|
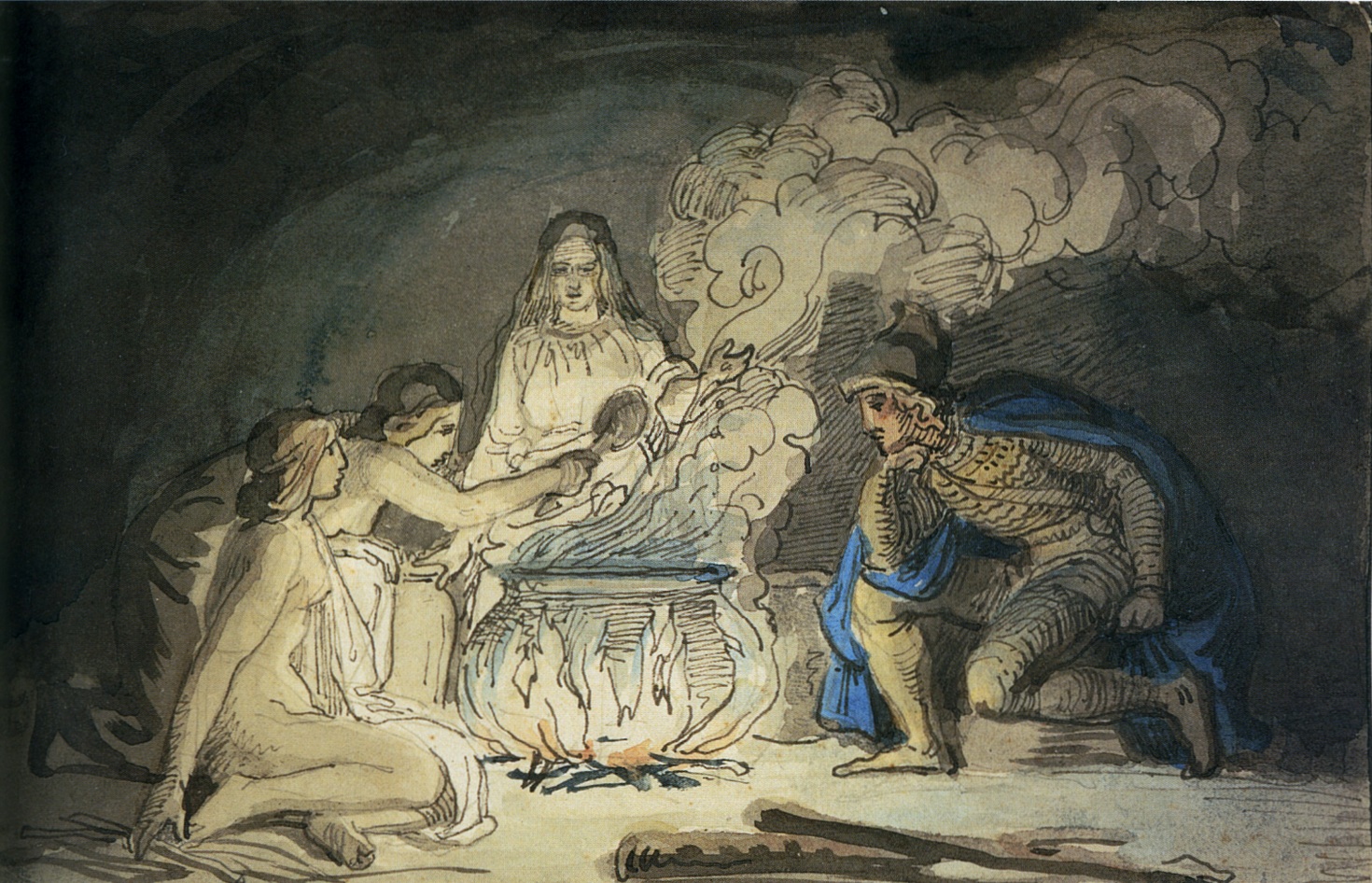
Origin Myth
An origin myth is a type of myth that explains the beginnings of a natural or social aspect of the world. Creation myths are a type of origin myth narrating the formation of the universe. However, numerous cultures have stories that take place after the initial origin. These stories aim to explain the origins of natural phenomena or human institutions within an already existing world. In Greco-Roman scholarship, the terms founding myth or etiological myth (from 'cause') are occasionally used to describe a myth that clarifies an origin, particularly how an object or custom came into existence. In modern political discourse the terms "founding myth", "foundational myth", etc. are often used as critical references to official or widely accepted narratives about the origins or early history of a nation, a society, a culture, etc. Nature of origin myths Origin myths are narratives that explain how a particular reality came into existence.Eliade 1963, p. 21 They often serve to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myth
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the veracity of a myth is not a defining criterion. Myths are often endorsed by religious (when they are closely linked to religion or spirituality) and secular authorities. Many societies group their myths, legends, and history together, considering myths and legends to be factual accounts of their remote past. In particular, creation myths take place in a primordial age when the world had not achieved its later form. Origin myths explain how a society's Norm (social), customs, institutions, and taboos were established and sanctified. National myths are narratives about a nation's past that symbolize the nation's values. There is a complex relationship between Myth and ritual, recital of myths and the enactment of rituals. Etymology The w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herwig Wolfram
Herwig Wolfram (born 14 February 1934) is an Austrian historian who is Professor Emeritus of Medieval History and Auxiliary Sciences of History at the University of Vienna and the former Director of the . He is a leading member of the Vienna School of History, and internationally known for his authoritative works on the history of Austria, the Goths, and relationships between the Germanic peoples and the Roman Empire. Biography Herwig Wolfram was born in Vienna, Austria on 14 February 1934. He studied history and Latin at the University of Vienna since 1952, gaining a Ph.D. there in 1957. He subsequently served as University Assistant at the Institute of History at the University of Vienna (1959–1961) and the (1962–1969). Wolfram gained his habilitation at the Faculty of Philosophy at the University of Vienna in 1966. Wolfram was Visiting Professor at the University of California, Los Angeles from 1968 to 1969, and has subsequently made many visits to the United States. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hou Ji
Hou Ji (or Houji; ) was a legendary Chinese culture hero credited with introducing millet to humanity during the time of the Xia dynasty.. Millet was the original staple grain of north and South China, northern China, prior to the introduction of wheat. His name translates as Lord of Millet and was a title granted to him by Emperor Shun, according to Records of the Grand Historian. Houji was credited with developing the philosophy of Agriculturalism and with service during the Great Flood (China), Great Flood in the reign of Emperor Yao, Yao; he was also claimed as an ancestor of the Jī (surname), Ji clan that became the ruling family of the Zhou dynasty or a founder of the Zhou. After the Zhou dynasty, ancient Chinese historians, folklorists, and religious practitioners had a variety of opinions on Hou Ji, including the opinion that he became deified as the god Shennong after his death. History Hou Ji's original name was Qi (), meaning "abandoned". Two separate versions of hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern Period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There is no exact date that marks the beginning or end of the period and its extent may vary depending on the area of history being studied. In general, the early modern period is considered to have lasted from around the start of the 16th century to the start of the 19th century (about 1500–1800). In a European context, it is defined as the period following the Middle Ages and preceding the advent of modernity; but the dates of these boundaries are far from universally agreed. In the context of World history (field), global history, the early modern period is often used even in contexts where there is no equivalent "medieval" period. Various events and historical transitions have been proposed as the start of the early modern period, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzungar Khanate
The Dzungar Khanate ( Mongolian: ), also known as the Zunghar Khanate or Junggar Khanate, was an Inner Asian khanate of Oirat Mongol origin. At its greatest extent, it covered an area from southern Siberia in the north to present-day Kyrgyzstan in the south, and from present-day west of Mongolia and the Great Wall of China in the east to present-day Kazakhstan in the west. The core of the Dzungar Khanate is today part of northern Xinjiang, also called Dzungaria. About 1620 the western Mongols, known as the Oirats, united in the Junggar Basin in Dzungaria. In 1678, Galdan received from the Dalai Lama the title of ''Boshogtu Khan'', making the Dzungars the leading tribe within the Oirats. The Dzungar rulers used the title of Khong Tayiji, which translates into English as "crown prince". Between 1680 and 1688, the Dzungars conquered the Tarim Basin, which is now southern Xinjiang, and defeated the Khalkha Mongols to the east. In 1696, Galdan was defeated by the Qing dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats and the Buryats are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or as subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity, descending from the Proto-Mongols. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The contiguous geographical area in which the Mongols primarily live is referred to as the Mongol heartland, especially in discussions of the Mongols' history under the Mongol Empire. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyks and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Arkhorchin, Asud, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish People
Turks (), or Turkish people, are the largest Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group, comprising the majority of the population of Turkey and Northern Cyprus. They generally speak the various Turkish dialects. In addition, centuries-old Turkish communities in the former Ottoman Empire, ethnic Turkish communities still exist across other former territories of the Ottoman Empire. Article 66 of the Constitution of Turkey defines a ''Turk'' as anyone who is a citizen of the Turkish state. While the legal use of the term ''Turkish'' as it pertains to a citizen of Turkey is different from the term's ethnic definition, the majority of the Turkish population (an estimated 70 to 75 percent) are of Turkish ethnicity. The vast majority of Turks are Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, with a notable minority practicing Alevism. The ethnic Turks can therefore be distinguished by a number of cultural and regional variants, but do not function as separate ethnic groups. In particular, the culture of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, Rome known together as the Greco-Roman world, centered on the Mediterranean Basin. It is the period during which ancient Greece and Rome flourished and had major influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and West Asia. Classical antiquity was succeeded by the period now known as late antiquity. Conventionally, it is often considered to begin with the earliest recorded Homeric Greek, Epic Greek poetry of Homer (8th–7th centuries BC) and end with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD. Such a wide span of history and territory covers many disparate cultures and periods. ''Classical antiquity'' may also refer to an idealized vision among later people of what was, in Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC – 668 AD) (; ; Old Korean: Guryeo) also later known as Goryeo (; ; Middle Korean: 고ᇢ롕〮, ''kwòwlyéy''), was a Korean kingdom which was located on the northern and central parts of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of modern-day Northeast China (Manchuria). At its peak of power, Goguryeo encompassed most of the Korean Peninsula and large parts of Manchuria, along with parts of eastern Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and modern-day Russia. Along with Baekje and Silla, Goguryeo was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. It was an active participant in the power struggle for control of the Korean peninsula and was also associated with the foreign affairs of neighboring polities in China and Yamato period, Japan. Goguryeo was one of the great powers in East Asia until its defeat by a Silla–Tang alliance in 668 after prolonged exhaustion and internal strife following the death of Yeon Gaesomun. After its fall, its territory was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wusun
The Wusun ( ) were an ancient semi-Eurasian nomads, nomadic Eurasian Steppe, steppe people of unknown origin mentioned in Chinese people, Chinese records from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD. The Wusun originally lived between the Qilian Mountains and Dunhuang (Gansu) near the Yuezhi. Around 176 BC the Xiongnu raided the lands of the Yuezhi, who subsequently attacked the Wusun, killing their king and seizing their land. The Xiongnu adopted the surviving Wusun prince and made him one of their generals and leader of the Wusun. Around 162 BC the Yuezhi were driven into the Ili River Valley in Jetisu, Zhetysu, Dzungaria and Tian Shan, which had formerly been inhabited by the Saka. The Wusun then resettled in Gansu as vassals of the Xiongnu. In 133–132 BC, the Wusun drove the Yuezhi out of the Ili Valley and settled the area. The Wusun then became close allies of the Han dynasty and remained a powerful force in the region for several cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people who had migrated during the 9th to 8th centuries BC from Central Asia to the Pontic Steppe in modern-day Ukraine and Southern Russia, where they remained established from the 7th century BC until the 3rd century BC. Skilled in Horses in warfare, mounted warfare, the Scythians replaced the Agathyrsi and the Cimmerians as the dominant power on the western Eurasian Steppe in the 8th century BC. In the 7th century BC, the Scythians crossed the Caucasus Mountains and frequently raided West Asia along with the Cimmerians. After being expelled from West Asia by the Medes, the Scythians retreated back into the Pontic Steppe in the 6th century BC, and were later conquered by the Sarmatians in the 3rd to 2nd centuries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |