|
Oreobeiline
Oreobeiline is an morphinan alkaloid of ''Beilschmiedia'' with anti-acetylcholinesterase, anti-alpha-glucosidase, anti-leishmanial, and anti-fungal activities. See also * Sinomenine Sinomenine or cocculine is an alkaloid found in the root of the climbing plant ''Sinomenium acutum'' which is native to Japan and China. The plant is traditionally used in herbal medicine in these countries for rheumatism and arthritis. However, ... External links Anti-acetylcholinesterase, anti-α-glucosidase, anti-leishmanial and anti-fungal activities of chemical constituents of Beilschmiedia species Benzylisoquinoline alkaloids Morphinans Methoxy compounds Heterocyclic compounds with 4 rings {{alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinomenine
Sinomenine or cocculine is an alkaloid found in the root of the climbing plant ''Sinomenium acutum'' which is native to Japan and China. The plant is traditionally used in herbal medicine in these countries for rheumatism and arthritis. However, its analgesic action against other kinds of pain is limited. Sinomenine is a morphinan derivative, related to opioids such as levorphanol and the non-opioid cough suppressant dextromethorphan. Its anti-rheumatic effects are thought to be primarily mediated via release of histamine, but other effects such as inhibition of prostaglandin, leukotriene and nitric oxide synthesis may also be involved. See also * Hasubanan Hasubanan is an alkaloid with the chemical formula of C16H21N. It forms the central core of a class of alkaloids known collectively as hasubanans. The compound is derived from reticuline, as is morphinan, but is comparatively more oxidized an ... * Oreobeiline References {{Glycinergics Benzylisoquinolin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphinan
Morphinan is the prototype chemical structure of a large chemical class of psychoactive drugs, consisting of opiate analgesics, cough suppressants, and dissociative hallucinogens, among others. Structure Morphinan has a phenanthrene core structure with the ''A'' ring remaining aromatic and the ''B'' and ''C'' rings being saturated, and an additional nitrogen-containing, six-membered, saturated ring, the ''D'' ring, being attached to carbons 9 and 13 of the core, and with the nitrogen being at position 17 of the composite. Of the major naturally occurring opiates of the morphinan type—morphine, codeine and thebaine—thebaine has no therapeutic properties (it causes seizures in mammals), but it provides a low-cost feedstock for the industrial production of at least four semi-synthetic opiate agonists, including hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxycodone and oxymorphone, and the opioid antagonist naloxone. Structure-activity relationship The physiological behavior of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beilschmiedia
''Beilschmiedia'' is a genus of trees and shrubs in family Lauraceae. Most of its species grow in tropical climates, but a few of them are native to temperate regions, and they are widespread in tropical Asia, Africa, Madagascar, Australia, New Zealand, North America, Central America, the Caribbean, and South America. The best-known species to gardeners in temperate areas are '' B. berteroana'' and '' B. miersii'' because of their frost tolerance. Seeds of ''B. bancroftii'' were used as a source of food by Australian Aborigines. Timbers of some species are very valuable. Overview ''Beilschmiedia'' is a genus of about 240-250 species, that are trees or shrubs; it has about 80 species in tropical Africa and Madagascar. They are commonly canopy trees, growing at altitudes from near sea level to 2200 m. The trees grow in well-developed rainforests, and in warm or temperate forests on poorer sedimentary soils. Most species grow in tropical climates, but a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
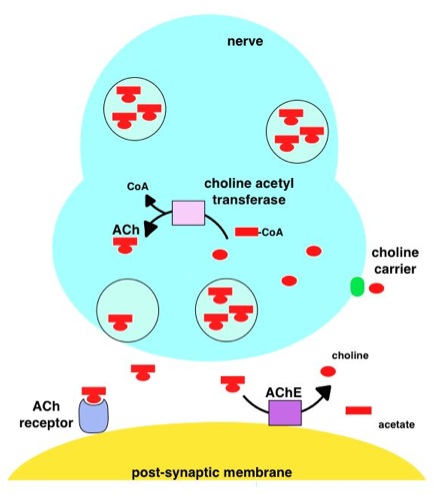
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechanism AChE is a hydrolase that hydrolyzes choline esters. It has a very high catalytic activity—each molecule of AChE degrades about 25,000 molecules of acetylcholine (ACh) per second, approaching the limit allowed by diffusion of the substrate. The active site of AChE comprises 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-glucosidase
α-Glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.20, maltase, glucoinvertase, glucosidosucrase, maltase-glucoamylase, α-glucopyranosidase, glucosidoinvertase, α-D-glucosidase, α-glucoside hydrolase, α-1,4-glucosidase, α-D-glucoside glucohydrolase; systematic name α-D-glucoside glucohydrolase) is a glucosidase located in the brush border of the small intestine that acts upon α(1→4) bonds: : Hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (1→4)-linked α-D-glucose residues with release of D-glucose This is in contrast to β-glucosidase. α-Glucosidase breaks down starch and disaccharides to glucose. Other glucosidases include: * Cellulase * Beta-glucosidase * Debranching enzyme Mechanism α-Glucosidase hydrolyzes terminal non-reducing (1→4)-linked α-glucose residues to release a single α-glucose molecule. α-Glucosidase is a carbohydrate-hydrolase that releases α-glucose as opposed to β-glucose. β-Glucose residues can be released by glucoamylase, a functionally similar enzyme. The sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids
Substitution of the heterocycle isoquinoline at the C1 position by a benzyl group provides 1‑benzylisoquinoline, the most widely examined of the numerous benzylisoquinoline structural isomers. The 1-benzylisoquinoline moiety can be identified within numerous compounds of pharmaceutical interest, such as moxaverine; but most notably it is found within the structures of a wide variety of plant natural products, collectively referred to as benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. This class is exemplified in part by the following compounds: papaverine, noscapine, codeine, morphine, apomorphine, berberine, tubocurarine. Biosynthesis (''S'')- Norcoclaurine ( higenamine) has been identified as the central 1-benzyl-tetrahydro-isoquinoline precursor from which numerous complex biosynthetic pathways eventually emerge. These pathways collectively lead to the structurally disparate compounds comprising the broad classification of plant natural products referred to as benzylisoquinoline alkal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphinans
Morphinan is the prototype chemical structure of a large chemical class of psychoactive drugs, consisting of opiate analgesics, cough suppressants, and dissociative hallucinogens, among others. Structure Morphinan has a phenanthrene core structure with the ''A'' ring remaining aromatic and the ''B'' and ''C'' rings being saturated, and an additional nitrogen-containing, six-membered, saturated ring, the ''D'' ring, being attached to carbons 9 and 13 of the core, and with the nitrogen being at position 17 of the composite. Of the major naturally occurring opiates of the morphinan type—morphine, codeine and thebaine—thebaine has no therapeutic properties (it causes seizures in mammals), but it provides a low-cost feedstock for the industrial production of at least four semi-synthetic opiate agonists, including hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxycodone and oxymorphone, and the opioid antagonist naloxone. Structure-activity relationship The physiological behavior of morphinans (n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methoxy Compounds
In organic chemistry, a methoxy group is the functional group consisting of a methyl group bound to oxygen. This alkoxy group has the formula . On a benzene ring, the Hammett equation classifies a methoxy substituent at the ''para'' position as an electron-donating group, but as an electron-withdrawing group if at the ''meta'' position. At the ''ortho'' position, steric effects are likely to cause a significant alteration in the Hammett equation prediction which otherwise follows the same trend as that of the ''para'' position. Occurrence The simplest of methoxy compounds are methanol and dimethyl ether. Other methoxy ethers include anisole and vanillin. Many alkoxides contain methoxy groups, e.g. tetramethyl orthosilicate and titanium methoxide. Such compounds are often classified as methoxides. Esters with a methoxy group can be referred to as methyl esters, and the —COOCH3 substituent is called a methoxycarbonyl. Biosynthesis In nature, methoxy groups are found on nucleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |