|
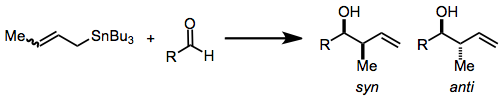
Organostannane Addition
Organostannane addition is reaction involving the nucleophilic addition of an allyl-, allenyl-, or propargyl- stannane to an aldehyde, imine, or (in rare cases) a ketone. This reaction is widely used for carbonyl allylation. The addition of an organostannane to carbonyl group is one of the most common and efficient methods for the production of contiguous, oxygen-containing stereocenters in organic molecules. Since many naturally-occurring polymers contain this stereochemical motif, such as poly propionate and polyacetate, organostannane addition has been studied extensively by natural products chemists as a synthetically and commercially-important reaction. Organostannanes are very stable molecules, favoured for their ease of handling and selective reactivity. Chiral allylstannanes are known to react stereoselectively, yielding single diastereomers. The production of substituted allylstannanes containing either one or two ''new'' stereocenters can be achieved by this method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophilic Addition
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition (AN) reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound with an electrophilic double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile, such that the double or triple bond is broken. Nucleophilic additions differ from electrophilic additions in that the former reactions involve the group to which atoms are added accepting electron pairs, whereas the latter reactions involve the group donating electron pairs. Addition to carbon–heteroatom double bonds Nucleophilic addition reactions of nucleophiles with electrophilic double or triple bond (π bonds) create a new carbon center with two additional single, or σ, bonds.March Jerry; (1985). Advanced Organic Chemistry reactions, mechanisms and structure (3rd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, inc. Addition of a nucleophile to carbon–heteroatom double or triple bonds such as >C=O or -C≡N show great variety. These types of bonds are polar (have a large difference in electronegativit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiomeric Excess
In stereochemistry, enantiomeric excess (ee) is a measurement of purity used for chiral substances. It reflects the degree to which a sample contains one enantiomer in greater amounts than the other. A racemic mixture has an ee of 0%, while a single completely pure enantiomer has an ee of 100%. A sample with 70% of one enantiomer and 30% of the other has an ee of 40% (70% − 30%). Definition Enantiomeric excess is defined as the absolute difference between the mole fraction of each enantiomer: :\ ee = , F_R - F_S, where :\ F_R + F_S = 1 In practice, it is most often expressed as a percent enantiomeric excess. The enantiomeric excess can be determined in another way if we know the amount of each enantiomer produced. If one knows the moles of each enantiomer produced then: Enantiomeric excess is used as one of the indicators of the success of an asymmetric synthesis. For mixtures of diastereomers, there are analogous definitions and uses for diastereomeric excess and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BINAP
BINAP (2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthyl) is an organophosphorus compound. This Optical isomerism, chiral diphosphines, diphosphine ligand is widely used in chiral synthesis, asymmetric synthesis. It consists of a pair of 2-diphenylphosphinonaphthalene, naphthyl groups linked at the 1 and 1′ positions. This C2-Symmetric ligands, C2-symmetric framework lacks a stereocenter, stereogenic atom, but has axial chirality due to restricted rotation (atropisomerism). The barrier to racemization is high due to steric hindrance, which limits rotation about the bond linking the naphthyl rings. The dihedral angle between the naphthyl groups is approximately 90°. The natural bite angle is 93°. Use as ligand in asymmetric catalysis BINAP is used in organic synthesis for enantioselective transformations catalyzed by its complex (chemistry), complexes of ruthenium, rhodium, and palladium. As pioneered by Ryōji Noyori and his co-workers, rhodium complexes of BINAP are usefu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide (TiO2), is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and cata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirality (chemistry)
In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral () if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotation (geometry), rotations, translation (geometry), translations, and some Conformational isomerism, conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality (). The terms are derived from Ancient Greek (''cheir'') 'hand'; which is the canonical example of an object with this property. A chiral molecule or ion exists in two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, called enantiomers; they are often distinguished as either "right-handed" or "left-handed" by their absolute configuration or some other criterion. The two enantiomers have the same chemical properties, except when reacting with other chiral compounds. They also have the same physics, physical properties, except that they often have opposite optical activity, optical activities. A homogeneous mixture of the two enantiomers in equal parts is said to be racemic mixture, racem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |