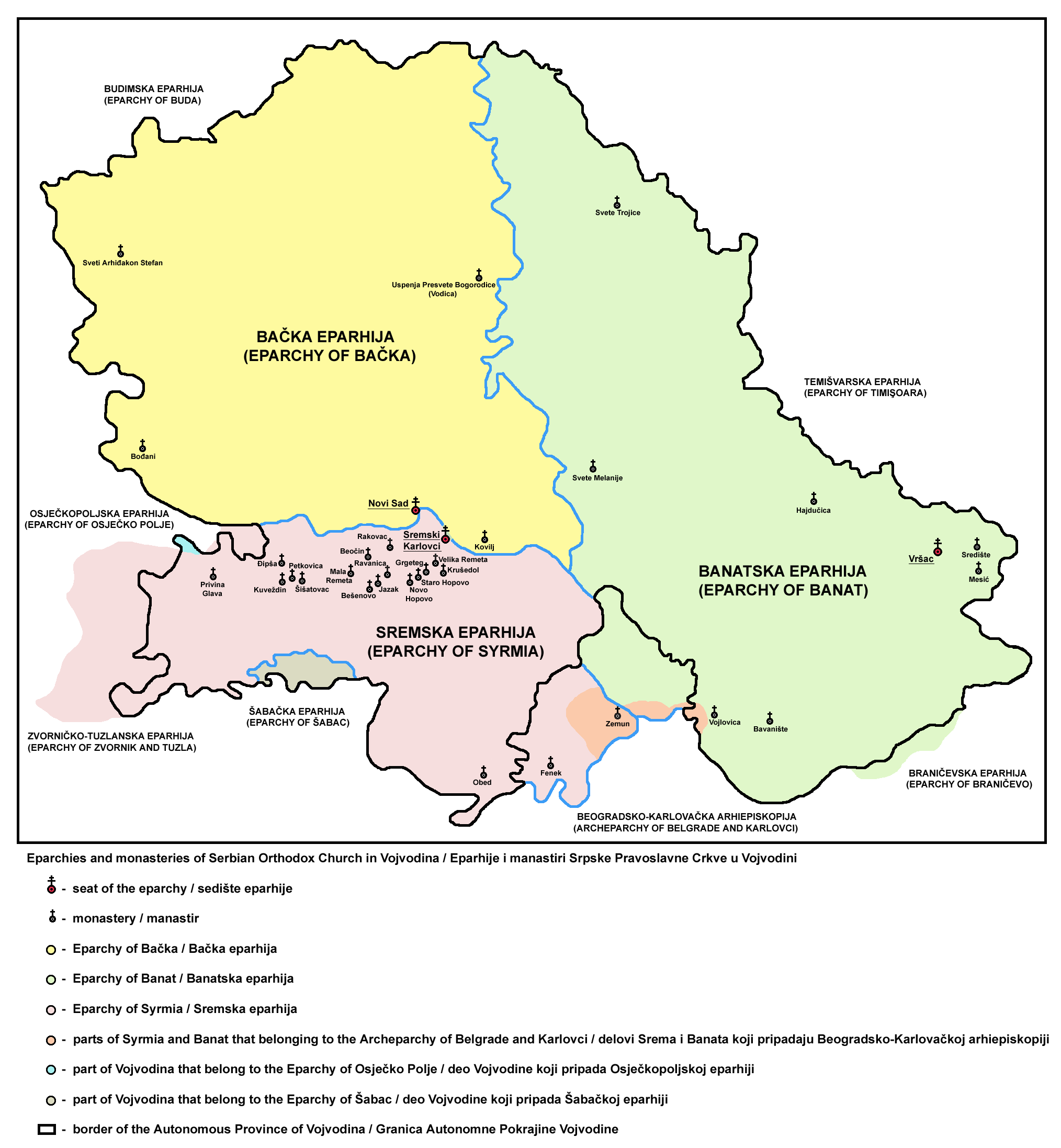
Fruška Gora
Fruška gora ( sr-Cyrl, Фрушка гора) is a mountain in Syrmia, with most of the mountain being part of Serbia and its westernmost edge extending into eastern Croatia. The Serbian part of the mountain forms the country's oldest National parks of Serbia, national park. Sometimes also referred to as the ''Jewel of Serbia'', due to its largely pristine landscape and protection effort, or the ''Serbian Mount Athos'', being the home of a large number of historical Serbian Orthodox monasteries. Name In Serbian language, Serbian, it is known as ''Fruška gora'' (, Фрушка гора), in Hungarian language, Hungarian as ''Tarcal'' (also ''Almus-hegy'' or ''Árpatarló''), in German language, German as ''Frankenwald'', and in Latin language, Latin as ''Alma Mons''. In Medieval Greek, it was known as ''Frangochoria''. The mountain's name originates in the old Serbian language, Serbian word ''"Fruzi"'' derived from the singular form ''"Frug"''; and its adjective is ''Fruški'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( ; sr-Cyrl, Војводина, ), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital Belgrade and the Sava and Danube Rivers. The administrative centre, Novi Sad, is the second-largest city in Serbia. The historic regions of Banat, Bačka, Syrmia and northernmost part of Mačva overlap the province. Modern Vojvodina is multi-ethnic and multi-cultural, with some 26 ethnic groups and six official languages. Fewer than two million people, nearly 27% of Serbia's population, live in the province. Name ''Vojvodina'' is also the Serbian word for voivodeship, a type of duchy overseen by a voivode. The Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar, Serbian Voivodeship, a precursor to modern Vojvodina, was an Austrian province from 1849 to 1860. Its official name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria–Hungary Border
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military and diplomatic alliance, it consisted of two sovereign states with a single monarch who was titled both the Emperor of Austria and the King of Hungary. Austria-Hungary constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy: it was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War, following wars of independence by Hungary in opposition to Habsburg rule. It was dissolved shortly after Dissolution of Austria-Hungary#Dissolution, Hungary terminated the union with Austria in 1918 at the end of World War 1. One of Europe's major powers, Austria-Hungary was geographically the second-largest country in Europe (after Russian Empire, Russia) and the third-most populous (afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kőszeg Mountains
The Kőszeg Mountains , sometimes called the Guns or Güns Mountains (, ), are a mountain range in the Alpokalja area, the easternmost region of the Alps. The territory of the range is shared between Austria and Hungary. Geologically, the mountains represent a Penninic window, formed from metamorphic rocks transformed about 28–31 million years ago and uplifted between 15–18 million years ago. The landscape features a main north-south ridge with multiple east-west tributary ridges, creating a distinctive pattern of parallel valleys shaped by streams flowing eastward toward the Gyöngyös. The mountain range's hydrology includes a network of permanent and intermittent streams that have shaped the terrain through erosion and occasional flash floods. The varied habitats of the Kőszeg Mountains support rich biodiversity, including dozens of species of soil-dwelling enchytraeid worms and orthopteran insects ( grasshoppers and crickets), with distinct species assemblages cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecsek
Mecsek (; ; Serbian language, Serbian: ''Meček'' or Мечек; ) is a mountain range in southern Hungary. It is situated in the Baranya (region), Baranya region, in the north of the city of Pécs. Etymology The Hungarian toponym "Mecsek" derives from the sobriquet version of the name Mihály (Michael). Originally applied only to the hills adjacent to Pécs, the name Mecsek was first mentioned in 16th century. Geography The mountains cover an area of approximately 500 km2. The highest peak in the mountain range is Zengő (literally translates to 'resonant'), which has an elevation of 682 metres (2,238 feet). The Mecsek Hills consist of plateau-like block mountains of a broken, folded structure. Its basis is crystalline rock of Variscan origin surmounted by Triassic and Jurassic limestone and dolomite and Tertiary formations that form the main block. The mountains are divided by a structural fault running NW to SE. The eastern part consists mainly of high ridges of sedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |