|
Outline Of Automation
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to automation: Automation – use of control systems and information technologies to reduce the need for human work in the production of goods and services. In the scope of industrialization, automation is a step beyond mechanization. Essence of automation * Control system – a device, or set of devices to manage, command, direct or regulate the behavior of other devices or systems. * Industrial control system (ICS) – encompasses several types of control systems used in industrial production, including supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, distributed control systems (DCS), and other smaller control system configurations such as skid-mounted programmable logic controllers (PLC) often found in industrial sectors and critical infrastructures. * Industrialization – period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcast Automation
Broadcast automation incorporates the use of broadcast programming technology to automate broadcasting operations. Used either at a broadcast network, radio station or a television station, it can run a facility in the absence of a human operator. They can also run in a ''live assist'' mode when there are on-air personnel present at the master control, television studio or control room. The radio transmitter end of the airchain is handled by a separate automatic transmission system (ATS). History Originally, in the US, many (if not most) broadcast licensing authorities required a licensed board operator to run every station at all times, meaning that every DJ had to pass an exam to obtain a license to be on-air, if their duties also required them to ensure proper operation of the transmitter. This was often the case on overnight and weekend shifts when there was no broadcast engineer present, and all of the time for small stations with only a contract engineer on c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
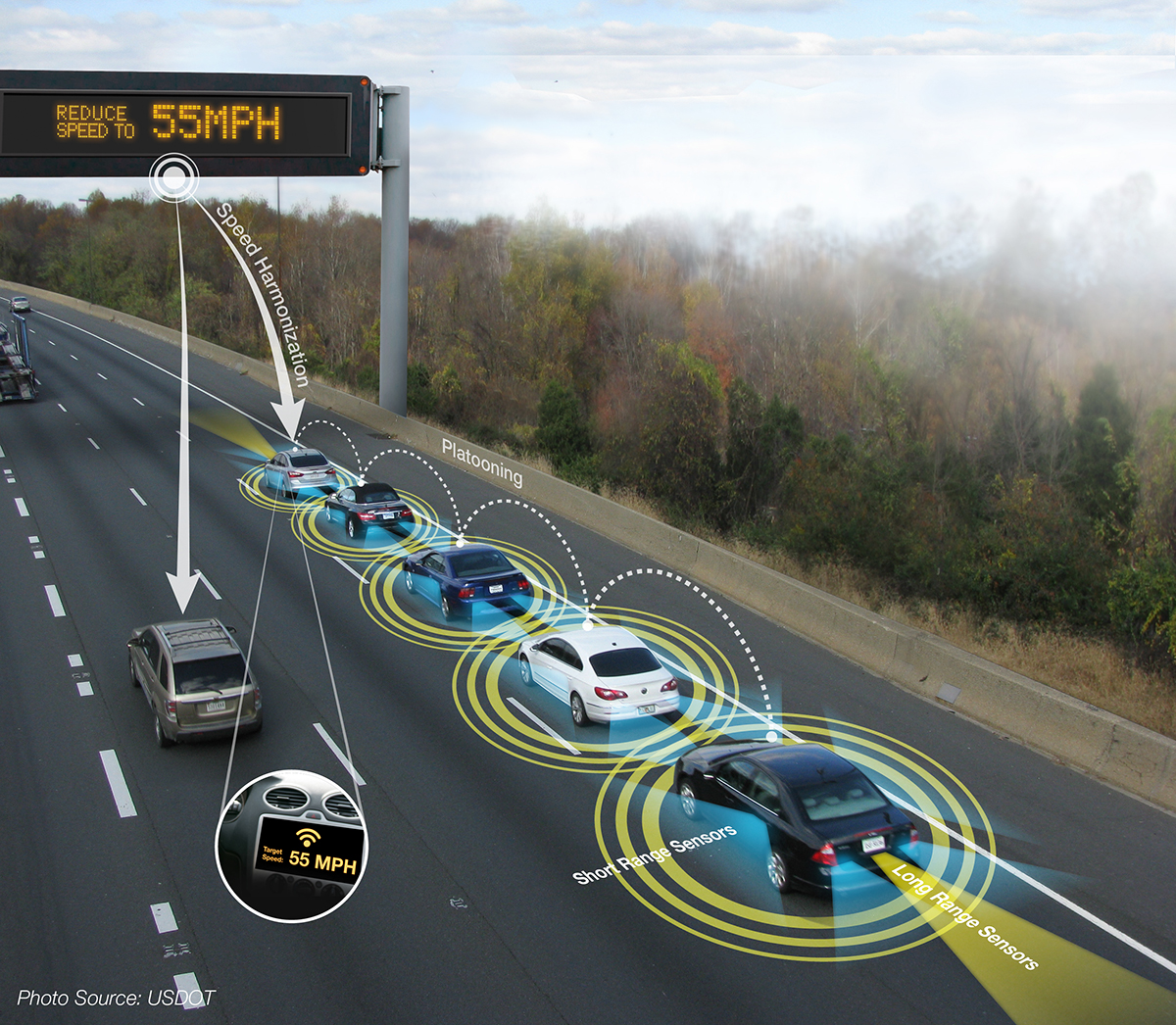
Automated Highway System
In transportation, platooning or flocking is a method for driving a group of vehicles together. It is meant to increase the capacity of roads via an automated highway system. Platoons decrease the distances between cars or trucks using electronic, and possibly mechanical, coupling. This capability would allow many cars or trucks to accelerate or brake simultaneously. This system also allows for a closer headway between vehicles by eliminating reacting distance needed for human reaction. Platoon capability might require buying new vehicles, or it may be something that can be retrofitted. Drivers would probably need a special license endorsement on account of the new skills required and the added responsibility when driving in the lead. Smart cars with artificial intelligence could automatically join and leave platoons. The automated highway system is a proposal for one such system, where cars organise themselves into platoons of 8 to 25. Potential benefits * Greater fuel eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Mobile Robot
An autonomous robot is a robot that acts without recourse to human control. Historic examples include space probes. Modern examples include self-driving vacuums and cars. Industrial robot arms that work on assembly lines inside factories may also be considered autonomous robots, though their autonomy is restricted due to a highly structured environment and their inability to locomote. Components and criteria of robotic autonomy Self-maintenance The first requirement for complete physical autonomy is the ability for a robot to take care of itself. Many of the battery-powered robots on the market today can find and connect to a charging station, and some toys like Sony's ''Aibo'' are capable of self-docking to charge their batteries. Self-maintenance is based on "proprioception", or sensing one's own internal status. In the battery charging example, the robot can tell proprioceptively that its batteries are low, and it then seeks the charger. Another common proprioceptive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automated Guided Vehicle
An automated guided vehicle (AGV), different from an autonomous mobile robot (AMR), is a portable robot that follows along marked long lines or wires on the floor, or uses radio waves, vision cameras, magnets, or lasers for navigation. They are most often used in industrial applications to transport heavy materials around a large industrial building, such as a factory or warehouse. Application of the automatic guided vehicle broadened during the late 20th century. Introduction The AGV can tow objects behind them in trailers to which they can autonomously attach. The trailers can be used to move raw materials or finished products. The AGV can also store objects on a bed. The objects can be placed on a set of motorized rollers (conveyor) and then pushed off by reversing them. AGVs are employed in nearly every industry, including pulp, paper, metals, newspaper, and general manufacturing. Transporting materials such as food, linen or medicine in hospitals is also done. An AG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automated Attendant
In telephony, an automated attendant (also auto attendant, auto-attendant, autoattendant, automatic phone menus, AA, or virtual receptionist) allows callers to be automatically transferred to an extension without the intervention of an operator/receptionist. Many AAs will also offer a simple menu system ("for sales, press 1, for service, press 2," etc.). An auto attendant may also allow a caller to reach a live operator by dialing a number, usually "0". Typically the auto attendant is included in a business's phone system such as a PBX, but some services allow businesses to use an AA without such a system. Modern AA services (which now overlap with more complicated interactive voice response or IVR systems) can route calls to mobile phones, VoIP virtual phones, other AAs/IVRs, or other locations using traditional land-line phones or voice message machines. Feature description Telephone callers will recognize an automated attendant system as one that greets calls incoming to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Automation
Laboratory automation is a multi-disciplinary strategy to research, develop, optimize and capitalize on technologies in the laboratory that enable new and improved processes. Laboratory automation professionals are academic, commercial and government researchers, scientists and engineers who conduct research and develop new technologies to increase productivity, elevate experimental data quality, reduce lab process cycle times, or enable experimentation that otherwise would be impossible. The most widely known application of laboratory automation technology is laboratory robotics. More generally, the field of laboratory automation comprises many different automated laboratory instruments, devices (the most common being autosamplers), software algorithms, and methodologies used to enable, expedite and increase the efficiency and effectiveness of scientific research in laboratories. The application of technology in today's laboratories is required to achieve timely progress a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Library System
An integrated library system (ILS), also known as a library management system (LMS), is an enterprise resource planning system for a library, used to track items owned, orders made, bills paid, and patrons who have borrowed. An ILS is usually made up of a relational database, software to interact with that database, and two graphical user interfaces (one for patrons, one for staff). Most ILSes separate software functions into discrete programs called modules, each of them integrated with a unified interface. Examples of modules might include: * acquisitions (ordering, receiving, and invoicing materials) * cataloging (classifying and indexing materials) * circulation (lending materials to patrons and receiving them back) * serials (tracking magazine, journals, and newspaper holdings) * online public access catalog or OPAC (public user interface) Each patron and item has a unique ID in the database that allows the ILS to track its activity. History Pre-computerization Prior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database Automation
Database administration is the function of managing and maintaining database management systems (DBMS) software. Mainstream DBMS software such as Oracle, IBM Db2 and Microsoft SQL Server need ongoing management. As such, corporations that use DBMS software often hire specialized information technology personnel called database administrators or DBAs. Responsibilities * Installation, configuration and upgrading of Database server software and related products. * Evaluate Database features and Database related products. * Establish and maintain sound backup and recovery policies and procedures. * Take care of the Database design and implementation. * Implement and maintain database security (create and maintain users and roles, assign privileges). * Database tuning and performance monitoring. * Application tuning and performance monitoring. * Setup and maintain documentation and standards. * Plan growth and changes (capacity planning). * Work as part of a team and provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Console Automation
In music recording, mix automation allows the mixing console to remember the audio engineer's adjustment of faders during the post-production editing process. A timecode is necessary for the synchronization of automation. Modern mixing consoles and digital audio workstations use comprehensive mix automation. The need for mix automation originates from the 1970s and the changeover from studios mostly using eight-track tape machines to multiple, synchronized 24-track recorders. Mixing could be laborious and require up to four people, and the results could be almost impossible to reproduce. Manufacturers such as Solid State Logic and AMS Neve developed systems that enabled one engineer to oversee every detail of a complex mix, although the computers required to power these desks remained a rarity into the late 1970s. According to record producer Roy Thomas Baker, Queen's 1975 single "Bohemian Rhapsody" was one of the first mixes to be done with automation. Types ;Voltage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotic Process Automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a form of business process automation that is based on software robots (bots) or artificial intelligence (AI) agents. RPA should not be confused with artificial intelligence as it is based on automation technology following a predefined workflow. It is sometimes referred to as ''software robotics'' (not to be confused with robot software). In traditional workflow automation tools, a software developer produces a list of actions to automate a task and interface to the back end system using internal application programming interfaces (APIs) or dedicated scripting language. In contrast, RPA systems develop the action list by watching the user perform that task in the application's graphical user interface (GUI) and then perform the automation by repeating those tasks directly in the GUI. This can lower the barrier to the use of automation in products that might not otherwise feature APIs for this purpose. RPA tools have strong technical simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |