|
Palace Of Poitiers
The Palace of Poitiers was the palace of the Counts of Poitiers and subsequent Dukes of Aquitaine in Poitiers, in Poitou, western France. It is a medieval testimony of the Plantagenet style of architecture. Until 2019, this building was used as a courthouse. Origin The former Merovingian kingdom of Aquitaine was re-established by Charlemagne for his son Louis the Pious; in the 9th century, a palace was constructed or reconstructed for him, one among many, above a Roman wall datable to the late 3rd century, at the highest spot of the town. Louis stayed there many times as a king and then returned to the palace after becoming emperor, in 839 and 840. The ''palatium'' was specifically called a palace in the reign of Charles the Bald. After the disintegration of the Carolingian realm, the palace became the seat of the Counts of Poitiers. The first palace of Poitiers was completely destroyed by a fire in 1018. The palace was completely rebuilt, straddling the wall, by the Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poitiers Palais De Justice
Poitiers is a city on the river Clain in west-central France. It is a commune, the capital of the Vienne department and the historical center of Poitou Province. In 2021, it had a population of 90,240. Its conurbation had 134,397 inhabitants in 2021 and is the municipal center of an urban area of 281,789 inhabitants. It is a city of art and history, still known popularly as "Ville aux cent clochers" (literal translation: "City of hundred bell towers"). With more than 30,000 students, Poitiers has been a major university town since the creation of its university in 1431, having hosted world-renowned figures and thinkers such as René Descartes, Joachim du Bellay and François Rabelais, among others. The plaza of the town is picturesque; its streets including predominantly preserved historical architecture and half-timbered houses, especially religious edifices, commonly from the Romanesque period. The latter includes notably the 4th century baptistery of Saint-Jean (Baptistè ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
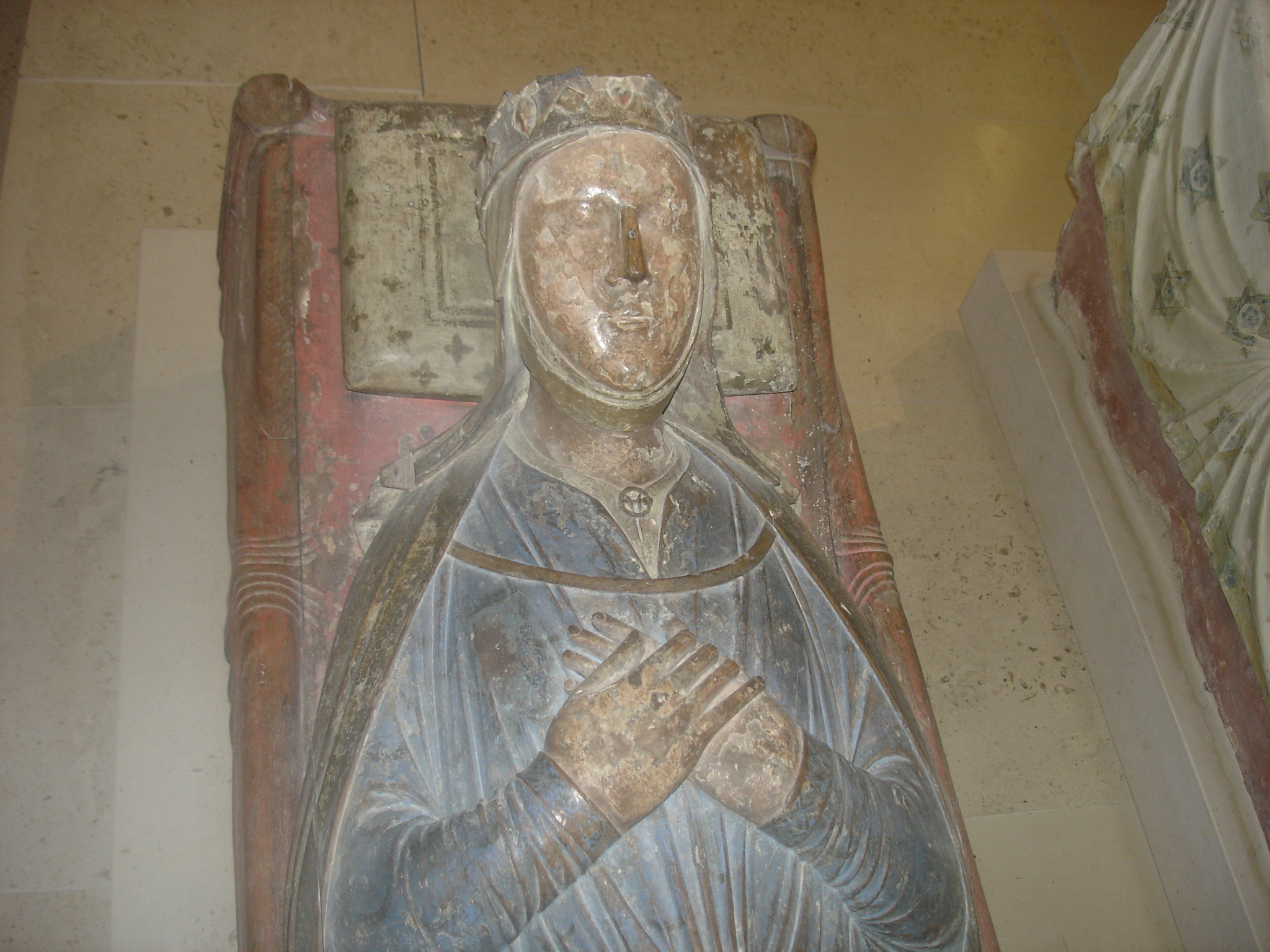
Henry Of Grosmont
Henry of Grosmont, Duke of Lancaster (– 23 March 1361) was an English statesman, diplomat, soldier, and Christian writer. The owner of Bolingbroke Castle in Lincolnshire, Grosmont was a member of the House of Plantagenet, which was ruling over England at that time. He was the wealthiest and most powerful peer of the realm. The son and heir of Henry, 3rd Earl of Lancaster, and Maud Chaworth, Grosmont became one of King Edward III's most trusted captains in the early phases of the Hundred Years' War and distinguished himself with victory in the Battle of Auberoche. He was a founding member and the second knight of the Order of the Garter in 1348, and in 1351 was created Duke of Lancaster. An intelligent and reflective man, Grosmont taught himself to write and was the author of the book ''Livre de Seyntz Medicines'', a highly personal devotional treatise. He is remembered as one of the founders and early patrons of Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, which was established by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh X Of Lusignan
Hugh X de Lusignan or Hugh V of La Marche (c. 1183 – c. 5 June 1249, Angoulême) was Seigneur de Lusignan and Count of La Marche in November 1219 and was Count of Angoulême by marriage. He was the son of Hugh IX. Background Hugh's father, Hugh IX of Lusignan, was betrothed to marry 12-year-old Isabel of Angoulême in 1200, but King John of England married her instead. As a result, the entire de Lusignan family rebelled against the English king. Hugh IX married Agathe de Preuilly instead. Hugh was born in 1183. He married Isabella, widow of King John of England, on 10 May 1220. By Hugh's marriage to Isabella, he became Count of Angoulême until her death in 1246. Together they founded the abbey of Valence. In 1224, Hugh joined with King Louis VIII of France against the Angevins, being promised the city of Bordeaux. By 1226, he had become embittered against Louis' lack of support in conquering Gascony. Marriage and issue Hugh and Isabella had: * Hugh XI de Lusign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin-glazed Pottery
Tin-glazed pottery is earthenware covered in lead glaze with added tin oxide which is white, shiny and opaque (see tin-glazing for the chemistry); usually this provides a background for brightly painted decoration. It has been important in Islamic and European pottery, but very little used in East Asia. The pottery body is usually made of red or buff-colored earthenware and the white glaze imitated Chinese porcelain. The decoration on tin-glazed pottery is usually applied to the unfired glaze surface by brush with metallic oxides, commonly cobalt oxide, copper oxide, iron oxide, manganese dioxide and antimony oxide. The makers of Italian tin-glazed pottery from the late Renaissance blended oxides to produce detailed and realistic polychrome paintings. The earliest tin-glazed pottery appears to have been made in Iraq in the 9th century, the oldest fragments having been excavated during the First World War from the palace of Samarra about fifty miles north of Baghdad.Caiger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valencia, Spain
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (river), Turia, on the east coast of the Iberian Peninsula on the Mediterranean Sea. It is the Ranked lists of Spanish municipalities, third-most populated municipality in the country, with 825,948 inhabitants. The urban area of Valencia has 1.5 million people while the metropolitan region has 2.5 million. Valencia was founded as a Roman Republic, Roman colony in 138 BC as '. As an autonomous city in late antiquity, its militarization followed the onset of the threat posed by the Spania, Byzantine presence to the South, together with effective integration to the Visigothic Kingdom of Toledo in the late 6th century. Al-Andalus, Islamic rule and acculturation ensued in the 8th century, together with the introduction of new irrigation syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maiolica
Maiolica is tin-glazed pottery decorated in colours on a white background. The most renowned Italian maiolica is from the Renaissance period. These works were known as ''istoriato'' wares ("painted with stories") when depicting historical and mythical scenes. By the late 15th century, multiple locations,L. Arnoux, 1877, British Manufacturing Industries – Pottery "Most of the Italian towns had their manufactory, each of them possessing a style of its own. Beginning at Caffagiolo and Deruta, they extended rapidly to Gubbio, Ferrara, and Ravenna, to be continued to Casteldurante, Rimini, Urbino, Florence, Venice, and many other places." mainly in northern and central Italy, were producing sophisticated pieces for a luxury market in Italy and beyond. In France, maiolica developed as faience, in the Netherlands and England as delftware, and in Spain as talavera. In English, the spelling was anglicised to ''majolica'' (). Name The name is thought to come from the medieval Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poitiers Palais Justice Salle Pas Perdus(4)
Poitiers is a city on the river Clain in west-central France. It is a commune, the capital of the Vienne department and the historical center of Poitou Province. In 2021, it had a population of 90,240. Its conurbation had 134,397 inhabitants in 2021 and is the municipal center of an urban area of 281,789 inhabitants. It is a city of art and history, still known popularly as "Ville aux cent clochers" (literal translation: "City of hundred bell towers"). With more than 30,000 students, Poitiers has been a major university town since the creation of its university in 1431, having hosted world-renowned figures and thinkers such as René Descartes, Joachim du Bellay and François Rabelais, among others. The plaza of the town is picturesque; its streets including predominantly preserved historical architecture and half-timbered houses, especially religious edifices, commonly from the Romanesque period. The latter includes notably the 4th century baptistery of Saint-Jean (Baptistè ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
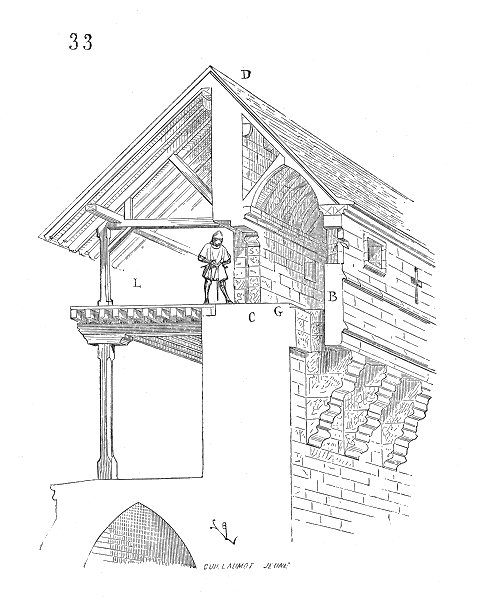
Machicolation
In architecture, a machicolation () is an opening between the supporting corbels of a battlement through which defenders could target attackers who had reached the base of the defensive wall. A smaller related structure that only protects key points of a fortification are referred to as Bretèche. Machicolation, hoarding, bretèche, and murder holes are all similar defensive features serving the same purpose, that is to enable defenders atop a defensive structure to target attackers below. The primary benefit of the design allowed defenders to remain behind cover rather than being exposed when leaning over the parapet. They were common in defensive fortifications until the widespread adoption of gunpowder weapons made them obsolete. Etymology The word machicolation derives from Old French , mentioned in Medieval Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... , mentioned in Medieval Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archives Nationales (France)
The Archives nationales (; abbreviated AN; English: National Archives) are the national archives of France. They preserve the archives of the French state, apart from the archives of the Ministry of Armed Forces and Ministry of Foreign Affairs, as these two ministries have their own archive services, the Defence Historical Service (SHD) and respectively. The National Archives of France also keep the archives of local secular and religious institutions from the Paris Region seized at the time of the French Revolution (such as local royal courts of Paris, suburban abbeys and monasteries, etc), as well as the archives produced by the notaries of Paris during five centuries, and many private archives donated or placed in the custody of the National Archives by prominent aristocratic families, industrialists, and historical figures. The National Archives have one of the largest and oldest archival collections in the world. As of 2022, they held of physical records (the total le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy of Aquitaine and was triggered by English claims to the French throne, a claim to the French throne made by Edward III of England. The war grew into a broader military, economic, and political struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The periodisation of the war typically charts it as taking place over 116 years. However, it was an intermittent conflict which was frequently interrupted by external factors, such as the Black Death, and several years of truces. The Hundred Years' War was a significant conflict in the Middle Ages. During the war, five generations of kings from two rival Dynasty, dynasties fought for the throne of France, then the wealthiest and most populous kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flamboyant
Flamboyant () is a lavishly-decorated style of Gothic architecture that appeared in France and Spain in the 15th century, and lasted until the mid-sixteenth century and the beginning of the Renaissance.Encyclopedia Britannica, "Flamboyant style" (by subscription), accessed April 2024 Elaborate stone tracery covered both the exterior and the interior. Windows were decorated with a characteristic s-shaped curve. Masonry wall space was reduced further as windows grew even larger. Major examples included the northern spire of Chartres Cathedral, Trinity Abbey, Vendôme, Trinity Abbey, Vendôme, and Burgos Cathedral and Segovia Cathedral in Spain. It was gradually replaced by Renaissance architecture in the 16th century. The Period French scholars define Flamboyant as the fourth phase of Gothic style, preceded by Primary Gothic, Classic Gothic and Rayonnant Gothic. British and American historians describe it as a period of Late Gothic architecture, following Early Gothic architectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a monarch, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture (where only the eldest inherits). It was common in much of Europe. The system of appanage greatly influenced the territorial construction of France and the German states and explains why many of the former provinces of France had coats of arms which were modified versions of the king's arms. Etymology Late Latin , from or 'to give bread' (), a for food and other necessities, hence for a "subsistence" income, notably in kind, as from assigned land. Original appanage: in France History of the French appanage An appanage was a concession of a fief by the sovereign to his younger sons, while the eldest son became king on the death of his father. Appanages were considered as part of the inheritance transmitted to the (younger sons). The word was specifically used for the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |