|
Otto Cycle
An Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle that describes the functioning of a typical spark ignition piston engine. It is the thermodynamic cycle most commonly found in automobile engines. The Otto cycle is a description of what happens to a gas as it is subjected to changes of pressure, temperature, volume, addition of heat, and removal of heat. The gas that is subjected to those changes is called the system. The system, in this case, is defined to be the fluid (gas) within the cylinder. Conversely, by describing the changes that take place within the system it also describes the system's effect on the environment. The purpose of the Otto cycle is to study the production of net work from the system that can propel a vehicle and its occupants in the environment. The Otto cycle is constructed from: :Top and bottom of the loop: a pair of quasi-parallel and isentropic processes (frictionless, adiabatic reversible). :Left and right sides of the loop: a pair of parallel i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OTTO CYCLE
An Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle that describes the functioning of a typical spark ignition piston engine. It is the thermodynamic cycle most commonly found in automobile engines. The Otto cycle is a description of what happens to a gas as it is subjected to changes of pressure, temperature, volume, addition of heat, and removal of heat. The gas that is subjected to those changes is called the system. The system, in this case, is defined to be the fluid (gas) within the cylinder. Conversely, by describing the changes that take place within the system it also describes the system's effect on the environment. The purpose of the Otto cycle is to study the production of net work from the system that can propel a vehicle and its occupants in the environment. The Otto cycle is constructed from: :Top and bottom of the loop: a pair of quasi-parallel and isentropic processes (frictionless, adiabatic reversible). :Left and right sides of the loop: a pair of parallel i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston Engines
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.''Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach'' by Yunus A. Cengal and Michael A. Boles Common features in all types There may be one or more pistons. Each piston is inside a cylinder, into which a gas is introduced, eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines. Internal combustion engines Most commonly used with turbocharged engines, an intercooler is used to counteract the heat of compression and heat soak in the pressurised intake air. By reducing the temperature of the intake air, the air becomes denser (allowing more fuel to be injected, resulting in increased power) and less likely to suffer from pre-ignition or knocking. Additional cooling can be provided by externally spraying a fine mist onto the intercooler surface, or even into the intake air itself, to further reduce intake charge temperature through evaporative cooling. Intercoolers can vary dramatically in size, shape and design, depending on the performance and space requirements of the system. Many passenger cars use either front-mounted intercoolers locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. Turbochargers are distinguished from superchargers in that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases, whereas a is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the inv ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Knocking
In spark-ignition internal combustion engines, knocking (also knock, detonation, spark knock, pinging or pinking) occurs when combustion of some of the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder does not result from propagation of the flame front ignited by the spark plug, but when one or more pockets of air/fuel mixture explode outside the envelope of the normal combustion front. The fuel–air charge is meant to be ignited by the spark plug only, and at a precise point in the piston's stroke. Knock occurs when the peak of the combustion process no longer occurs at the optimum moment for the four-stroke cycle. The shock wave creates the characteristic metallic "pinging" sound, and cylinder pressure increases dramatically. Effects of engine knocking range from inconsequential to completely destructive. Knocking should not be confused with pre-ignition—they are two separate events. However, pre-ignition can be followed by knocking. The phenomenon of detonation was described in Novem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Gas Constant
The molar gas constant (also known as the gas constant, universal gas constant, or ideal gas constant) is denoted by the symbol or . It is the molar equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, expressed in units of energy per temperature increment per amount of substance, rather than energy per temperature increment per ''particle''. The constant is also a combination of the constants from Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. It is a physical constant that is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law, the Arrhenius equation, and the Nernst equation. The gas constant is the constant of proportionality that relates the energy scale in physics to the temperature scale and the scale used for amount of substance. Thus, the value of the gas constant ultimately derives from historical decisions and accidents in the setting of units of energy, temperature and amount of substance. The Boltzmann constant and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isentropic Process
An isentropic process is an idealized thermodynamic process that is both Adiabatic process, adiabatic and Reversible process (thermodynamics), reversible. The work (physics), work transfers of the system are friction, frictionless, and there is no net transfer of heat or matter. Such an idealized process is useful in engineering as a model of and basis of comparison for real processes. This process is idealized because reversible processes do not occur in reality; thinking of a process as both adiabatic and reversible would show that the initial and final entropies are the same, thus, the reason it is called isentropic (entropy does not change). Thermodynamics, Thermodynamic processes are named based on the effect they would have on the system (ex. isovolumetric: constant volume, isenthalpic: constant enthalpy). Even though in reality it is not necessarily possible to carry out an isentropic process, some may be approximated as such. The word "isentropic" derives from the proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics. The requirement of zero interaction can often be relaxed if, for example, the interaction is perfectly elastic or regarded as point-like collisions. Under various conditions of temperature and pressure, many real gases behave qualitatively like an ideal gas where the gas molecules (or atoms for monatomic gas) play the role of the ideal particles. Many gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, noble gases, some heavier gases like carbon dioxide and mixtures such as air, can be treated as ideal gases within reasonable tolerances over a considerable parameter range around standard temperature and pressure. Generally, a gas behaves more like an ideal gas at higher temperature and lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
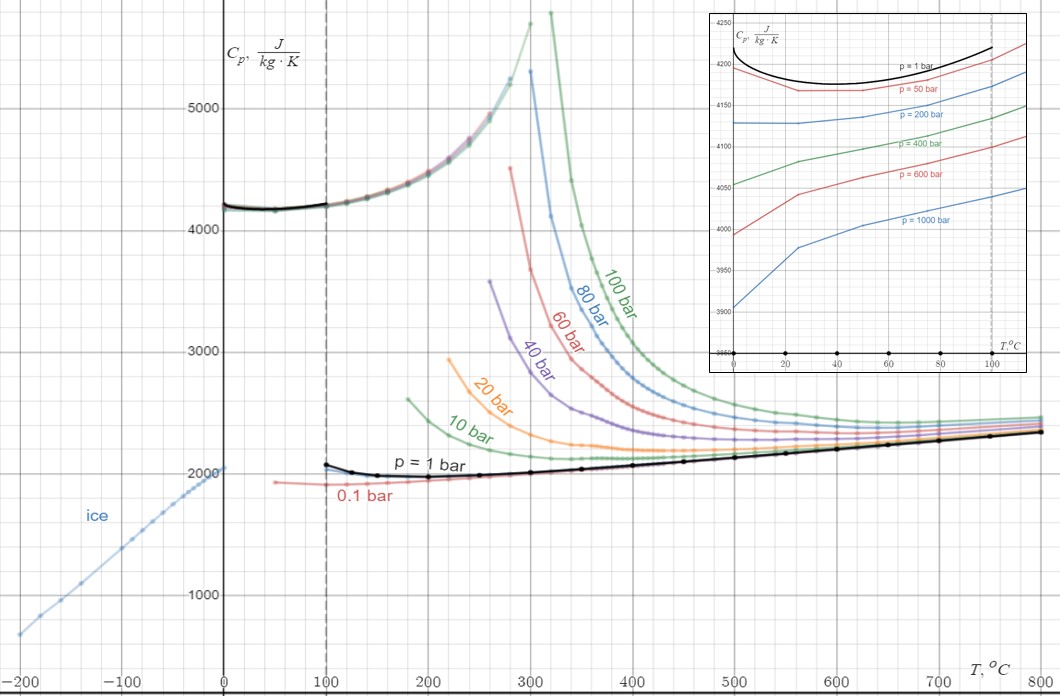
Heat Capacity
Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin (J/K). Heat capacity is an extensive property. The corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity, found by dividing the heat capacity of an object by its mass. Dividing the heat capacity by the amount of substance in moles yields its molar heat capacity. The volumetric heat capacity measures the heat capacity per volume. In architecture and civil engineering, the heat capacity of a building is often referred to as its '' thermal mass''. Definition Basic definition The heat capacity of an object, denoted by C, is the limit C = \lim_\frac, where \Delta Q is the amount of heat that must be added to the object (of mass ''M'') in order to raise its temperature by \Delta T. The value of this parameter usually varies considerably depending o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Volume
In thermodynamics, the specific volume of a substance (symbol: , nu) is the quotient of the substance's volume () to its mass (): :\nu = \frac It is a mass-specific intrinsic property of the substance. It is the reciprocal of density (rho) and it is also related to the molar volume and molar mass: :\nu = \rho^ = \frac The standard unit of specific volume is cubic meters per kilogram (m3/kg), but other units include ft3/lb, ft3/slug, or mL/g. Specific volume for an ideal gas is related to the molar gas constant () and the gas's temperature (), pressure (), and molar mass (): : \nu = \frac It's based on the ideal gas law, PV = , and the amount of substance In chemistry, the amount of substance (symbol ) in a given sample of matter is defined as a ratio () between the particle number, number of elementary entities () and the Avogadro constant (). The unit of amount of substance in the International ..., n = m/M Applications Specific volume is commonly applied to: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Energy
Specific energy or massic energy is energy per unit mass. It is also sometimes called gravimetric energy density, which is not to be confused with energy density, which is defined as energy per unit volume. It is used to quantify, for example, stored heat and other thermodynamic properties of substances such as specific internal energy, specific enthalpy, specific Gibbs free energy, and specific Helmholtz free energy. It may also be used for the kinetic energy or potential energy of a body. Specific energy is an intensive property, whereas energy and mass are extensive properties. The SI unit for specific energy is the joule per kilogram (J/kg). Other units still in use worldwide in some contexts are the kilocalorie per gram (Cal/g or kcal/g), mostly in food-related topics, and watt-hours per kilogram (W⋅h/kg) in the field of batteries. In some countries the Imperial unit BTU per pound (Btu/lb) is used in some engineering and applied technical fields. Kenneth E. Hese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |