|
Oligodon Formosanus
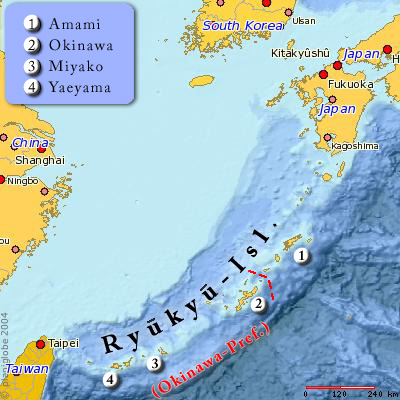
''Oligodon formosanus'', also knowwn as the Formosa kukri snake or beautiful kukri snake, is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. The species epithet is named after its range in Taiwan (''Formosa''). Description The scale colorings range in the brown-red spectrum. The body is a tawny light brown with two darker russet stripes running down either side of the spine, where thin black lines that break into smaller dotted patterns occasionally diagonally intersect. The underbelly is off-white. Distribution The snake is found in China (including Hong Kong and Hainan), Japan (including Ryukyu Islands, Okinawa is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi). Naha is the capital and largest city ..., Miyako and Yaeyama), Taiwan, and northern Vietnam. References formosanus Snakes of China Snakes of Vietnam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Charles Lewis Günther
Albert may refer to: Companies * Albert (supermarket), a supermarket chain in the Czech Republic * Albert Heijn, a supermarket chain in the Netherlands * Albert Market, a street market in The Gambia * Albert Productions, a record label * Albert Computers, Inc., a computer manufacturer in the 1980s Entertainment * ''Albert'' (1985 film), a Czechoslovak film directed by František Vláčil * ''Albert'' (2015 film), a film by Karsten Kiilerich * ''Albert'' (2016 film), an American TV movie * ''Albert'' (Ed Hall album), 1988 * "Albert" (short story), by Leo Tolstoy * Albert (comics), a character in Marvel Comics * Albert (''Discworld''), a character in Terry Pratchett's ''Discworld'' series * Albert, a character in Dario Argento's 1977 film ''Suspiria'' Military * Battle of Albert (1914), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France * Battle of Albert (1916), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France * Battle of Albert (1918), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France People * Albert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligodon
''Oligodon'' is genus of colubrid snakes that was first described by the Austrian zoologist Fitzinger in 1826. This genus is widespread throughout central and tropical Asia. The snakes of this genus are commonly known as kukri snakes.. Description They are egg eaters and are usually under 90 cm (35 in) in length; different species display widely variable patterns and colorations. They subsist mostly by scavenging the eggs of birds and reptiles. Besides eggs, species of this genus also feeds on lizards, frogs, and small rodents. ''Oligodon'' is a rear-fanged snake genus. They have a set of enlarged teeth placed in the back of their mouths, as well as functional Duvernoy's glands. They are not dangerous to humans, though. Bites by some species have been reported to bleed excessively, suggesting presence of anticoagulants in the Duvernoy's gland secretions. Species of ''Oligodon'' are mostly nocturnal, and live on the floor of mature forests. The common name of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Vietnam
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snakes Of Japan
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads ( cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most have only one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs about twenty-five times independently via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, although this rule is not universal (see Amphisbaenia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Hong Kong
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snakes Of Asia
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads (cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most have only one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs about twenty-five times independently via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, although this rule is not universal (see Amphisbaenia, Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snakes Of China
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads (cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most have only one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs about twenty-five times independently via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, although this rule is not universal (see Amphisbaenia, Dibamida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaeyama Islands
The Yaeyama Islands (八重山列島 ''Yaeyama-rettō'', also 八重山諸島 ''Yaeyama-shotō'', Yaeyama: ''Yaima'', Yonaguni: ''Daama'', Okinawan: ''Yeema'', Northern Ryukyuan: ''Yapema'') are an archipelago in the southwest of Okinawa Prefecture, Japan, and cover . The islands are located southwest of the Miyako Islands, part of the Ryukyu Islands archipelago. The Yaeyama Islands are the remotest part of Japan from the main islands and contain Japan's most southern ( Hateruma) and most western (Yonaguni) inhabited islands. The city of Ishigaki serves as the political, cultural, and economic center of the Yaeyama Islands. Natural history The Yaeyama Islands are home to numerous species of subtropical and tropical plants, and mangrove forests. The islands produce sugarcane and pineapples. Coral reefs around the islands are ideal habitats for dolphins, sea turtles, and larger fish such as manta rays and whale sharks. Before being wiped out by humans, whales and dugong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oskar Boettger
Oskar Boettger (german: Böttger; 31 March 1844 – 25 September 1910) was a German zoologist who was a native of Frankfurt am Main. He was an uncle of the noted malacologist Caesar Rudolf Boettger (1888–1976). From 1863 to 1866 he studied at the Bergakademie Freiberg, then worked for a year in a chemical factory in Frankfurt am Main."Boettger, Oskar" p. 410. In: (1955). '' Neue Deutsche Biographie (NDB). Band 2''. Berlin: Duncker & Humblot. . (in German). In 1869 he received his doctorate from the . The following year (1870), he became a |
Miyako Islands
The (also Miyako Jima group) are a group of islands in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan, belonging to the Ryukyu Islands. They are situated between the Okinawa Island and Yaeyama Islands. In the early 1870s, the population of the islands was estimated to number approximately 10,000. Miyako island has 55,914 people. A bridge connects Miyako Island to Ikema Island, which has 801 people. Tarama village has 1,214 people, between the two islands of Minna and Tarama. Important Bird Area The islands have been recognised as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because they support populations of the resident Ryukyu green pigeons, as well as migrating whimbrels. Inhabited islands * Miyakojima City ** ** ** ** ** ( ja) ** * Tarama Village ( Miyako District) ** ** ( ja) See also *Miyako people * Sakishima Islands *Miyakoan language The Miyakoan language ( ''Myākufutsu/Myākufutsї'' or ''Sumafutsu/Sїmafutsї'') is a diverse dialect cluster spoken in the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |