|
OpenAM
OpenAM is an open-source access management, entitlements and federation server platform. Now it is supported by Open Identity Platform Community. OpenAM (Open Access Management) originated as OpenSSO, (Open Single Sign-On) an access management system created by Sun Microsystems and now owned by Oracle Corporation. OpenAM is a fork which was initiated following Oracle's purchase of Sun. History Announced by Sun Microsystems in July 2005, OpenSSO was based on Sun Java System Access Manager, and was the core of Sun's commercial access management and federation product, OpenSSO Enterprise (formerly Sun Access Manager and Sun Federation Manager). In July 2008, Sun announced paid support for regular "Express" builds of OpenSSO. Sun's stated intent was that express builds would be released approximately every three months, allowing customers early access to new features. In September 2008, Sun announced OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0, the first commercial product derived from the OpenSSO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle Corporation
Oracle Corporation is an American Multinational corporation, multinational computer technology company headquartered in Austin, Texas. Co-founded in 1977 in Santa Clara, California, by Larry Ellison, who remains executive chairman, Oracle was the List of the largest software companies, third-largest software company in the world in 2020 by revenue and market capitalization. The company's 2023 ranking in the Forbes Global 2000, ''Forbes'' Global 2000 was 80. The company sells Database, database software, particularly Oracle Database, and cloud computing. Oracle's core application software is a suite of enterprise software products, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, human capital management (HCM) software, customer relationship management (CRM) software, enterprise performance management (EPM) software, Customer Experience Commerce (CX Commerce) and supply chain management (SCM) software. History Larry Ellison, Bob Miner, and Ed Oates co-founded Oracle in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ForgeRock Access Management
ForgeRock, Inc. was an identity and access management software company headquartered in San Francisco. On August 23, 2023, Thoma Bravo announced that it had completed the acquisition of the company for approximately $2.3 billion. On acquisition completion, ForgeRock merged into Ping Identity, and both product portfolios continue being developed. Overview ForgeRock was founded in Norway in February 2010 by a group of former Sun Microsystems employees, after Sun was acquired by Oracle Corporation. After the acquisition, the software was scheduled for phase-out in favor of Oracle’s in-house product, so the founders "started their own company to fork the code and continue developing Sun’s software." In April 2020, ForgeRock announced that it has raised $93.5 million in funding, a Series E it will use to continue expanding, which "brings the total raised by the company to $230 million." The company went public in September 2021. It is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ForgeRock
ForgeRock, Inc. was an identity and access management software company headquartered in San Francisco. On August 23, 2023, Thoma Bravo announced that it had completed the acquisition of the company for approximately $2.3 billion. On acquisition completion, ForgeRock merged into Ping Identity, and both product portfolios continue being developed. Overview ForgeRock was founded in Norway in February 2010 by a group of former Sun Microsystems employees, after Sun was acquired by Oracle Corporation. After the acquisition, the software was scheduled for phase-out in favor of Oracle’s in-house product, so the founders "started their own company to fork the code and continue developing Sun’s software." In April 2020, ForgeRock announced that it has raised $93.5 million in funding, a Series E it will use to continue expanding, which "brings the total raised by the company to $230 million." The company went public in September 2021. It is listed on the New York Stock Exchange unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WS-Federation
WS-Federation (Web Services Federation) is an Identity Federation specification, developed by a group of companies: BEA Systems, BMC Software, CA Inc. (along with Layer 7 Technologies now a part of CA Inc.), IBM, Microsoft, Novell, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, and VeriSign. Part of the larger Web Services Security framework, WS-Federation defines mechanisms for allowing different security realms to broker information on identities, identity attributes and authentication. Associated specifications The following draft specifications are associated with WS-Security: * WS-SecureConversation *WS-Federation * WS-Authorization * WS-Policy * WS-Trust * WS-Privacy See also * List of Web service specifications *Web Services *SAML *XACML * Liberty Alliance *OpenID OpenID is an open standard and decentralized authentication protocol promoted by the non-profit OpenID Foundation. It allows users to be authenticated by co-operating sites (known as relying parties, or RP) using a third-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XACML
__NOTOC__ The eXtensible Access Control Markup Language (XACML) is an XML-based standard markup language for specifying access control policies. The standard, published by OASIS (organization), OASIS, defines a declarative fine-grained, attribute-based access control policy language, an architecture, and a processing model describing how to evaluate access requests according to the rules defined in policies. XACML is primarily an attribute-based access control system. In XACML, attributes – information about the subject accessing a resource, the resource to be addressed, and the environment – act as inputs for the decision of whether access is granted or not. XACML can also be used to implement role-based access control.See for example In XACML, access control decisions to be taken are expressed as Rules. Each Rule comprises a series of conditions which decide whether a given request is approved or not. If a Rule is applicable to a request but the conditions within t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk-based Authentication
In authentication Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an Logical assertion, assertion, such as the Digital identity, identity of a computer system user. In contrast with iden ..., risk-based authentication is a non-static authentication system which takes into account the profile (IP address, User-Agent HTTP header, time of access, and so on) of the agent requesting access to the system to determine the risk profile associated with that transaction. The risk profile is then used to determine the complexity of the challenge. Higher risk profiles leads to stronger challenges, whereas a static username/password may suffice for lower-risk profiles. Risk-based implementation allows the application to challenge the user for additional credentials only when the risk level is appropriate. The point is that user validation accuracy is improved without inconveniencing a user, and risk-based authenticat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federation (information Technology)
A federation is a group of computing or network providers agreeing upon standards of operation in a collective fashion. The most widely known example is the Internet, which is Federated around the Internet Protocol (IP) stack of protocols. Another, more visible, example is Email, where the common use of the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), allows [email protected] to communicate with [email protected] and [email protected] although the software implementing each of these systems can be completely different. The term may be used when describing the inter-operation of two distinct, formerly disconnected, telecommunications networks that may have different internal structures. The term "federated cloud" refers to facilitating the interconnection of two or more geographically separate computing clouds. The term may also be used when groups attempt to delegate collective authority of development to prevent fragmentation. In a telecommunication interconnection, the internal '' mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Assertion Markup Language
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML, pronounced ''SAM-el'', ) is an open standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, in particular, between an identity provider and a service provider. SAML is an XML-based markup language for security assertions (statements that service providers use to make access-control decisions). SAML is also: * A set of XML-based protocol messages * A set of protocol message bindings * A set of profiles (utilizing all of the above) An important use case that SAML addresses is web-browser single sign-on (SSO). Single sign-on is relatively easy to accomplish within a security domain (using cookies, for example) but extending SSO across security domains is more difficult and resulted in the proliferation of non-interoperable proprietary technologies. The SAML Web Browser SSO profile was specified and standardized to promote interoperability.J. Hughes et al. ''Profiles for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug tracking system, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, GitHub, Inc. has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. GitHub reported having over 100 million developers and more than 420 million Repository (version control), repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the world's largest source code host Over five billion developer contributions were made to more than 500 million open source projects in 2024. About Founding The development of the GitHub platform began on October 19, 2005. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Windows Authentication
Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) is a term associated with Microsoft products that refers to the SPNEGO, Kerberos, and NTLMSSP authentication protocols with respect to SSPI functionality introduced with Microsoft Windows 2000 and included with later Windows NT-based operating systems. The term is used more commonly for the automatically authenticated connections between Microsoft Internet Information Services, Internet Explorer, and other Active Directory aware applications. IWA is also known by several names like ''HTTP Negotiate authentication'', ''NT Authentication'', ''NTLM Authentication'', ''Domain authentication'', ''Windows Integrated Authentication'', ''Windows NT Challenge/Response authentication'', or simply ''Windows Authentication''. Overview Integrated Windows Authentication uses the security features of Windows clients and servers. Unlike Basic Authentication or Digest Authentication, initially, it does not prompt users for a user name and password. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenID Connect
OpenID is an open standard and decentralized authentication protocol promoted by the non-profit OpenID Foundation. It allows users to be authenticated by co-operating sites (known as relying parties, or RP) using a third-party identity provider (IDP) service, eliminating the need for webmasters to provide their own ''ad hoc'' login systems, and allowing users to log in to multiple unrelated websites without having to have a separate identity and password for each. Users create accounts by selecting an OpenID identity provider, and then use those accounts to sign on to any website that accepts OpenID authentication. Several large organizations either issue or accept OpenIDs on their websites. The OpenID standard provides a framework for the communication that must take place between the identity provider and the OpenID acceptor (the "relying party"). An extension to the standard (the OpenID Attribute Exchange) facilitates the transfer of user attributes, such as name and gend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
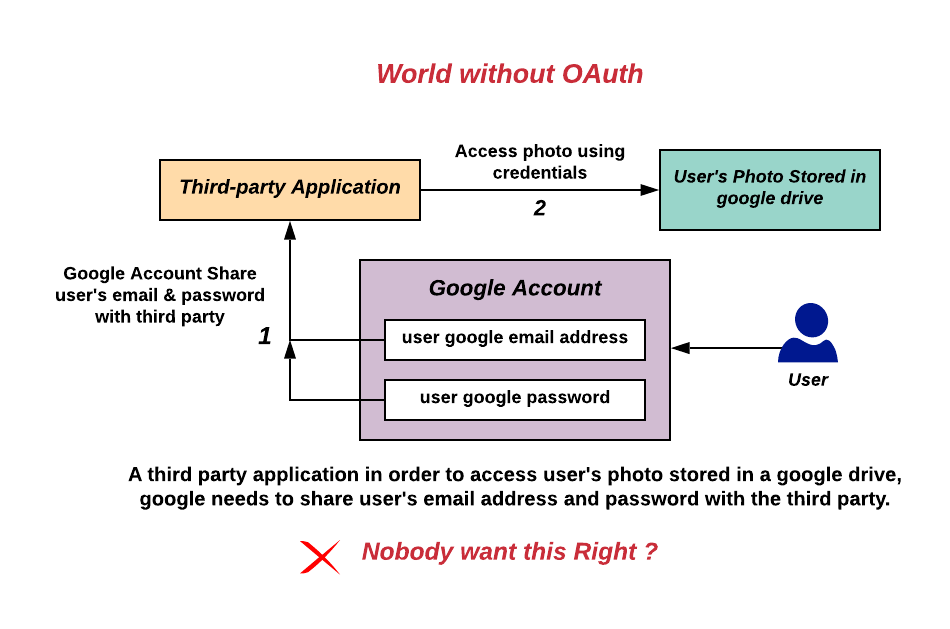
OAuth2
OAuth (short for open authorization) is an Open standard , open standard for access Delegation (computer security), delegation, commonly used as a way for internet users to grant websites or applications access to their information on other websites but without giving them the passwords. This mechanism is used by companies such as Amazon (company), Amazon, Google, Meta Platforms, Microsoft, and Twitter to permit users to share information about their accounts with third-party applications or websites. Generally, the OAuth protocol provides a way for resource owners to provide a client application with secure delegated access to server resources. It specifies a process for resource owners to authorize third-party access to their server resources without providing credentials. Designed specifically to work with Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), OAuth essentially allows access tokens to be issued to third-party clients by an authorization server, with the approval of the resourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |