|
P-wave
A P wave (primary wave or pressure wave) is one of the two main types of elastic body waves, called seismic waves in seismology. P waves travel faster than other seismic waves and hence are the first signal from an earthquake to arrive at any affected location or at a seismograph. P waves may be transmitted through gases, liquids, or solids. Nomenclature The name ''P wave'' can stand for either pressure wave (as it is formed from alternating compressions and rarefactions) or primary wave (as it has high velocity and is therefore the first wave to be recorded by a seismograph). The name '' S wave'' represents another seismic wave propagation mode, standing for secondary or shear wave. Seismic waves in the Earth Primary and secondary waves are body waves that travel within the Earth. The motion and behavior of both P and S waves in the Earth are monitored to probe the interior structure of the Earth. Discontinuities in velocity as a function of depth are indicative of ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Waves
A seismic wave is a wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth. It can result from an earthquake, volcanic eruption, magma movement, a large landslide, and a large man-made explosion that produces low-frequency acoustic energy. Seismic waves are studied by seismologists, who record the waves using seismometers, hydrophones (in water), or accelerometers. Seismic waves are distinguished from seismic noise (ambient vibration), which is persistent low-amplitude vibration arising from a variety of natural and anthropogenic sources. The propagation velocity of a seismic wave depends on density and elasticity of the medium as well as the type of wave. Velocity tends to increase with depth through Earth's crust and mantle, but drops sharply going from the mantle to Earth's outer core. Earthquakes create distinct types of waves with different velocities. When recorded by a seismic observatory, their different travel times help scientists locate the quake's hypocen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake Wave Shadow Zone
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-wave Modulus
There are two kinds of seismic body waves in solids, ''pressure waves'' (P-waves) and ''shear waves.'' In linear elasticity, the P-wave modulus M, also known as the longitudinal modulus, or the constrained modulus, is one of the elastic moduli available to describe isotropic homogeneous materials. It is defined as the ratio of axial stress to axial strain in a uniaxial strain state. This occurs when expansion in the transverse direction is prevented by the inertia of neighboring material, such as in an earthquake, or underwater seismic blast. :\sigma_ = M \epsilon_ where all the other strains \epsilon_ are zero. This is equivalent to stating that :M_ = \rho_ V_\mathrm^2 , where ''V''P is the velocity of a P-wave and ''ρ'' is the density Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake Early Warning
An earthquake warning system or earthquake early warning system is a system of accelerometers, seismometers, communication, computers, and alarms that is devised for notifying adjoining regions of a substantial earthquake while it is in progress. This is not the same as earthquake prediction, which is currently incapable of producing decisive event warnings. Time lag and wave projection An earthquake is caused by the release of stored elastic strain energy during rapid sliding along a fault. The sliding starts at some location and progresses away from the hypocenter in each direction along the fault surface. The speed of the progression of this fault tear is slower than, and distinct from the speed of the resultant pressure and shear waves, with the pressure wave traveling faster than the shear wave. The pressure waves generate an abrupt shock. The shear waves generate periodic motion (at about 1 Hz) that is the most destructive to structures, particularly buildings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitudinal Wave
Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel ("along") to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called ''compressional'' or compression waves, because they produce compression and rarefaction when traveling through a medium, and pressure waves, because they produce increases and decreases in pressure. A wave along the length of a stretched Slinky toy, where the distance between coils increases and decreases, is a good visualization. Real-world examples include sound waves ( vibrations in pressure, a particle of displacement, and particle velocity propagated in an elastic medium) and seismic P-waves (created by earthquakes and explosions). The other main type of wave is the transverse wave, in which the displacements of the medium are at right angles to the direction of propagation. Transverse waves, for instance, des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
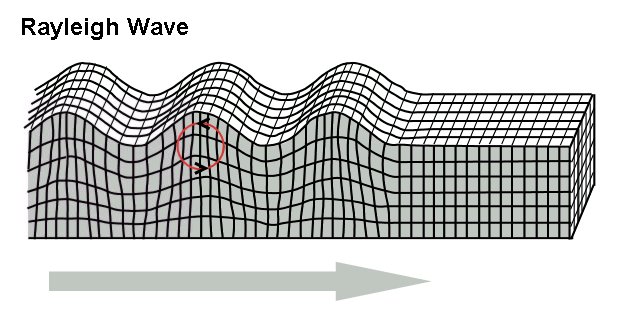
Rayleigh Wave
Rayleigh waves are a type of surface acoustic wave that travel along the surface of solids. They can be produced in materials in many ways, such as by a localized impact or by piezo-electric transduction, and are frequently used in non-destructive testing for detecting defects. Rayleigh waves are part of the seismic waves that are produced on the Earth by earthquakes. When guided in layers they are referred to as Lamb waves, Rayleigh–Lamb waves, or generalized Rayleigh waves. Characteristics Rayleigh waves are a type of surface wave that travel near the surface of solids. Rayleigh waves include both longitudinal and transverse motions that decrease exponentially in amplitude as distance from the surface increases. There is a phase difference between these component motions. The existence of Rayleigh waves was predicted in 1885 by Lord Rayleigh, after whom they were named. In isotropic solids these waves cause the surface particles to move in ellipses in planes normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastic Moduli
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity) is the unit of measurement of an object's or substance's resistance to being deformed elastically (i.e., non-permanently) when a stress is applied to it. The elastic modulus of an object is defined as the slope of its stress–strain curve in the elastic deformation region: A stiffer material will have a higher elastic modulus. An elastic modulus has the form: :\delta \ \stackrel\ \frac where stress is the force causing the deformation divided by the area to which the force is applied and strain is the ratio of the change in some parameter caused by the deformation to the original value of the parameter. Since strain is a dimensionless quantity, the units of \delta will be the same as the units of stress. Specifying how stress and strain are to be measured, including directions, allows for many types of elastic moduli to be defined. The three primary ones are: # ''Young's modulus'' (E) describes tensile and compressive e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulk Modulus
The bulk modulus (K or B) of a substance is a measure of how resistant to compression the substance is. It is defined as the ratio of the infinitesimal pressure increase to the resulting ''relative'' decrease of the volume. Other moduli describe the material's response ( strain) to other kinds of stress: the shear modulus describes the response to shear stress, and Young's modulus describes the response to normal (lengthwise stretching) stress. For a fluid, only the bulk modulus is meaningful. For a complex anisotropic solid such as wood or paper, these three moduli do not contain enough information to describe its behaviour, and one must use the full generalized Hooke's law. The reciprocal of the bulk modulus at fixed temperature is called the isothermal compressibility. Definition The bulk modulus K (which is usually positive) can be formally defined by the equation :K=-V\frac , where P is pressure, V is the initial volume of the substance, and dP/dV denotes the derivative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shadow Zone
A seismic shadow zone is an area of the Earth's surface where seismographs cannot detect direct P waves and/or S waves from an earthquake. This is due to liquid layers or structures within the Earth's surface. The most recognized shadow zone is due to the core-mantle boundary where P waves are refracted and S waves are stopped at the liquid outer core; however, any liquid boundary or body can create a shadow zone. For example, magma reservoirs with a high enough percent melt can create seismic shadow zones. Background The earth is made up of different structures: the crust, the mantle, the inner core and the outer core. The crust, mantle, and inner core are typically solid; however, the outer core is entirely liquid. A liquid outer core was first shown in 1906 by Geologist Richard Oldham. Oldham observed seismograms from various earthquakes and saw that some seismic stations did not record direct S waves, particularly ones that were 120° away from the hypocenter of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P Wave (electrocardiography)
The P wave on the ECG represents atrial depolarization, which results in atrial contraction, or atrial systole. Physiology The P wave is a summation wave generated by the depolarization front as it transits the atria. Normally the right atrium depolarizes slightly earlier than left atrium since the depolarization wave originates in the sinoatrial node, in the high right atrium and then travels to and through the left atrium. The depolarization front is carried through the atria along semi-specialized conduction pathways including Bachmann's bundle resulting in uniform shaped waves. Depolarization originating elsewhere in the atria (atrial ectopics) result in P waves with a different morphology from normal. Pathology Peaked P waves (> 0.25 mV) suggest right atrial enlargement, cor pulmonale, (''P pulmonale'' rhythm), but have a low predictive value (~20%). A P wave with increased amplitude can indicate hypokalemia. It can also indicate right atrial enlargement Rights ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rarefaction
Rarefaction is the reduction of an item's density, the opposite of compression. Like compression, which can travel in waves ( sound waves, for instance), rarefaction waves also exist in nature. A common rarefaction wave is the area of low relative pressure following a shock wave (see picture). Rarefaction waves expand with time (much like sea waves spread out as they reach a beach); in most cases rarefaction waves keep the same overall profile ('shape') at all times throughout the wave's movement: it is a ''self-similar expansion''. Each part of the wave travels at the local speed of sound, in the local medium. This expansion behaviour contrasts with that of pressure increases, which gets narrower with time until they steepen into shock waves. When angle of incidence is greater than angle of refraction, then light travels from denser to rarer medium. When angle of incidence is smaller than angle of refraction then light travels from rarer to denser medium Physical examples A n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compression (physical)
In mechanics, compression is the application of balanced inward ("pushing") forces to different points on a material or structure, that is, forces with no net sum or torque directed so as to reduce its size in one or more directions.Ferdinand Pierre Beer, Elwood Russell Johnston, John T. DeWolf (1992), "Mechanics of Materials". (Book) McGraw-Hill Professional, It is contrasted with tension or traction, the application of balanced outward ("pulling") forces; and with shearing forces, directed so as to displace layers of the material parallel to each other. The compressive strength of materials and structures is an important engineering consideration. In uniaxial compression, the forces are directed along one direction only, so that they act towards decreasing the object's length along that direction. The compressive forces may also be applied in multiple directions; for example inwards along the edges of a plate or all over the side surface of a cylinder, so as to reduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |