|
PPO Inhibitor Herbicide
Protoporphyrinogen oxidase or protox is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PPOX'' gene. Protoporphyrinogen oxidase is responsible for the seventh step in biosynthesis of protoporphyrin IX. This porphyrin is the precursor to hemoglobin, the oxygen carrier in animals, and chlorophyll, the dye in plants. The enzyme catalyzes the dehydrogenation (removal of hydrogen atoms) of protoporphyrinogen IX (the product of the sixth step in the production of heme) to form protoporphyrin IX. One additional enzyme must modify protoporphyrin IX before it becomes heme. Inhibition of this enzyme is a strategy used in certain herbicides. Gene The PPOX gene is located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 1 at position 22, from base pair 157,949,266 to base pair 157,954,082. Function This gene encodes the penultimate enzyme of heme biosynthesis, which catalyzes the 6-electron oxidation of protoporphyrinogen IX to form protoporphyrin IX. This protein is a flavoprotein associated with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol (a gel-like substance), the cell's internal sub-structures, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. In eukaryotes the cytoplasm also includes the nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance, or cytoplasmic matrix, that remains after the exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, plant plasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALAD
Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (porphobilinogen synthase, or ALA dehydratase, or aminolevulinate dehydratase) is an enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the ''ALAD'' gene. Porphobilinogen synthase (or ALA dehydratase, or aminolevulinate dehydratase) synthesizes porphobilinogen through the asymmetric condensation of two molecules of aminolevulinic acid. All natural tetrapyrroles, including hemes, chlorophylls and vitamin B12, share porphobilinogen as a common precursor. Porphobilinogen synthase is the prototype morpheein. Function It catalyzes the following reaction, the second step of the biosynthesis of porphyrin: :2 5- Aminolevulinic acid \rightleftharpoons porphobilinogen + 2 H2O It therefore catalyzes the condensation of 2 molecules of 5-aminolevulinate to form porphobilinogen (a precursor of heme, cytochromes and other hemoproteins). This reaction is the first common step in the biosynthesis of all biological tetrapyrroles. Zinc is essential for enzymatic activity. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the pseudoelement symbol for ethyl group, ethyl. Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. As a psychoactive depressant, it is the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, and the second most consumed drug globally behind caffeine. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. Historically it was used as a general anesthetic, and has modern medical applications as an antiseptic, disinfectant, solvent for some medications, and antidote for methanol poisoning and ethylene glycol poisoning. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
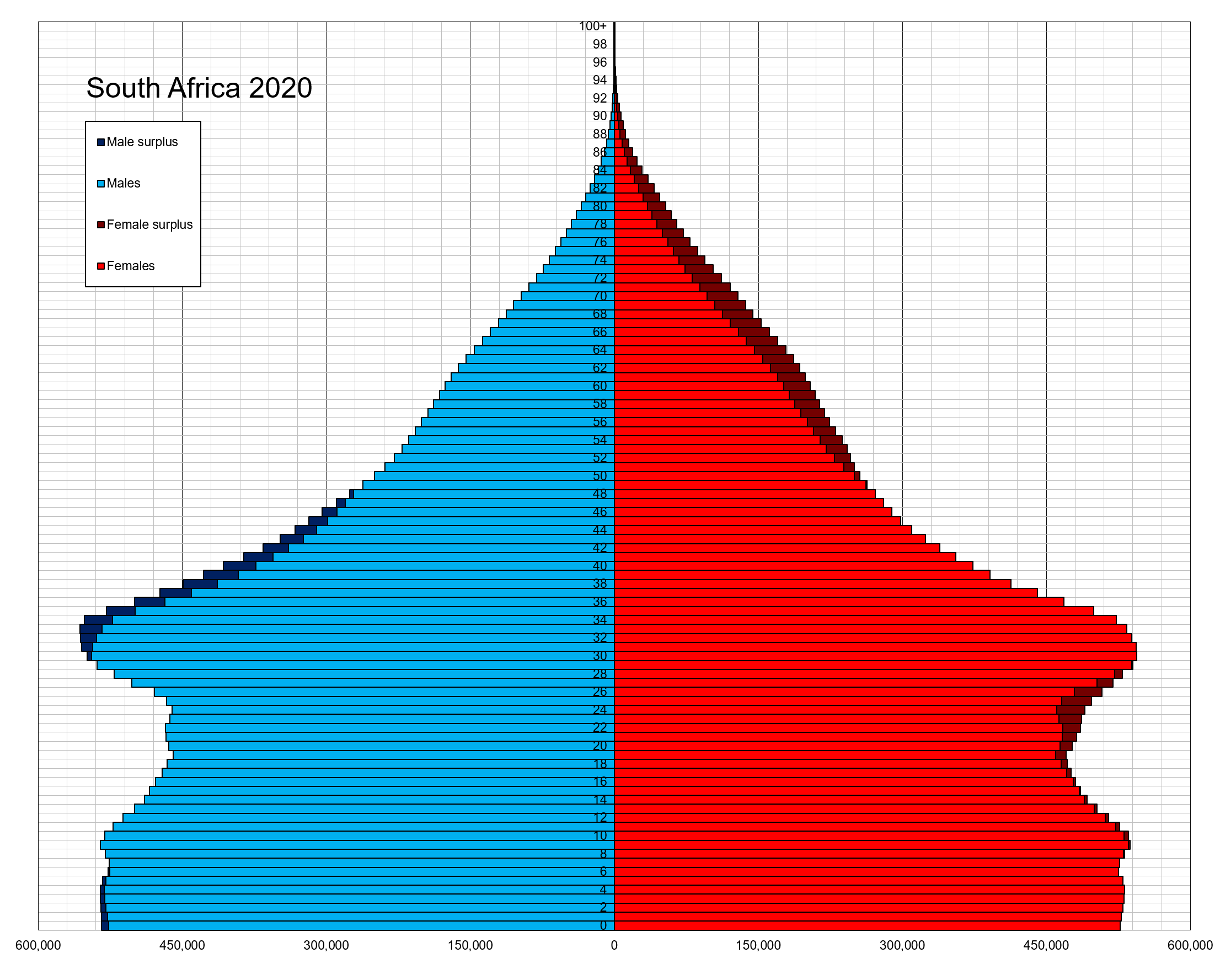
South African People
According to the 2022 census, the population of South Africa is about 62 million people of diverse origins, cultures, Languages of South Africa, languages, and Religion in South Africa, religions, with a majority being Black Africans. The South African National Census of 2022 was the most recent census held; the next will be in 2032. In 2011, Statistics South Africa counted 2.1 million foreigners in total. Reports suggest that is an underestimation. The real figure may be as high as five million, including some three million Demographics of Zimbabwe, Zimbabweans. History The earliest creatures that can be identified as human ancestors in South Africa are Australopithecine, australopithecines. The first evidence of this was a Taung Child, child's skull found in the Taung quarry site. This was in the modern day North West (South African province), North-West province. More Fossil, fossils australopithecines were found in limestone caves Sterkfontein, Swartkrans, and Kromdraai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the amino and guanidino groups are protonated, resulting in a cation. Only the -arginine (symbol Arg or R) enantiomer is found naturally. Arg residues are common components of proteins. It is Genetic code, encoded by the DNA codon table, codons CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG. The guanidine group in arginine is the Precursor (chemistry), precursor for the biosynthesis of nitric oxide. Like all amino acids, it is a white, water-soluble solid. The one-letter symbol R was assigned to arginine for its phonetic similarity. History Arginine was first isolated in 1886 from Lupinus luteus, yellow lupin seedlings by the German chemist Ernst Schulze (chemist), Ernst Schulze and his assistant Ernst Steiger. He named it from the Greek ''árg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic beta carbon substituent. Tryptophan is also a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, the hormone melatonin, and vitamin B3 (niacin). It is encoded by the codon UGG. Like other amino acids, tryptophan is a zwitterion at physiological pH where the amino group is protonated (–; pKa = 9.39) and the carboxylic acid is deprotonated ( –COO−; pKa = 2.38). Humans and many animals cannot synthesize tryptophan: they need to obtain it through their diet, making it an essential amino acid. Tryptophan is named after the digestive enzymes trypsin, which were used in its first isolation from casein proteins. It was assigned the one-letter symbol W based on the double ring being visually suggestive to the bulky letter. Function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variegate Porphyria
Variegate porphyria, also known by several other names, is an autosomal dominant porphyria that can have acute (severe but usually not long-lasting) symptoms along with symptoms that affect the skin. The disorder results from low levels of the enzyme responsible for the seventh step in heme production. Heme is a vital molecule for all of the body's organs. It is a component of hemoglobin, the molecule that carries oxygen in the blood. Signs and symptoms When symptoms occur, they can include acute attacks (similar to acute intermittent porphyria) or skin damage. Acute attacks usually begin in adulthood and cause abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhoea and constipation. During an attack, a person may also experience muscle weakness, seizures, and mental changes such as anxiety and hallucinations. These signs and symptoms are triggered by nongenetic factors such as certain drugs, dieting or fasting, certain hormones and stress. Some people with variegate porphyria have skin that is over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UROS
The Uru or Uros () are an indigenous people of Bolivia and Peru. They live on a still-growing group of about 120 self-fashioned floating islands in Lake Titicaca near Puno. They form three main groups: the Uru-Chipaya, Uru-Murato, and Uru-Iruito. The Uru-Iruito still inhabit the Bolivian side of Lake Titicaca and the Desaguadero River. The indigenous Urus have darker skin than their neighbours Aymaras and Quechuas. History According to legend, the Uru descend from a people that spoke the Puquina language. While most of the Uru have shifted to Aymara and Spanish, two people still spoke in 2004 the nearly extinct Uru language, which is closely related to the Chipaya language. The Uru considered themselves the owners of the lake and water. According to the legend, Uru used to say that they had black blood, because they did not feel the cold. They historically called themselves ''Lupihaques'', "sons of the Sun". Although the Uru language is nearly extinct, the Uru cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UROD
Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase (uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase, or UROD) is an enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the ''UROD'' gene. Function Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase is a homodimeric enzyme () that catalyzes the fifth step in heme biosynthesis, which corresponds to the elimination of carboxyl groups from the four acetate side chains of uroporphyrinogen III to yield coproporphyrinogen III: : uroporphyrinogen III \rightleftharpoons coproporphyrinogen III + 4 CO2 Clinical significance Mutations and deficiency in this enzyme are known to cause familial porphyria cutanea tarda and hepatoerythropoietic porphyria. At least 65 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered. Mechanism At low substrate concentrations, the reaction is believed to follow an ordered route, with the sequential removal of CO2 from the D, A, B, and C rings, whereas at higher substrate/enzyme levels a random route seems to be operative. The enzyme functions as a dim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMBS (gene)
Porphobilinogen deaminase (hydroxymethylbilane synthase, or uroporphyrinogen I synthase) is an enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the HMBS gene. Porphobilinogen deaminase is involved in the third step of the heme biosynthetic pathway. It catalyzes the head to tail condensation of four porphobilinogen molecules into the linear hydroxymethylbilane while releasing four ammonia molecules: :4 porphobilinogen + H2O \rightleftharpoons hydroxymethylbilane + 4 NH3 Structure and function Functionally, porphobilinogen deaminase catalyzes the loss of ammonia from the porphobilinogen monomer (deamination) and its subsequent polymerization to a linear tetrapyrrole, which is released as hydroxymethylbilane: The structure of 40-42 kDa porphobilinogen deaminase, which is highly conserved amongst organisms, consists of three domains. Domains 1 and 2 are structurally very similar: each consisting of five beta-sheets and three alpha helices in humans. Domain 3 is positioned between the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrochelatase
Protoporphyrin ferrochelatase (EC 4.98.1.1, formerly EC 4.99.1.1, or ferrochelatase; systematic name protoheme ferro-lyase (protoporphyrin-forming)) is an enzyme encoded by the ''FECH'' gene in humans. Ferrochelatase catalyses the eighth and terminal step in the biosynthesis of heme, converting protoporphyrin IX into heme B. It catalyses the reaction: : Function Ferrochelatase catalyzes the insertion of ferrous iron into protoporphyrin IX in the heme biosynthesis pathway to form heme B. The enzyme is localized to the matrix-facing side of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Ferrochelatase is the best known member of a family of enzymes that add divalent metal cations to tetrapyrrole structures. For example, magnesium chelatase adds magnesium to protoporphyrin IX in the first step of bacteriochlorophyll biosynthesis. Heme B is an essential cofactor in many proteins and enzymes. In particular, heme b plays a key role as the oxygen carrier in hemoglobin in red blood cells a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |