|
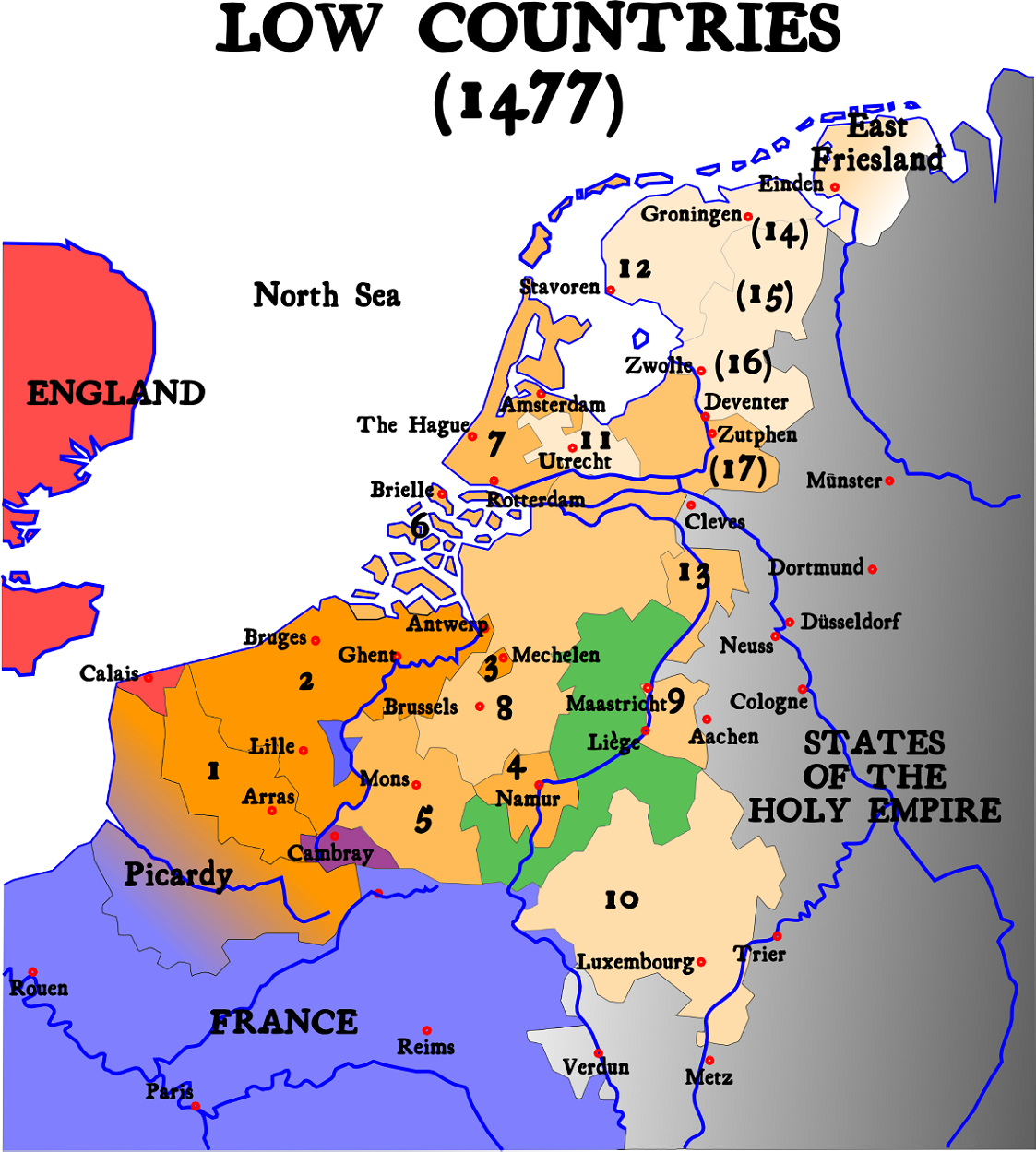
Pacification Of Ghent
The Pacification of Ghent, signed on 8 November 1576, was an alliance between the provinces of the Habsburg Netherlands. The main objectives were to remove Habsburg Spain, Spanish mercenaries who had made themselves hated by all sides due to their plundering, and to promote a formal peace with the rebellious provinces of Holland and Zeeland. Background In 1566, the Habsburg Netherlands experienced considerable political upheaval and civil unrest, which culminated in the Beeldenstorm, iconoclastic fury of that year. Its ruler, Philip II of Spain, responded by appointing Fernando Álvarez de Toledo, 3rd Duke of Alba as List of governors of the Habsburg Netherlands, Governor-general, and in 1567 he arrived there to restore order, accompanied by an army of mercenaries. Philip soon replaced the most important advisors to former regent Margaret of Parma, either by summarily executing those such as the counts of Lamoral, Count of Egmont, Egmont and Philip de Montmorency, Count of Hoorn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands were the parts of the Low Countries that were ruled by sovereigns of the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. This rule began in 1482 and ended for the Northern Netherlands in 1581 and for the Southern Netherlands in 1797. The rule began with the death in 1482 of Mary of Burgundy of the House of Valois-Burgundy who was the ruler of the Low Countries and the wife of Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I of Austria. Their grandson, Emperor Charles V, was born in the Habsburg Netherlands and made Brussels one of his capitals. Becoming known as the Seventeen Provinces in 1549, they were held by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556, known as the Spanish Netherlands from that time on. In 1581, in the midst of the Dutch Revolt, the Seven United Provinces seceded from the rest of this territory to form the Dutch Republic. The remaining Spanish Southern Netherlands became the Austrian Netherlands in 1714, after Austrian acquisition under the Treaty of Rastatt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stadtholder
In the Low Countries, a stadtholder ( ) was a steward, first appointed as a medieval official and ultimately functioning as a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and Habsburg period (1384 – 1581/1795). The title was used for the highest executive official of each province performing several duties, such as appointing lower administrators and maintaining peace and order, in the early Dutch Republic. As multiple provinces appointed the same stadtholder, the stadtholder of the powerful province of Holland at times functioned as the ''de facto'' head of state of the Dutch Republic as a whole during the 16th to 18th centuries, in an effectively hereditary role. For the last half century of its existence, it became an officially hereditary title under Prince William IV of Orange. His son, Prince William V, was the last ''stadtholder'' of all provinces of the Republic, until fleeing French revolutionary tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands and the first independent Dutch people, Dutch nation state. The republic was established after seven Dutch provinces in the Spanish Netherlands Dutch Revolt, revolted against Spanish Empire, Spanish rule, forming a mutual alliance against Spain in 1579 (the Union of Utrecht) and declaring their independence in 1581 (the Act of Abjuration). The seven provinces it comprised were Lordship of Groningen, Groningen (present-day Groningen (province), Groningen), Lordship of Frisia, Frisia (present-day Friesland), Lordship of Overijssel, Overijssel (present-day Overijssel), Duchy of Guelders, Guelders (present-day Gelderland), lordship of Utrecht, Utrecht (present-day Utrecht (province), Utrecht), county of Holland, Holland (present-day North Holla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pensionary
A pensionary (or syndic) was a name given to the leading functionary and legal adviser of the principal town corporations in the Low Countries because they received a salary or pension. History The office originated in Flanders. Initially, the role was referred to as clerk or advocate. The earliest pensionaries in the county of Holland were those of Dordrecht (1468) and of Haarlem (1478). The pensionary conducted the town's legal business and was the secretary of the town council and its representative and spokesman at the meetings of the Provincial States. The post of pensionary was permanent, and he had great influence. In the States of the province of Holland the pensionary of the order of nobles ''( Ridderschap)'' was the foremost official of that assembly and, until the death of Oldenbarneveldt in 1619, he was named Land's Advocate, or more shortly the advocate. His importance was much increased after the revolt in 1572, and still more so during the long period 1586–16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip I Of Castile
Philip the Handsome (22 June/July 1478 – 25 September 1506), also called the Fair, was ruler of the Burgundian Netherlands and titular Duke of Burgundy from 1482 to 1506, as well as the first Habsburg King of Castile (as Philip I) for a brief time in 1506. The son of Maximilian of Austria (later Holy Roman Emperor as Maximilian I) and Mary of Burgundy, Philip was not yet four years old when his mother died as a result of a riding accident, and upon her death, he inherited the Burgundian Netherlands. Despite his young age, Philip quickly proved himself an effective ruler beloved by his people in the Low Countries, pursuing policies that favored peace and economic development, while maintaining a steady course of the government building. In 1496, Philip's father arranged for him to marry Joanna, the second daughter of Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon. Around the same time, Philip's sister, Margaret, was given in marriage to Joanna's brother John, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
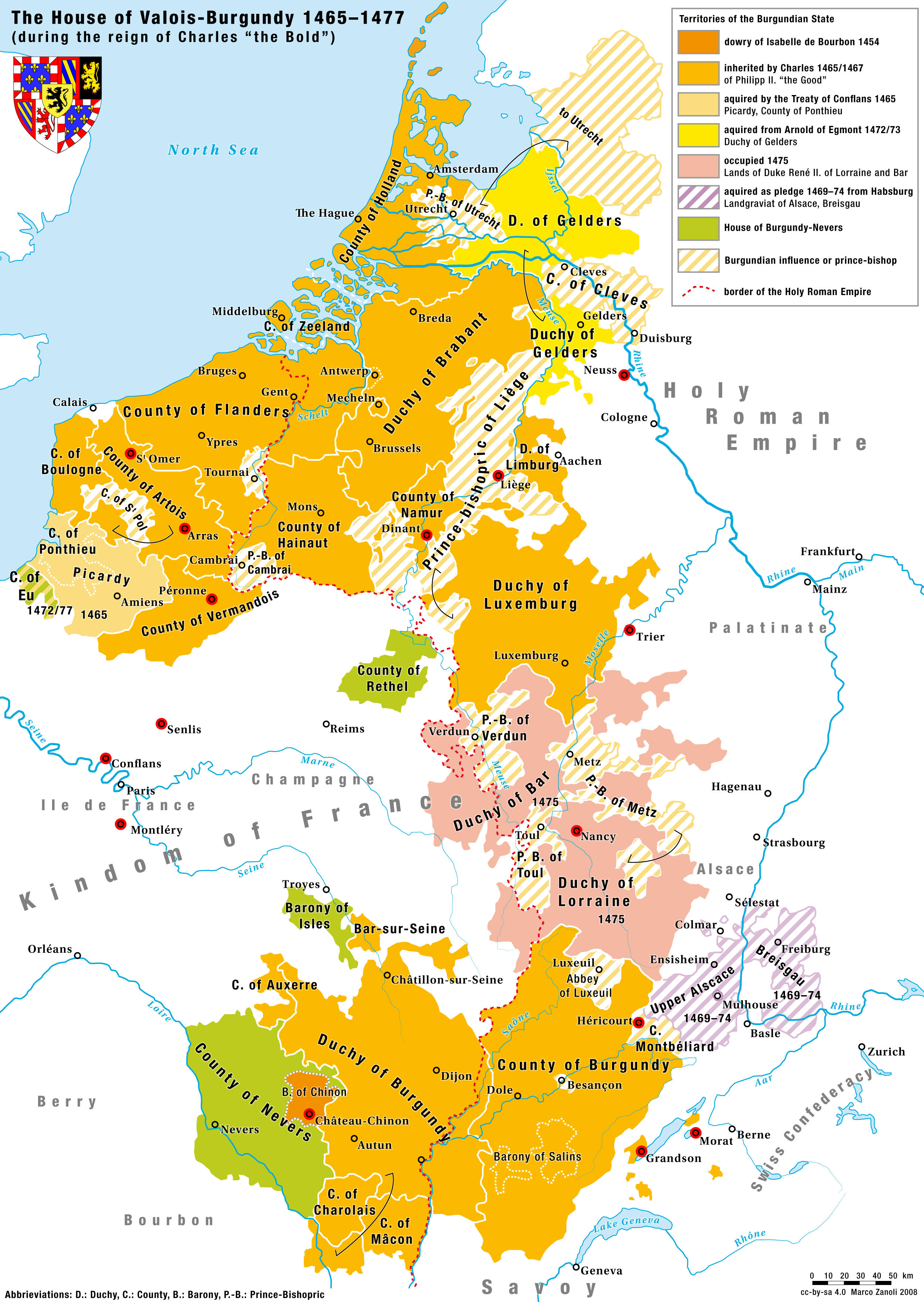
Charles The Bold
Charles Martin (10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), called the Bold, was the last duke of Burgundy from the House of Valois-Burgundy, ruling from 1467 to 1477. He was the only surviving legitimate son of Philip the Good and his third wife, Isabella of Portugal. As heir and as ruler, Charles vied for power and influence with rivals such as his overlord, King Louis XI of France. In 1465 Charles led a successful revolt of Louis's vassals in the War of the Public Weal. After becoming the Duke of Burgundy in 1467, Charles pursued his ambitions for a kingdom, independent from France, that would stretch contiguously from the North Sea in the north to the borders of Savoy in the south. For this purpose, he acquired Guelders and Upper Alsace; sought the title King of the Romans; and gradually became an enemy of the Germans. Charles married Margaret of York for an English alliance. He arranged the betrothal between his sole child, Mary, with Maximilian of Austria. A passiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Hainaut
The County of Hainaut ( ; ; ; ), sometimes spelled Hainault, was a territorial lordship within the medieval Holy Roman Empire that straddled the present-day border of Belgium and France. Its most important towns included Mons, Belgium, Mons (), now in Belgium, and Valenciennes, now in France. The core of the county, named after the river Haine, stretched southeast to include the ''Avesnois'' region and southwest to the Selle (Scheldt tributary). In the Middle Ages, its Counts also gained control of part of the original Pagus of Brabant, ''pagus'' of Brabant to its north and the ''pagus'' of Oosterbant to the east, but they did not form part of the old ''pagus'' of Hainaut. In modern terms, the original core of Hainaut consisted of the central part of the Belgian province of Hainaut (province) , Hainaut, and the eastern part of the French ''département'' of Nord (département) , Nord (the Arrondissements of France, arrondissements of Arrondissement of Avesnes-sur-Helpe, Avesnes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States Of Brabant
The States of Brabant were the representation of the three estates (nobility, clergy and commons) to the court of the Duke of Brabant. The three estates were also called the States. Supported by the economic strength of the cities Antwerp, Brussels and Leuven, the States always were an important power before the rulers of the country, as was reflected by the charter of the duchy. After the Duchy of Brabant and all Seventeen Provinces of the Netherlands came under the rule of the dukes of Burgundy, the States of Brabant became the host of the States-General of the Netherlands, who used to assemble in Brussels. In 1579 and 1580, during the Eighty Years' War, most cities and States of Brabant joined Dutch independence declaration (Union of Utrecht and Act of Abjuration), but Spanish troops reconquered most of the territory of the duchy and restored Spanish Catholic rule (except for North Brabant. See also Siege of Antwerp (1584-1585)). By the end of 1789, the States of Brabant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States General Of The Netherlands
The States General of the Netherlands ( ) is the Parliamentary sovereignty, supreme Bicameralism, bicameral legislature of the Netherlands consisting of the Senate (Netherlands), Senate () and the House of Representatives (Netherlands), House of Representatives (). Both chambers meet at the Binnenhof in The Hague. The States General originated in the 15th century as an assembly of all the provincial states of the Burgundian Netherlands. In 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, the States General split as the northern provinces openly rebelled against Philip II of Spain, Philip II, and the northern States General replaced Philip II as the supreme authority of the Dutch Republic in 1581. The States General were replaced by the National Assembly of the Batavian Republic, National Assembly after the Batavian Revolution of 1795, only to be restored in 1814, when the country had regained its sovereignty. The States General was divided into a Senate and a House of Representatives in 1815, with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Zierikzee
{{Infobox military conflict , conflict = Siege of Zierikzee , partof = the Eighty Years' War , image = Zierikzee 1595 Bor.jpg , image_size = 260 , caption = The siege of Zierikzee , date = October 1575 – 29 July 1576 , place = Zierikzee (present-day Zeeland) , coordinates = {{WikidataCoord, display=it , map_type = Netherlands#North Sea , map_relief = yes , map_size = , map_marksize = , map_caption = , map_label = , map_mark = , casus = , territory = , result = Spanish victory , combatant1 = {{flagicon, Dutch Republic, 1581 Dutch Rebels , combatant2 = {{flagicon, Spain, 1506 Spain , commander1 = Arend van der Dorp , commander2 = Cristóbal de Mondragón , strength1 = 1,200 , strength2 = 3,000 infantry, 400 cavalry , casualties1 = , casualties2 = , campaignbox = {{Campaignbox Eighty Ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of State Of The Netherlands
The Council of State () is a constitutionally established advisory body in the Netherlands to the government and States General that officially consists of members of the royal family and Crown-appointed members generally having political, commercial, diplomatic or military experience. It was founded in 1531, making it one of the world's oldest still-functioning state organisations. The Council of State must be consulted by the cabinet on proposed legislation before a law is submitted to parliament. The Council of State Administrative Law division also serves as one of the four highest courts of appeal in administrative matters. The King is president of the Council of State but he seldom chairs meetings. The Vice-President of the Council of State chairs meetings in his absence and is the ''de facto'' major personality of the institution. Under Dutch constitutional law, the Vice-President of the Council is acting head of state when there is no monarch such as if the royal family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Austria
John of Austria (, ; 24 February 1547 – 1 October 1578) was the illegitimate son of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. Charles V recognized him in a codicil to his will. John became a military leader in the service of his half-brother, King Philip II of Spain, Charles V's heir, and was addressed to as a Don. He is best known for his role as the admiral of the Holy League fleet at the Battle of Lepanto and as Governor of the Spanish Netherlands. Life Early years John of Austria was born in Regensburg, Upper Palatinate. His mother was Barbara Blomberg, the daughter of a burgher, and his father was Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, who had been widowed since 1539. In the summer of 1554, he was taken to the castle of Luis de Quijada in Villagarcía de Campos, Valladolid. Magdalena de Ulloa, de Quijada's wife, took charge of his education, assisted by Latin teacher Guillén Prieto, chaplain García de Morales, and Juan Galarza, a squire. Charles V wrote a codicil, dated 6 June ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |