|
Ottoman Monuments Of Ilok
The remaining Ottoman Empire era monuments of Ilok, town in eastern Croatia, include the hammam and the türbe which makes the town the location with the largest number of preserved Ottoman buildings in Slavonia. The hammam in Ilok is the only preserved Ottoman era hammam in Croatia. Evliya Çelebi, Ottoman explorer who travelled through the Empire, described the hammam of Ilok in his recollections from the town. Together with Požega, Ilok gained the town status during the Ottoman rule over the region. The town of Ilok was together with Sremska Mitrovica one of the seats of the Sanjak of Syrmia of the Budin Eyalet. Systematic demolition of all symbols of Islam happened in the late 17th century after the region of southern Ottoman Hungary was reconquered by the Habsburg monarchy, making the monuments in Ilok some of the last architectural traces of the Ottoman era in modern day Croatia. See also * Suleiman Bridge * Gunja Mosque * Rumelia * Hundred Years' Croatian–Ottoman Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammam
A hammam ( ar, حمّام, translit=ḥammām, tr, hamam) or Turkish bath is a type of steam bath or a place of public bathing associated with the Islamic world. It is a prominent feature in the culture of the Muslim world and was inherited from the model of the Roman ''thermae.'' Muslim bathhouses or hammams were historically found across the Middle East, North Africa, al-Andalus (Islamic Spain and Portugal), Central Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and in Southeastern Europe under Ottoman rule. A variation on the Muslim bathhouse, the Victorian Turkish bath, became popular as a form of therapy, a method of cleansing, and a place for relaxation during the Victorian era, rapidly spreading through the British Empire, the United States of America, and Western Europe. In Islamic cultures the significance of the hammam was both religious and civic: it provided for the needs of ritual ablutions but also provided for general hygiene in an era before private plumbing and served o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities that were ruled by the House of Habsburg, especially the dynasty's Austrian branch. The history of the Habsburg monarchy can be traced back to the election of Rudolf I as King of Germany in 1273 and his acquisition of the Duchy of Austria for the Habsburg in 1282. In 1482, Maximilian I acquired the Netherlands through marriage. Both realms passed to his grandson and successor, Charles V, who also inherited the Spanish throne and its colonial possessions, and thus came to rule the Habsburg empire at its greatest territorial extent. The abdication of Charles V in 1556 led to a division within the dynasty between his son Philip II of Spain and his brother Ferdinand I, who had served as his lieutenant and the elected king of Hungary a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Baths
Ottoman is the Turkish spelling of the Arabic masculine given name Uthman ( ar, عُثْمان, ‘uthmān). It may refer to: Governments and dynasties * Ottoman Caliphate, an Islamic caliphate from 1517 to 1924 * Ottoman Empire, in existence from 1299 to 1922 ** Ottoman dynasty, ruling family of the Ottoman Empire *** Osmanoğlu family, modern members of the family * Ottoman architecture Ethnicities and languages * Ottoman Armenians, the Armenian ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire * Ottoman Greeks, the Greek ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire * Ottoman Serbs, the Serbian ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire * Ottoman Turks, the Turkic ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire ** Ottoman Turkish alphabet ** Ottoman Turkish language, the variety of the Turkish language that was used in the Ottoman Empire Products * Ottoman bed, a type of storage bed * Ottoman (furniture), padded stool or footstool * Ottoman (textile), fabric with a pronounced ribbed or corded effect, often made of silk or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Of The Ottoman Empire
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Vukovar-Syrmia County
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Springs In Stari Ledinci
Turkish Springs in Stari Ledinci are one of the last traces of the Ottoman Empire period architecture in norther Serbian region of Vojvodina. The areas north of Sava and Danube river, which at the time were part of Ottoman Hungary, were reconquered by the Habsburg monarchy already at the end of the Great Turkish War and the signing of the 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz, significantly before the independence of the Principality of Serbia, which led to preservation of significantly lesser number of artefacts from the Ottoman period in the region. Springs still standing in the village were reconstructed in 1842 and another one in 1885. Today, both springs are protected cultural monuments. Systematic demolition of all symbols of Islam happened in the late 17th century after the region of southern Ottoman Hungary was reconquered by the Habsburg monarchy with the practice less all encompassing at future stages of what some called the Balkan Reconquista. See also * Rumelia * Sanjak of Syrm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Rehatsek
Edward Rehatsek (3 July 1819 – 11 December 1891) was an Orientalist and translator of several works of Islamic literature including the ''Gulistan'' of Saadi Shirazi, ibn Ishaq’s ''Prophetic biography'', and the '' Rawẓat aṣ-ṣafāʾ''. All three translations were originally published by the Kama Shastra Society founded by Richard Francis Burton and Forster Fitzgerald Arbuthnot at the end of the 19th century. Biography Rehatsek was born in 1819 in the town of Ilok, Hungary, which at that time was within the borders of the Austrian Empire. The town today lies within Croatia. Rehatsek attended university in Budapest and received a master's degree in civil engineering. Between 1842 and 1847, he visited France, lived four years in the United States, and sailed at last to India, arriving in Bombay (now, Mumbai) where he spent the rest of his life.Thomas Wright The Life of Sir Richard Burton - 2010 -- Page 154 "Born on 3rd July 1819, at Illack, in Austria, Edward Rehatsek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian-Slavonian-Dalmatian Theater In Great Turkish War
Croatian-Slavonian theater in Great Turkish War, concerns military operations undertaken during Great Turkish War of 1684-1689 by the forces of Holy League (1684), Holy League against the Ottoman Empire on territories of Croatia, Slavonia and Dalmatia. The war was concluded by Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699, which significantly eased off the Ottoman grip off Croatia. Prelude Croatian-Ottoman Wars Following the Ottoman conquest of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Ottoman conquest of Kingdom of Bosnia in 1463, the territories of Slavonia, Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia and Dalmatia came under ever increasing Ottoman pressure. Initially, armies led by Croatian nobles resisted frequent akinji and martolos incursions, and even scored some victories such as the Battle of Una and Battle of Vrpile, Battle of Vrpile Pass. However, the regular attacks which usually came once a year, eventually proved to be too much for Croatia to handle alone and they culminated in Croatian defeat at Battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Turkish War
The Great Turkish War (german: Großer Türkenkrieg), also called the Wars of the Holy League ( tr, Kutsal İttifak Savaşları), was a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Poland-Lithuania, Venice, Russia, and Habsburg Hungary. Intensive fighting began in 1683 and ended with the signing of the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. The war was a defeat for the Ottoman Empire, which for the first time lost large amounts of territory, in Hungary and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, as well as part of the western Balkans. The war was significant also by being the first time that Russia was involved in an alliance with Western Europe. The French did not join the Holy League, as France had agreed to reviving an informal Franco-Ottoman alliance in 1673, in exchange for Louis XIV being recognized as a protector of Catholics in the Ottoman regime. Initially, Louis XIV took advantage of the start of the war to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Years' Croatian–Ottoman War
The Hundred Years' Croatian–Ottoman War ( hr, Stogodišnji hrvatsko-turski rat, links=no, Kratka politicka i kulturna povijest Hrvatske ''Stogodišnji rat protiv Turaka'', ''Stogodišnji rat s Osmanlijama'') is the name of a sequence of conflicts, mostly of relatively low intensity, ("Small War", Croatian: ''Mali rat'') between the and the medieval Kingdom of Croatia (ruled by the and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
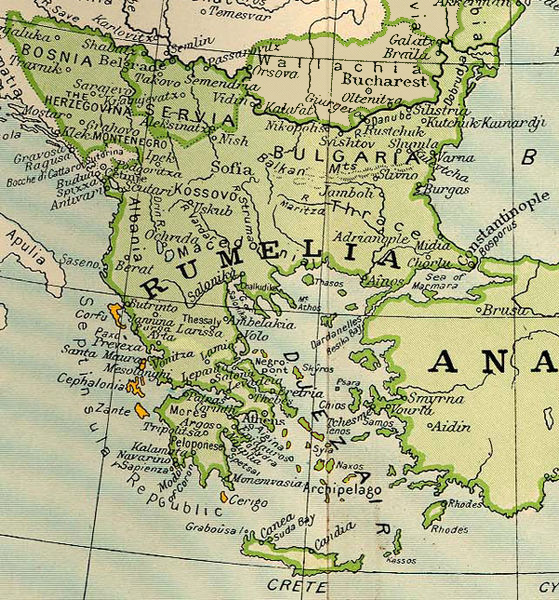
Rumelia
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the Byzantine rite, was the name of a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and vassals in Europe that would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans". During the period of its existence, it was more often known in English as Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means "Greek", or a Christian Greek speaker and ''ėli'' means "land" and ''Rumelia'' ( ota, روم ايلى, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans, which formerly belonged to the Byzantine Empire, known by its contemporaries as the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunja Mosque
Gunja Mosque (Croatian and Bosnian: ''Džamija u Gunji'') is the oldest active mosque in Croatia built in 1969. It is located in the village of Gunja in the Croatian part of Syrmia. History Today the Gunja Mosque is the oldest mosque in Croatia in continuous use. Historically, during the Ottoman rule, there was a significantly larger number of mosques in Croatia. At one point there were 250 of them, but as of 2014 only 3 structures remained standing. The largest and most representative one of them, Ibrahim Pasha's Mosque, is located in eastern Croatian town of Đakovo but is today used as the Roman Catholic Church of All Saints. Another mosque in eastern Croatia, which today does not exist, was located in Osijek. It was the Kasım Pasha Mosque constructed after 1526 at the site of modern-day Church of Saint Michael. Most of the Ottoman structures in the region were systematically destroyed after the Treaty of Karlowitz. Post-World War II history In contemporary history firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |