|
Palisaded Encapsulated Neuroma
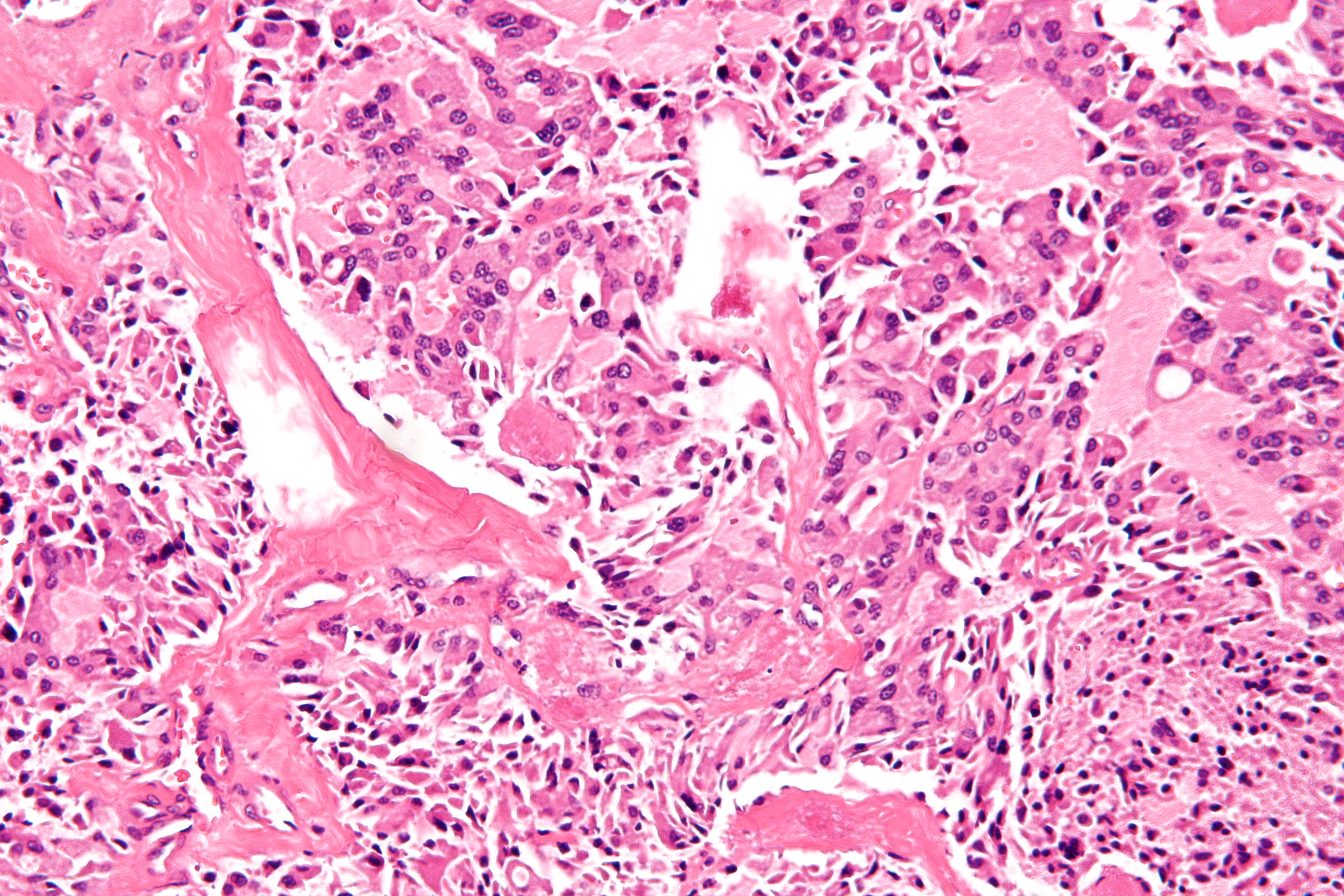
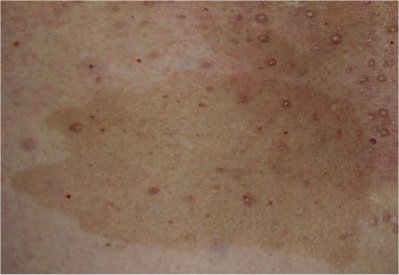
Palisaded encapsulated neuroma (PEN) is a rare, benign cutaneous condition characterized by small, firm, non-pigmented nodules or papules. They typically occur as a solitary (single) lesion near the mucocutaneous junction of the skin of the face, although they can occur elsewhere on the body. Symptoms PEN tumours are always painless, solid masses felt on the skin that, due to their slow-growing nature, typically take many years to grow to a size where they are noticeable. There are never any symptoms associated with systemic disease. Diagnosis As mentioned previously, PEN is a benign, firm, flesh-coloured lesion that typically occurs in dermis of the skin of the face. The lesions are typically between 2–6mm and are slow-growing. On the face, the lesions can be found on the eyelid, nose and in the oral mucosa, however, the lesions can also occur on the shoulder, arm, hand, foot and the glans of the penis. PEN is diagnosed by clinical recognition of the lesion and on subseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucocutaneous Junction
A mucocutaneous junction, or mucocutaneous boundary, is a region of the body in which mucosa transitions to skin. Mucocutaneous zones occur in animals, at the body orifices. In humans, mucocutaneous junctions are found at the lips, nostrils, conjunctivae, urethra, vagina (in females), foreskin (in males), clitoral hood (in females), and anus. In the nostrils the mucocutaneous junction has a dense microvascular network, and shows a marked similarity to that found in the mouth, between the oral mucosa and the lips. At a mucocutaneous junction, epithelium transitions to epidermis, lamina propria transitions to dermis, and smooth muscle transitions to skeletal muscle. A mucocutaneous junction is often the site of an arterial anastomosis An anastomosis (, : anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be normal (su ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Excision
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance ( cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical operations typically require a surgic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal-cell Carcinoma
Basal-cell carcinoma (BCC), also known as basal-cell cancer, basalioma, or rodent ulcer, is the most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a painless, raised area of skin, which may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it. It may also present as a raised area with ulceration. Basal-cell cancer grows slowly and can damage the tissue around it, but it is unlikely to spread to distant areas or result in death. Risk factors include exposure to ultraviolet light (UV), having lighter skin, radiation therapy, long-term exposure to arsenic, and poor immune-system function. Exposure to UV light during childhood is particularly harmful. Tanning beds have become another common source of ultraviolet radiation. Diagnosis often depends on skin examination, confirmed by tissue biopsy. Whether sunscreen affects the risk of basal-cell cancer remains unclear. Treatment is typically by surgical removal. This can be by simple excision if the cancer is small; otherwise, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurofibroma
A neurofibroma is a benign nerve-sheath tumor in the peripheral nervous system. In 90% of cases, they are found as stand-alone tumors (solitary neurofibroma, solitary nerve sheath tumor or sporadic neurofibroma), while the remainder are found in persons with neurofibromatosis type I (NF1), an autosomal-dominant genetically inherited disease. They can result in a range of symptoms from physical disfiguration and pain to cognitive disability. Neurofibromas arise from nonmyelinating-type Schwann cells that exhibit biallelic inactivation of the ''NF1'' gene that codes for the protein neurofibromin. This protein is responsible for regulating the RAS-mediated cell growth signaling pathway. In contrast to schwannomas, another type of tumor arising from Schwann cells, neurofibromas incorporate many additional types of cells and structural elements in addition to Schwann cells, making it difficult to identify and understand all the mechanisms through which they originate and develop. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (abbreviated MEN) is a condition which encompasses several distinct syndromes featuring tumors of endocrine glands, each with its own characteristic pattern. In some cases, the tumors are malignant, in others, benign. Benign or malignant tumors of nonendocrine tissues occur as components of some of these tumor syndromes. MEN syndromes are inherited as autosomal dominant disorders. Presentation Related conditions Although not officially categorized as multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes, Von Hippel–Lindau disease and Carney complex are two other autosomal dominant endocrine tumor syndromes with features that overlap the clinical features of the MEN syndromes. Although not transmitted in the germline, McCune–Albright syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by endocrine neoplastic features involving endocrine glands that overlap with those involved in MEN1 or MEN2. Comparison Percentages in the table below refer to the percentage of peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurofibromatosis Type I
Neurofibromatosis type I (NF-1), or von Recklinghausen syndrome, is a complex multi-system neurocutaneous disorder caused by a subset of genetic mutations at the neurofibromin 1 (''NF1'') locus. Other conditions associated with mutation of the ''NF1'' gene include Watson syndrome. NF-1 is a gene on chromosome 17 that is responsible for production of a protein (neurofibromin) which is needed for normal function in many human cell types. causes tumors along the nervous system that can grow anywhere on the body. is one of the most common genetic disorders and is not limited to any person's race or sex. NF-1 is an autosomal dominant disorder, which means that mutation or deletion of one copy (or allele) of the is sufficient for the development of , although presentation varies widely and is often different even between relatives affected by . , there are at least 100,000 people in the U.S. and about 25,000 people in the UK who have been diagnosed with NF. Common symptoms of inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incidental Finding
Incidental medical findings are previously undiagnosed medical or psychiatric conditions that are discovered unintentionally and during evaluation for a medical or psychiatric condition. Such findings may occur in a variety of settings, including routine medical care, during biomedical research, during post-mortem autopsy, or during genetic testing. Medical imaging An incidentaloma is a tumor found by coincidence which is often benign and does not cause any clinically significant symptoms; however a small percentage do turn out to be malignant. Incidentalomas are common, with up to 7% of all patients over 60 harboring a benign growth, often of the adrenal gland, which is detected when diagnostic imaging is used for the analysis of unrelated symptoms. As 37% of patients receiving whole-body CT scan may have abnormal findings that need further evaluation and with the increase of "whole-body CT scanning" as part of health screening programs, the chance of finding incidentalomas is e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwannoma
A schwannoma (or neurilemmoma) is a usually benign nerve sheath tumor composed of Schwann cells, which normally produce the insulating myelin sheath covering peripheral nerves. Schwannomas are homogeneous tumors, consisting only of Schwann cells. The tumor cells always stay on the outside of the nerve, but the tumor itself may either push the nerve aside and/or up against a bony structure (thereby possibly causing damage). Schwannomas are relatively slow-growing. For reasons not yet understood, schwannomas are mostly benign and less than 1% become malignant, degenerating into a form of cancer known as neurofibrosarcoma. These masses are generally contained within a capsule, so surgical removal is often successful. Schwannomas can be associated with neurofibromatosis type II, which may be due to a loss-of-function mutation in the protein merlin. They are universally S-100 positive, which is a marker for cells of neural crest cell origin. Schwannomas of the head and neck are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glans Of The Penis
In male human anatomy, the glans penis or penile glans, commonly referred to as the glans, (; from Latin ''glans'' meaning "acorn") is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and primary anatomical source of sexual pleasure. The glans penis is present in the male reproductive organs of humans and most other mammals where it may appear smooth, spiny, elongated or divided. It is externally lined with mucosal tissue, which creates a smooth texture and glossy appearance. In humans, the glans is located over the distal ends of the corpora cavernosa and is a continuation of the corpus spongiosum of the penis. At the summit appears the urinary meatus and at the base forms the corona glandis. An elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum, runs on its ventral surface. In men who are not circumcised, it is completely or partially covered by a fold of skin called the foreskin. In adults, the foreskin can gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Mucosa
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed '' lamina propria''. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved. Classification Oral mucosa can be divided into three main categories based on function and histology: * ''Lining mucosa'', nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, found almost everywhere else in the oral cavity, including the: ** ''Alveolar mucosa'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
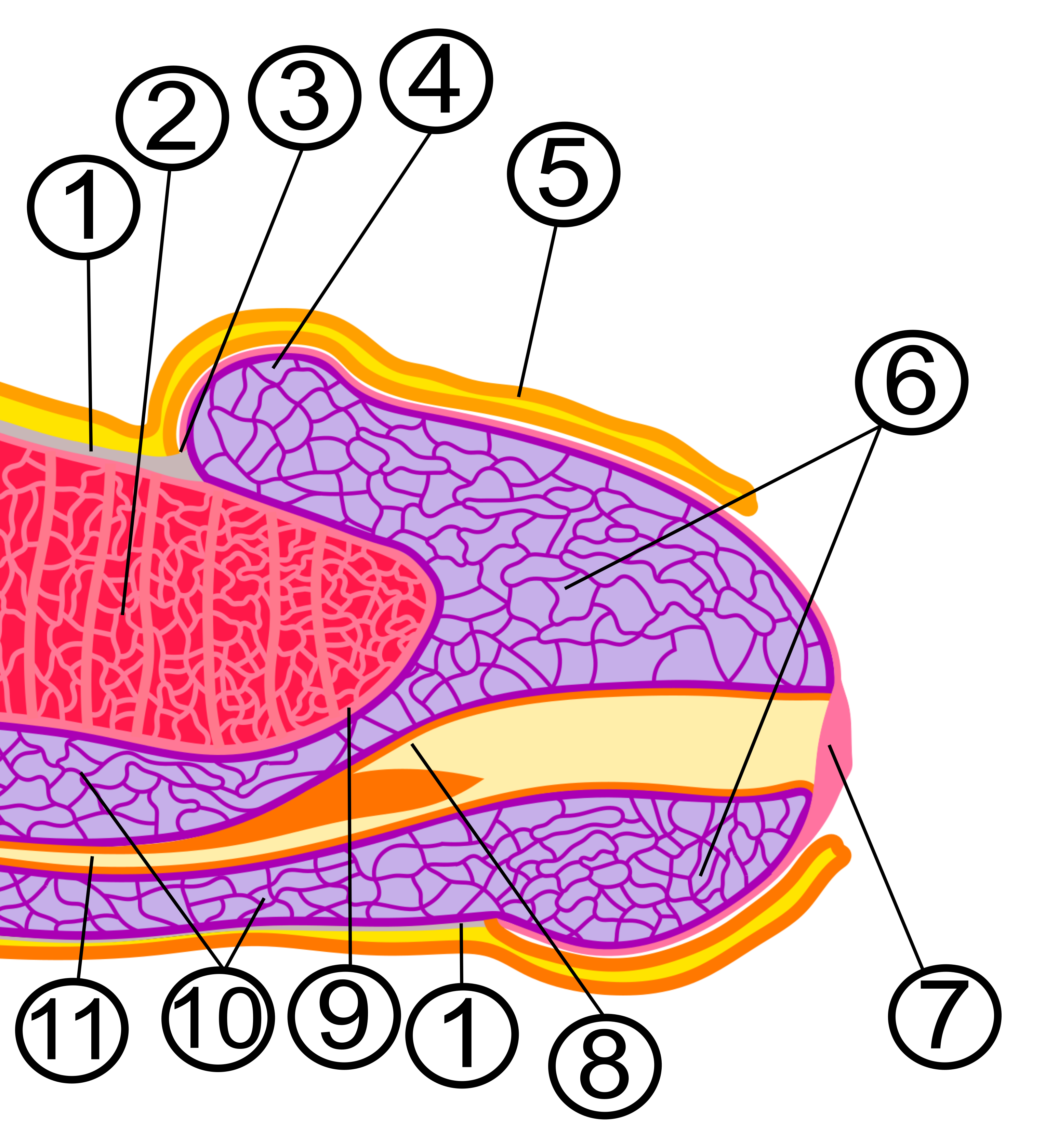
Dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (skin), epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis (anatomy), cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided into two layers, the superficial area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary region and a deep thicker area known as the reticular dermis.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology'' (10th ed.). Saunders. Pages 1, 11–12. . The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane. Structural components of the dermis are collagen, elastic fibers, and Ground substance, extrafibrillar matrix.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 8–9. . It also contains mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and thermoreceptors that provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |