|
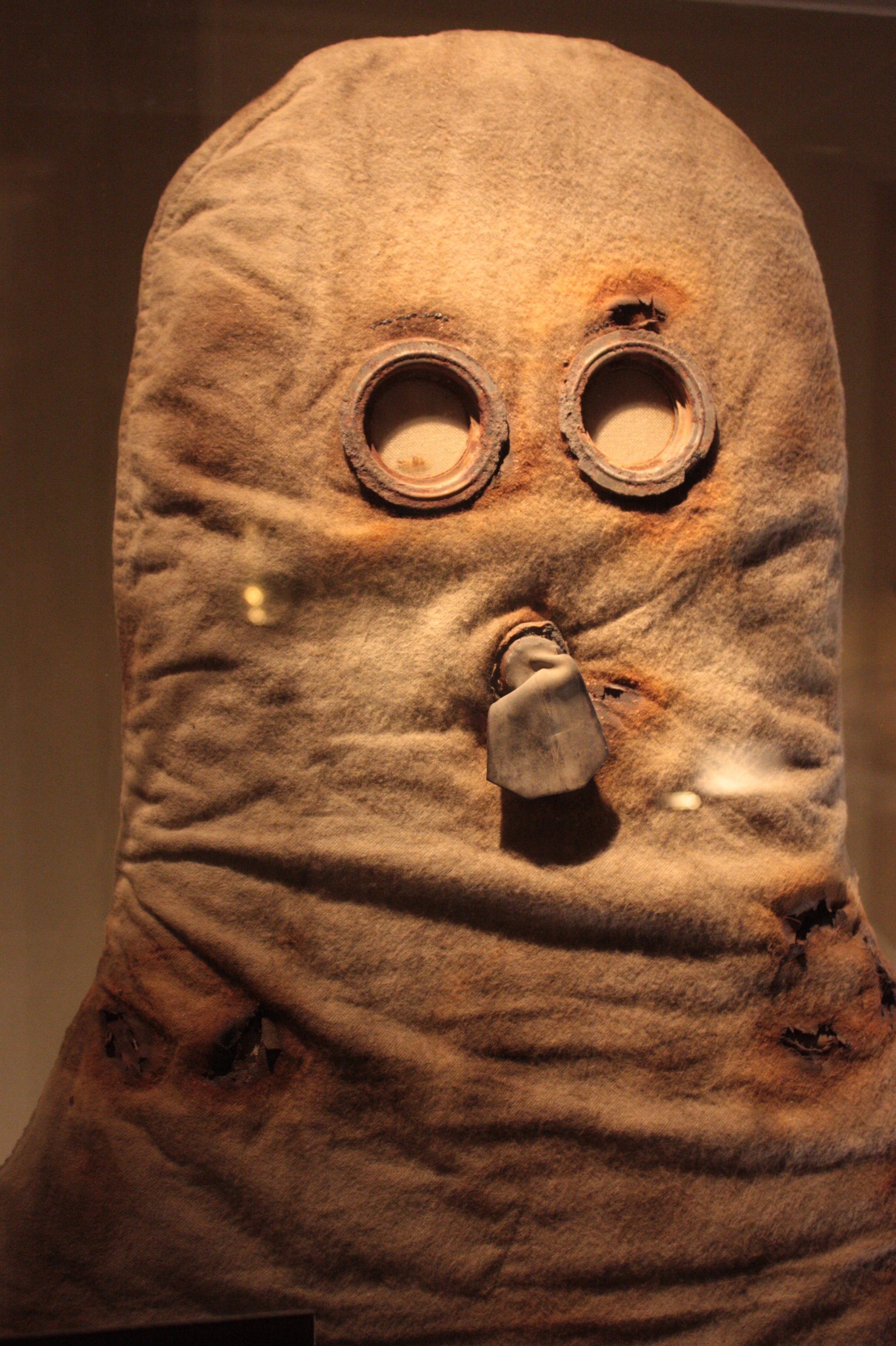
PH Helmet
The P helmet, PH helmet and PHG helmet were early types of gas mask issued by the British Army in the First World War, to protect troops against chlorine, phosgene and tear gases. Rather than having a separate filter for removing the toxic chemicals, they consisted of a gas-permeable hood worn over the head which was treated with chemicals. The P (or Phenate) Helmet, officially called the Tube Helmet, appeared in July 1915, replacing the simpler Hypo Helmet. It featured two mica eyepieces instead of the single visor of its predecessor, and added an exhale valve fed from a metal tube which the wearer held in his mouth. The exhale valve was needed because a double layer of flannel – one treated and one not – was needed because the solution attacked the fabric. It had flannel layers of cloth-dipped in sodium phenolate and glycerin and protected against chlorine and phosgene, but not against tear gas. Around 9 million were made. The PH Helmet (Phenate Hexamine) replaced it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Machine Gun Crew With Gas Masks
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public in 1867, acquired more businesses, and began branching out into military hardware and shipbuilding. In 1911, the company expanded into aircraft manufacture and opened a flying school. They expanded even further into electrical and railway manufacturing, and in 1928 acquired an interest in the Supermarine. Beginning in the 1960s, various parts of the company were nationalised, and in 1999 the rest of the company was acquired by Rolls-Royce plc, which sold the defence arm to Alvis plc. The Vickers name lived on in Alvis Vickers, until the latter was acquired by BAE Systems in 2004 to form BAE Systems Land Systems. History Early history Vickers was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law George Naylo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypo Helmet
The Hypo helmet, or British Smoke Hood (its official name), was an early British World War I gas mask, designed by Cluny Macpherson. Background The German army used poison gas, in the form of chlorine, for the first time against Triple Entente troops at the Second Battle of Ypres, Belgium, on 22 April 1915. The British began issuing cotton wool wrapped in muslin to its troops by 3 May. This was followed by the Black Veil Respirator, invented by John Scott Haldane, which began to be issued to troops on 20 May 1915. The Black Veil was a cotton pad soaked in an absorbent solution which was secured over the mouth using black cotton veiling. The veiling could be drawn up to cover the eyes, providing some protection against lachrymatory agents but the mask still provided little protection against chlorine gas. It was also of fragile construction, required training to use and largely immobilised men during a gas attack as they were concerned about their mask coming loose. Design Seek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Box Respirator
The Small Box Respirator (SBR) was a British gas mask of the First World War and a successor to the Large Box Respirator. In late 1916, the respirator was introduced by the British with the aim to provide reliable protection against chlorine and phosgene gases. The respirator offered a first line of defence against these. The use of mustard gas, was begun by the Germans; a vesicant ("blister agent") that burnt the skin of individuals that were exposed to it. Death rates were high with exposure to both the mixed phosgene, chlorine and mustard gas, however with soldiers having readily available access to the small box respirator, death rates had lowered significantly. Light and reasonably fitting, the respirator was a key piece of equipment to protect soldiers on the battlefield. Materials and construction The small box respirator consists of a face mask made of rubberized fabric connected by a rubber fabric hose to a canister made of tinplate containing a chemical absorbent. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide (formerly known as prussic acid) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula HCN and structural formula . It is a highly toxic and flammable liquid that boiling, boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is produced on an industrial scale and is a highly valued Precursor (chemistry), precursor to many chemical compounds ranging from polymers to pharmaceuticals. Large-scale applications are for the production of potassium cyanide and adiponitrile, used in mining and plastics, respectively. It is more toxic than solid cyanide compounds due to its Volatility (chemistry), volatile nature. A solution of hydrogen cyanide in water (molecule), water, represented as HCN(aqueous, aq), is called ''hydrocyanic acid''. The Salt (chemistry), salts of the cyanide anion are known as cyanides. Whether hydrogen cyanide is an organic compound or not is a topic of debate among chemists, and opinions vary from author to author. Traditionally, it is considered ino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexamethylene Tetramine
Hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA), also known as 1,3,5,7-tetraazaadamantane, is a heterocycle, heterocyclic organic compound with diverse applications. It has the chemical formula (CH2)6N4 and is a white crystalline compound that is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is useful in the chemical synthesis, synthesis of other organic compounds, including plastics, pharmaceuticals, and rubber additives. The compound is also used medically for certain conditions. It sublimation (chemistry), sublimes in vacuum at 280°C. It has a tetrahedron, tetrahedral cage-like structure similar to adamantane. The four vertices are occupied by nitrogen atoms, which are linked by methylene groups. Although the molecular shape defines a cage, no void space is available at the interior. Synthesis, structure, reactivity Hexamethylenetetramine was discovered by Aleksandr Butlerov in 1859. In this article, Butlerov discovered formaldehyde, which he called "dioxymethylen" (methylene dioxide) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycerin
Glycerol () is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting, viscous liquid. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations. Because of its three hydroxyl groups, glycerol is miscible with water and is Hygroscopy, hygroscopic in nature. Modern use of the word glycerine (alternatively spelled glycerin) refers to commercial preparations of less than 100% purity, typically 95% glycerol. Structure Although chirality, achiral, glycerol is prochirality, prochiral with respect to reactions of one of the two primary alcohols. Thus, in substituted derivatives, the Glycerophospholipid#Nomenclature and stereochemistry, stereospecific numbering labels the molecule with a ''sn''- prefix before the stem name of the molecule. Production Natural sources Glycerol is generally obtained from plant and animal sources where it occurs in triglycerides, est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Phenolate
Sodium phenoxide (sodium phenolate) is an organic compound with the formula NaOC6H5. It is a white crystalline solid. Its anion, phenoxide, also known as phenolate, is the conjugate base of phenol. It is used as a precursor to many other organic compounds, such as aryl ethers. Synthesis and structure Most commonly, solutions of sodium phenoxide are produced by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide. Anhydrous derivatives can be prepared by combining phenol and sodium. A related, updated procedure uses sodium methoxide instead of sodium hydroxide: :NaOCH3 + HOC6H5 → NaOC6H5 + HOCH3 Sodium phenoxide can also be produced by the "alkaline fusion" of benzenesulfonic acid, whereby the sulfonate groups are displaced by hydroxide: :C6H5SO3Na + 2 NaOH → C6H5OH + Na2SO3 This route once was the principal industrial route to phenol. Structure Like other sodium alkoxides, solid sodium phenoxide adopts a complex structure involving multiple Na-O bonds. Solvent-free material i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into fragile elastic plates. This characteristic is described as ''perfect basal cleavage''. Mica is common in igneous and metamorphic rock and is occasionally found as small flakes in sedimentary rock. It is particularly prominent in many granites, pegmatites, and schists, and "books" (large individual crystals) of mica several feet across have been found in some pegmatites. Micas are used in products such as drywalls, paints, and fillers, especially in parts for automobiles, roofing, and in electronics. The mineral is used in cosmetics and food to add "shimmer" or "frost". Properties and structure The mica group comprises 37 phyllosilicate minerals. All crystallize in the monoclinic system, with a tendency towards pseudohexagonal crystals, and are similar in structure but vary in chemical composition. Micas are translucent to opa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tear Gas
Tear gas, also known as a lachrymatory agent or lachrymator (), sometimes colloquially known as "mace" after the Mace (spray), early commercial self-defense spray, is a chemical weapon that stimulates the nerves of the lacrimal gland in the eye to produce tears. In addition, it can cause severe eye and respiratory pain, skin irritation, bleeding, and blindness. Common lachrymators both currently and formerly used as tear gas include pepper spray (OC gas), PAVA spray (nonivamide), CS gas, CR gas, CN gas (phenacyl chloride), bromoacetone, xylyl bromide, chloropicrin (PS gas) and Mace (spray), Mace (a branded mixture). While lachrymatory agents are commonly deployed for riot control by law enforcement and military personnel, its use in warfare is prohibited by various international treaties.E.g. the Geneva Protocol of 1925 prohibited the use of "asphyxiating gas, or any other kind of gas, liquids, substances or similar materials". During World War I, increasingly toxic and deadly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A World War I British Gas Hood C
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, '' a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest known ancestor of A is ''aleph''—the first letter of the Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosgene
Phosgene is an organic chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic, colorless gas; in low concentrations, its musty odor resembles that of freshly cut hay or grass. It can be thought of chemically as the double acyl chloride analog of carbonic acid, or structurally as formaldehyde with the hydrogen atoms replaced by chlorine atoms. In 2013, about 75–80 % of global phosgene was consumed for isocyanates, 18% for polycarbonates and about 5% for other fine chemicals. Phosgene is extremely poisonous and was used as a chemical weapon during World War I, where it was responsible for 85,000 deaths. It is a highly potent pulmonary irritant and quickly filled enemy trenches due to it being a heavy gas. It is classified as a Schedule 3 substance under the Chemical Weapons Convention. In addition to its industrial production, small amounts occur from the breakdown and the combustion of organochlorine compounds, such as chloroform. Structure and basic properties Phosgene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidizing agent, oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Electronegativity#Pauling electronegativity, Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval Alchemy, alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride Salt (chemistry), salts like ammonium chloride (sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and . However, the nature of fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |