|
Otto IV Of Burgundy
Otto IV ( 1248, in Ornans – 17 March 1303, in Melun) was the count of the Free County of Burgundy from 1279 until 1303. Life Otto was the son of Hugh of Châlons and Adelaide, Countess Palatine of Burgundy. Upon his father's death in 1266/7, he became Count of Châlons. In 1267, the pro-French Otto IV got in conflict with his half-uncle John I of Chalon-Arlay, who was supported by his vassals. His mother, Adelaide, died on 8 March 1279, and Otto inherited her county. However, he was unable to secure real power in the county until 1295. His elder daughter Joan II succeeded in the County of Burgundy, which was later given as dowry on her marriage to Philip. His wife Mahaut drew up a contract on 4 June 1312 with the famous tomb maker to make a tomb. The contract specifies a tomb made of stone and alabaster. Otto was to be shown as an armed knight with a shield, sword and armor. A lion was shown beneath his feet with two angels to support the pillow under his head. The tomb no lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Burgundy
This is a list of the County of Burgundy, counts of Burgundy, i.e., of the region known as Franche-Comté, not to be confused with the Duchy of Burgundy, from 982 to 1678. House of Ivrea (982–1184) House of Hohenstaufen (1190–1231) House of Andechs (1231–1279) House of Ivrea (1279–1330) House of Capet (1330–1347) House of Burgundy (1347–1361) House of Capet (1361–1382) House of Dampierre (1382–1404) House of Valois-Burgundy (1405–1482) House of Habsburg (1482–1678) In 1678 the County of Burgundy was annexed by France as part of the Treaty of Nijmegen. House of Bourbon, claimants to the title (1700–1713) *Philip V of Spain, Philip IX (King Philip V of Spain) (1700–1713, titular only) House of Habsburg (1713–present) *Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV (Emperor Charles VI) (1713–1740 titular only) *Maria Theresa of Austria, Maria Theresa (1740–1780 titular only) **Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalon-sur-Saône
Chalon-sur-Saône (, literally ''Chalon on Saône'') is a city in the Saône-et-Loire Departments of France, department in the Regions of France, region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France. It is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture of the department. It is the largest city in the department; however, the department capital is the smaller city of Mâcon. Geography Chalon-sur-Saône lies in the south of the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté and in the east of France, approximately north of Mâcon. It is located on the Saône river, and was once a busy port, acting as a distribution point for local wines which were sent up and down the Saône river and the Canal du Centre (France), Canal du Centre, opened in 1792. History Ancient times Though the site (ancient ''Cabillonum'') was a capital of the Aedui and objects of La Tène culture have been retrieved from the bed of the river here, the first mention of ''Cavillonum'' is found in Commentarii de Bello Gallico (VII, chs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Doubs
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1303 Deaths
Year 1303 ( MCCCIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. Events January–March * January 17 – A major earthquake strikes Byzantium and Constantinople (now Istanbul in Turkey). Byzantine Emperor Michael IX Palaiologos spreads the word that the former Patriarch of the Eastern Church, Athanasius I had given him a warning about the imminent wrath of God against the city.Donald M. Nicol, ''The Last Centuries of Byzantium, 1261-1453'' (Cambridge University Press, 1993) p.103 * January 21 – John XII is forced to resign as Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople and leader of the Eastern Orthodox Church after the January 17 earthquake. * January 28 – In India, the siege of Chittorgarh, capital of the Medapata Kingdom (now in the state of Rajasthan), begins as the Sultan of Delhi, Alauddin Khalji, seeks to acquire the territory of the Medapata Emperor, Ratnasimha."The Khaljis: Alauddin Khalji", by Banarsi Prasad Saksena, in ''A Compr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1240s Births
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Counts Of Burgundy
This is a list of the counts of Burgundy, i.e., of the region known as Franche-Comté, not to be confused with the Duchy of Burgundy, from 982 to 1678. House of Ivrea (982–1184) House of Hohenstaufen (1190–1231) House of Andechs (1231–1279) House of Ivrea (1279–1330) House of Capet (1330–1347) House of Burgundy (1347–1361) House of Capet (1361–1382) House of Dampierre (1382–1404) House of Valois-Burgundy (1405–1482) House of Habsburg (1482–1678) In 1678 the County of Burgundy was annexed by France as part of the Treaty of Nijmegen. House of Bourbon, claimants to the title (1700–1713) * Philip IX (King Philip V of Spain) (1700–1713, titular only) House of Habsburg (1713–present) * Charles IV (Emperor Charles VI) (1713–1740 titular only) *Maria Theresa (1740–1780 titular only) ** Francis I (Emperor Francis I) (1740–1765 with his wife, titular only) * Joseph (Emperor Joseph II) (1780–1790 titular only) * Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles IV Of France
Charles IV (18/19 June 1294 – 1 February 1328), called the Fair (''le Bel'') in France and the Bald (''el Calvo'') in Navarre, was the last king of the direct line of the House of Capet, List of French monarchs, King of France and List of Navarrese monarchs, King of Navarre (as Charles I) from 1322 to 1328. Charles was the third son of Philip IV of France, Philip IV; like his father, he was known as "the fair" or "the handsome".Kibler, p.201. Beginning in 1323 Charles was confronted with a Peasant revolt in Flanders 1323–1328, peasant revolt in County of Flanders, Flanders, and in 1324 he made an unsuccessful bid to be elected Holy Roman Emperor. As Duke of Guyenne, Edward II of England, King Edward II of England was a vassal of Charles, but he was reluctant to pay Homage (feudal), homage to another king. In retaliation, Charles conquered the Duchy of Guyenne in a conflict known as the War of Saint-Sardos (1324). In a peace agreement, Edward II accepted to swear allegiance t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip V Of France
Philip V ( 1291 – 3 January 1322), known as the Tall (), was King of France and List of Navarrese monarchs, Navarre (as Philip II) from 1316 to 1322. Philip engaged in a series of domestic reforms intended to improve the management of the kingdom. These reforms included the creation of an independent Court of Finances, the standardization of weights and measures, and the establishment of a single currency. Philip was the second son of King Philip IV of France and Queen Joan I of Navarre. He was granted an appanage, the County of Poitiers, while his elder brother, Louis X of France, Louis X, inherited the French and Navarrese thrones. When Louis died in 1316, he left a daughter and a pregnant wife, Clementia of Hungary. Philip the Tall successfully claimed the regency. Queen Clementia gave birth to a boy, who was proclaimed king as John I of France, John I, but the infant king lived only for five days. At the death of his nephew, Philip immediately had himself Coronation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
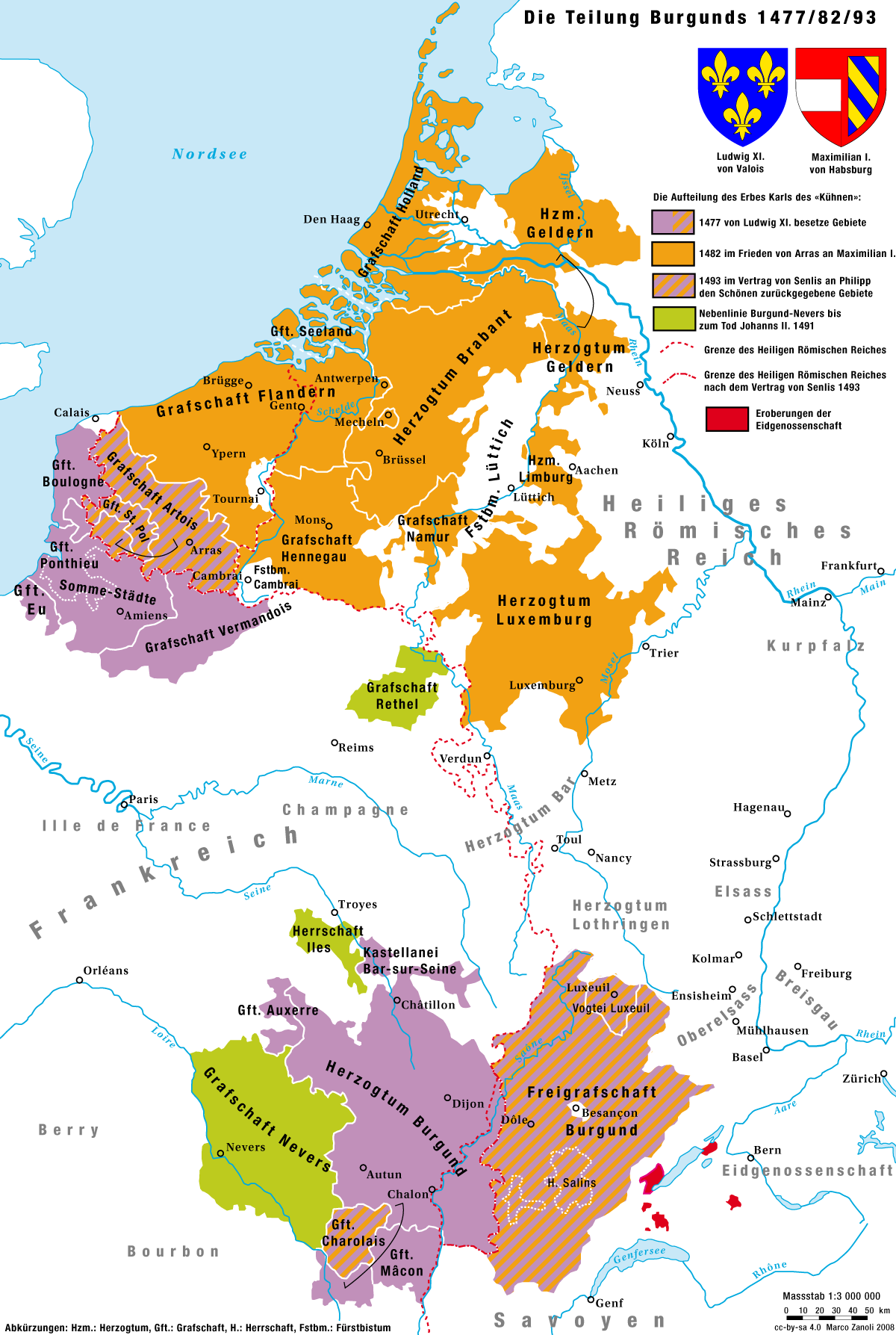
County Of Burgundy
The Free County of Burgundy (; ) was a medieval and early modern feudal polity ruled by a count from 982 to 1678. It became known as Franche-Comté (the ''Free County''), and was located in the modern region of Franche-Comté. It belonged to the wider historical region of Upper Burgundy, and bordered the Duchy of Burgundy to the west. Its territory had initially been part of the Kingdom of Upper Burgundy (888–933), and then the united Kingdom of Burgundy, later known as the Kingdom of Arles. The county was formed in 982 by count Otto-William, encompassing his domains in northern parts of the Burgundian realm. In 1032, the Kingdom of Arles was inherited by Conrad II, Holy Roman Emperor, who incorporated the Kingdom, including the County of Burgundy, into the Holy Roman Empire (HRE). As a state of the HRE, the county was granted a high degree of autonomy. The largest city, Besançon, was granted the status of free imperial city. The rest of the county was given imperial i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John I Of Chalon-Arlay
Jean I of Chalon-Arlay (1258–1315) was a French nobleman. He was the son of Jean, Count of Chalon and Laure de Commercy, a couple who had thirty castles built on the Jurassian part of the county of Burgundy around their new seigneurie of Salins, including the Château d'Arlay (upon the death of Otto III in 1248, the elder Jean had become regent of the county of Burgundy on behalf of his son Hugh III, his daughter-in-law Adelaide, and his grandson Otto). He was Seigneur of Arlay (1266–1315) and Viscount of Besançon (1295–1315). Marriage and issue Around 1272 John married Marguerite of Burgundy, daughter of Hugh IV, Duke of Burgundy, and then for a second time to Alix de Clermont-Nesle (daughter of seigneur Raoul II de Clermont-Nesle of the House of Clermont-Nesle). John and Marguerite had: * Hugh I (1288–1322), who became Seigneur of Arlay, Arguel and Cuiseaux and viscount of Besançon (1315–1322). * Isabelle of Chalon-Arlay, married Louis II of Vaud John and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free County Of Burgundy
The Free County of Burgundy (; ) was a medieval and early modern feudal polity ruled by a count from 982 to 1678. It became known as Franche-Comté (the ''Free County''), and was located in the modern region of Franche-Comté. It belonged to the wider historical region of Upper Burgundy, and bordered the Duchy of Burgundy to the west. Its territory had initially been part of the Kingdom of Upper Burgundy (888–933), and then the united Kingdom of Burgundy, later known as the Kingdom of Arles. The county was formed in 982 by count Otto-William, encompassing his domains in northern parts of the Burgundian realm. In 1032, the Kingdom of Arles was inherited by Conrad II, Holy Roman Emperor, who incorporated the Kingdom, including the County of Burgundy, into the Holy Roman Empire (HRE). As a state of the HRE, the county was granted a high degree of autonomy. The largest city, Besançon, was granted the status of free imperial city. The rest of the county was given imperial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelaide, Countess Palatine Of Burgundy
Adelaide of Merania (Adélaïde or Alice, Alix – died 8 March 1279, Évian) was reigning Countess of Burgundy from 1248 until her death. She was also Countess of Savoy and Bresse through her marriage in 1267 to Count Philip I of Savoy. Life Adelaide was the daughter of Duke Otto I of Merania and Countess Beatrice II of Burgundy.Guida Myrl Jackson-Laufer, ''Women Rulers Throughout the Ages: An Illustrated Guide'', (ABC-CLIO, 1999), 19. She inherited the county after the death of her brother, Otto III, Count Palatine of Burgundy, in 1248. As countess, she came into conflict with King Rudolph I. Adelaide died in 1279 and was buried in Cherlieu Abbey near Besançon. Family Adelaide married Hugh, Count of Salins (died 1266), from a younger branch of male-line dynasty of Ivrean-originated Counts of Burgundy, around 1239. They had, among others, the following children: :1. Otto IV, Count of Burgundy (died 1302), married ::in 1271 to 1. Philippa of Bar ::in 1285 to 2. Maha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |