|
One Country, One System
One country, one system ( zh, s=一国一制, p=yīguó yīzhì) means that the People's Republic of China governs Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan in the same political and judicial system as the Mainland China, mainland, unlike one country, two systems; meaning the abolition of the Special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Region and direct rule by the State Council of China, Central People's Government after the unification of Hong Kong, Macau or the future Chinese unification, unification with Taiwan. In addition, some outside radical pro-Beijing figures have expressed their support to the implementation of one country, one system in Hong Kong. History Hong Kong According to the Public Opinion Programme of the University of Hong Kong (HKUPOP), Hong Kong people's identification with the Chinese people had a slow upward trend after the handover of Hong Kong in 1997 and up to 2006, which can be attributed to the completion of the handover of Hong Kong's sovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Republic Of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 Province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions: 22 provinces of China, provinces, 5 autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, 4 direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is List of cities in China by population, its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Localist Camp
Localist camp or localist and self-determination groups refers to the various groups with localist ideologies in Hong Kong. It emerged from post-80s social movements in the late 2000s which centred on the preservation of the city's autonomy and local lifestyles and opposed the perceived growing encroachment of the Chinese government on the city's management of its own political, economic, and social affairs. Although grouped together with the pro-democracy camp, they have a distinct view as they advocate for Hongkongers’ right to self-determination. While milder elements advocates for greater autonomy while remaining part of China, the more radical elements call for the return to British rule or full independence as a sovereign state. Some also advocate for a more aggressive and militant stance against the mainland government in defending local interests. For that reason, they are labelled as "radicals" and " separatists" by the Chinese government. The localists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politics Of Hong Kong
The politics of Hong Kong takes place in a framework of a political system dominated by its quasi-constitutional document, the Hong Kong Basic Law, its own legislature, the Chief Executive as the head of government and of the Special Administrative Region and of a politically constrained multi-party presidential system. The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China is led by the Chief Executive, the head of government. The Basic Law, Hong Kong's constitutional document, was approved in March 1990 by National People's Congress of China, and entered into force on 1 July 1997, when sovereignty of Hong Kong was transferred to China (PRC), ending over one and a half centuries of British rule. Hong Kong became a Special Administrative Region (SAR) of the PRC with a high degree of autonomy in all matters except foreign affairs and defence, which are responsibilities of the PRC government. In accordance with Article 31 of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Extremism In China
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of status or resources. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. Politics may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and non-violent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but the word often also carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or in a limited way, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nationalism In China
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, Ideology, History''. Polity, 2010. pp. 9, 25–30; especially with the aim of gaining and maintaining its sovereignty (self-governance) over its perceived homeland to create a nation-state. It holds that each nation should govern itself, free from outside interference (self-determination), that a nation is a natural and ideal basis for a polity, and that the nation is the only rightful source of political power. It further aims to build and maintain a single national identity, based on a combination of shared social characteristics such as culture, ethnicity, geographic location, language, politics (or the government), religion, traditions and belief in a shared singular history, and to promote national unity or solidarity. There are variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
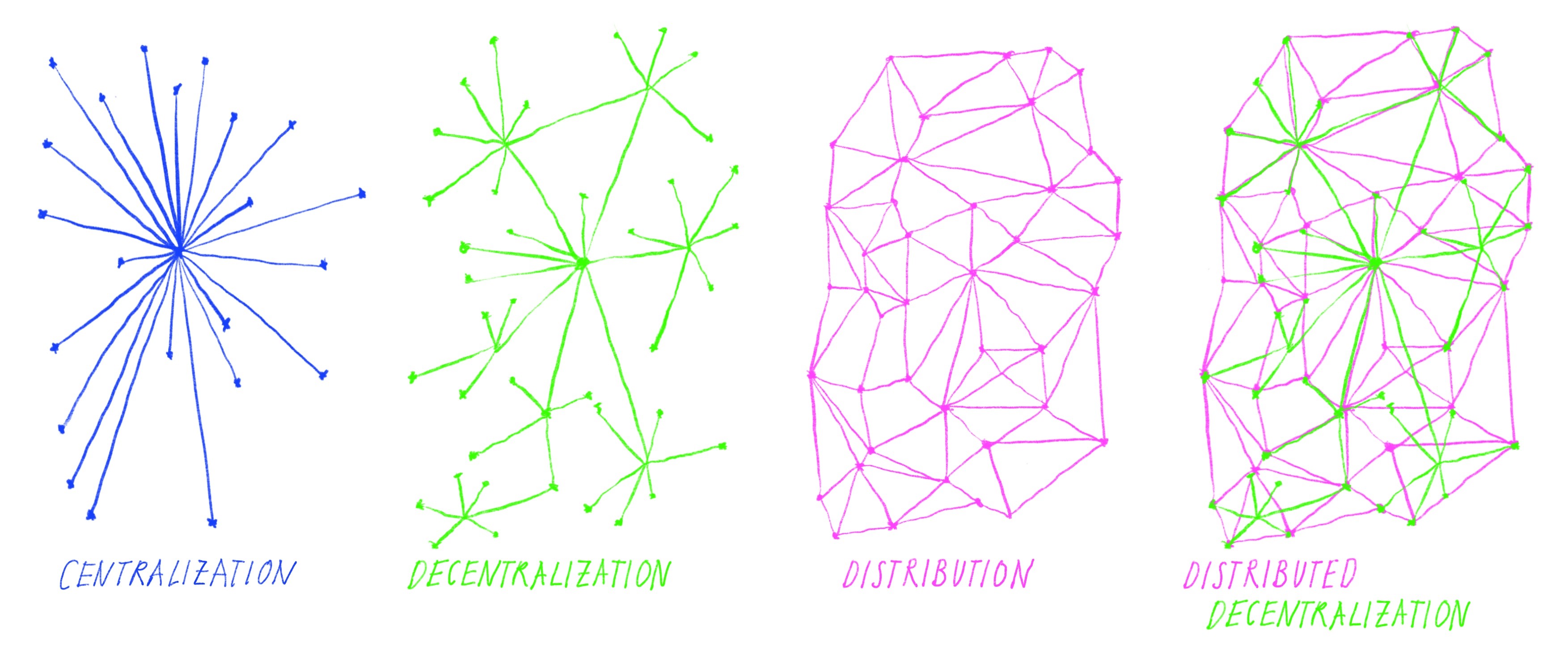
Centralisation
Centralisation or centralization (American English) is the process by which the activities of an organisation, particularly those regarding planning, decision-making, and framing strategies and policies, become concentrated within a particular group within that organisation. This creates a power structure where the said group occupies the highest level of hierarchy and has significantly more authority and influence over the other groups, who are considered its subordinates. An antonym of ''centralisation'' is ''decentralisation'', where authority is shared among numerous different groups, allowing varying degree of autonomy for each. The term has a variety of meanings in several fields. In political science, centralisation refers to the concentration of a government's power—both geographically and politically—into a centralized government, centralised government, which has sovereignty over all its administrative divisions. Conversely, a decentralized system, decentralised s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RTHK
Radio Television Hong Kong (RTHK) is the public broadcasting service of Hong Kong. GOW, the predecessor to RTHK, was established in 1928 as the first broadcasting service in Hong Kong. As a government department under the Commerce and Economic Development Bureau of the Hong Kong Government that directly supported by annual government funding, RTHK's educational, entertainment, and public affairs programmes are broadcast on its eight radio channels and five television channels, as well as commercial television channels. History The British Hong Kong Government launched its first radio broadcasting station, known as "GOW", on 20 June 1928, with a starting staff of only six people. Several name changes occurred over the next few years, and it eventually became known as "Radio Hong Kong" (RHK) () in 1948. In 1949, broadcasting operations were taken over by the Government Information Services (GIS), but by 1954, RHK had managed to establish itself as an independent departmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2020 Hong Kong National Security Law
The Law of the People's Republic of China on Safeguarding National Security in the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region is a national law of China on Hong Kong national security passed in 2020. It is implemented in Hong Kong in accordance with Hong Kong Basic Law Article 18, which allows for China's national laws to be valid in Hong Kong if they are included in Annex III. It was formulated under the authorization of the National People's Congress decision on Hong Kong national security legislation. The law was passed on 30 June 2020 by the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress as a means of resolving the 2019–2020 Hong Kong protests, anti-extradition bill protests instigated by a 2019 Hong Kong extradition bill, Hong Kong local bill proposed in 2019 to enable Extradition law in China, extradition to other territories including the mainland, and came into force the same day. Among others, the national security law established four particular crimes of Secessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xi Jinping
Xi Jinping, pronounced (born 15 June 1953) is a Chinese politician who has been the general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and Chairman of the Central Military Commission (China), chairman of the Central Military Commission (CMC), and thus the paramount leader of China, since 2012. Since 2013, Xi has also served as the seventh president of China. As a member of the fifth Generations of Chinese leadership, generation of Chinese leadership, Xi is the first CCP general secretary born after the Proclamation of the People's Republic of China, establishment of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The son of Chinese communist veteran Xi Zhongxun, Xi was exiled to rural Yanchuan County, Shaanxi Province, as a teenager following his father's purge during the Cultural Revolution. He lived in a yaodong in the village of Liangjiahe, where he joined the CCP after several failed attempts and worked as the local Chinese Communist Party Committee Secretary, party secretary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University (THU) is a public university in Haidian, Beijing, China. It is affiliated with and funded by the Ministry of Education of China. The university is part of Project 211, Project 985, and the Double First-Class Construction. It is also a member in the C9 League. Tsinghua University's campus is in northwest Beijing, on the site of the former imperial gardens of the Qing dynasty. The university has 21 schools and 59 departments, with faculties in science, engineering, humanities, law, medicine, history, philosophy, economics, management, education, and art. History Early 20th century (1911–1949) Tsinghua University was established in Beijing during a tumultuous period of national upheaval and conflicts with foreign powers which culminated in the Boxer Rebellion, an uprising against foreign influence in China. After the suppression of the revolt by a foreign alliance including the United States, the ruling Qing dynasty was required to pay inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City University Of Hong Kong School Of Law
The School of Law of City University of Hong Kong was founded in 1987, as the second law school in Hong Kong. History The Department of Law was established in 1987, followed by the Department of Professional Legal Education in 1992. In March 1993, the two departments were brought together to merge as the Faculty of Law, and later renamed as the School of Law since the administrations of the two departments were unified. The school publishes Asia Pacific Law Review since 1992 and a student-edited City University of Hong Kong Law Review since 2009. The school also has participated in various mooting competitions, having won moots such as ICC Moot and Vis East in 2012, and Willem C. Vis Moot in 2013. Notable alumni * Rimsky Yuen SC, former Secretary for Justice * Eunice Yung, Member of the 6th Legislative Council of Hong Kong * Paul Tse, Member of the 4th Legislative Council of Hong Kong * Richard Khaw SC, Recorder of the Court of First Instance of the High Court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |