|
Old Thuringian Dialect
Old Thuringian is a Central German dialect of Old High German that is known through onomastic proof. It may also be included in Old Low German alongside Old Saxon and Old Frisian. Background Thuringian emerged in the year 1100 A.D. when several groups such as Franconians, Bavarians, Saxons, and Flemish people migrants toward more eastern areas, where Polabian Slavs Polabian Slavs, also known as Elbe Slavs and more broadly as Wends, is a collective term applied to a number of Lechites, Lechitic (West Slavs, West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The ... once occupied. Sample text {{Lang, goh, Haribrig. Hiba liubi leob. References Central German languages German dialects Languages of Germany Thuringia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Thuringia
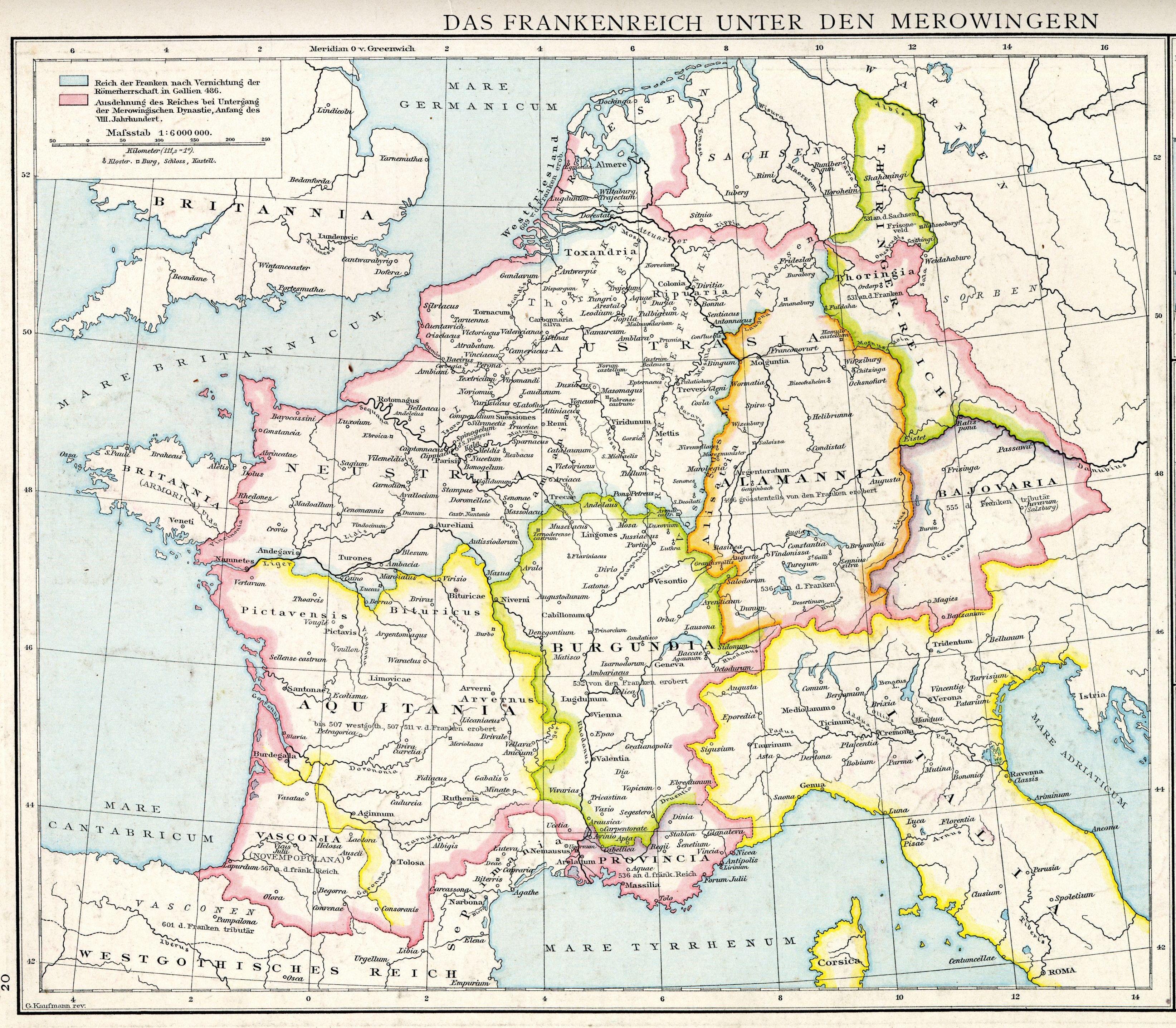
The Duchy of Thuringia was an eastern frontier march of the Merovingian kingdom of Austrasia, established about 631 by King Dagobert I after his troops had been defeated by the forces of the Slavic confederation of Samo at the Battle of Wogastisburg. It was recreated in the Carolingian Empire and its dukes were appointed by the king until it was absorbed by the Saxon dukes in 908. From about 1111/12 the territory was ruled by the Landgraves of Thuringia as Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. When Frederick IV, the last independent ruler of Thuringia died in 1440, the territory passed to his nephew, the Saxon elector Frederick II. History The former kingdom of the Thuringii arose during the Migration Period after the decline of the Hunnic Empire in Central Europe in the mid 5th century, culminating in their defeat in the 454 Battle of Nedao. With Bisinus a first Thuringian king is documented about 500, who ruled over extended estates that stretched beyond the Main Rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Frisian
Old Frisian was a West Germanic language spoken between the late 13th century and the end of 16th century. It is the common ancestor of all the modern Frisian languages except for the North Frisian language#Insular North Frisian, Insular North Frisian dialects, with which Old Frisian shares a common ancestor called Pre–Old Frisian or Proto-Frisian. Old Frisian was spoken by contemporary Frisians who comprised a loose confederacy along the North Sea coast from around modern-day Bruges in Belgium to the Weser in modern-day northern Germany, dominating Maritime transport, maritime trade. The vast majority of the surviving literature comprises legal documents and charters, though some poetry, historiographies, and religious documents are attested as well. Old Frisian was Ingvaeonic languages, closely related to and shared common characteristics with the Middle English, forms of English and Middle Low German, Low German spoken during the period. Although earlier scholarship contend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Dialects
German dialects are the various traditional local varieties of the German language. Though varied by region, those of the southern half of Germany beneath the Benrath line are dominated by the geographical spread of the High German consonant shift, and the dialect continuum that connects High German to the neighboring varieties of Low Franconian ( Dutch) and Low German. The varieties of German are conventionally grouped into Upper German, Central German and Low German; Upper and Central German form the High German subgroup. Standard German is a standardized form of High German, developed in the early modern period based on a combination of Central German and Upper German varieties. Etymology and nomenclature Traditionally, all of the major dialect groupings of German dialects are typically named after so-called " stem duchies" or "tribal duchies" (German: ''Stammesherzogtümer'') by early German linguists, among whom the Brothers Grimm were especially influential. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central German Languages
Central German or Middle German () is a group of High German languages spoken from the Rhineland in the west to the former eastern territories of Germany. Central German divides into two subgroups, West Central German and East Central German. Central German is distinguished by having experienced the High German consonant shift to a lesser degree than Upper German. It is spoken in the linguistic transition region separated from Northern Germany (Low German/Low Franconian) by the Benrath line isogloss and separated from Southern Germany ( Upper German) by the Speyer line. Central German is spoken in large and influential German cities such as Berlin, the former West German capital Bonn, Cologne, Düsseldorf, the main German financial center Frankfurt, Leipzig, and Dresden. The area corresponds to the geological region of the hilly Central Uplands that stretches from the North German plain to the South German Scarplands, covering the states of Saarland, Rhineland-Palatina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs, also known as Elbe Slavs and more broadly as Wends, is a collective term applied to a number of Lechites, Lechitic (West Slavs, West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The approximate territory stretched from the Baltic Sea in the north, the Saale and the ''Limes Saxoniae''Christiansen, 18 in the west, the Ore Mountains and the Western Sudetes in the south, and medieval History of Poland (966–1385), Poland in the east. The Polabian Slavs, largely conquered by Saxons and Danish people, Danes from the 9th century onwards, were included and gradually cultural assimilation, assimilated within the Holy Roman Empire. The tribes became gradually Germanization, Germanized and assimilated in the following centuries; the Sorbs are the only descendants of the Polabian Slavs to have retained their identity and culture. The Polabian language is now extinct. However, the two Sorbian languages are spoken by approximate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flemish People
Flemish people or Flemings ( ) are a Germanic peoples, Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Flemish Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%. ''Flemish'' was historically a geographical term, as all inhabitants of the medieval County of Flanders in modern-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands were referred to as "Flemings" irrespective of their ethnicity or language. The contemporary region of Flanders comprises a part of this historical county, as well as parts of the medieval Duchy of Brabant and the medieval County of Loon, where the modern national identity and Flemish culture, culture gradually formed. History The sense of "Flemish" identity increased significantly after the Belgian Revolution. Prior to this, the term "" in the Dutch language was in first place used for the inhabitants of the former County of Flanders. Flemish, however, had been used since the 14th century to refer to the language and dialects of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like them, speakers of West Germanic dialects, including the inland Franks and Thuringians to the south, and the coastal Frisians and Angles to the north who were among the peoples who were originally referred to as "Saxons" in the context of early raiding and settlements in Roman Britain and Gaul. To their east were Obotrites and other Slavic-speaking peoples. The political history of these continental Saxons is unclear until the 8th century and the conflict between their semi-legendary hero Widukind and the Frankish emperor Charlemagne. They do not appear to have been politically united until the generations leading up to that conflict, and before then they were reportedly ruled by regional "satraps". Previous Frankish rulers of Austrasia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavarians
Bavarians are a Germans, German ethnographic group native to Bavaria, a state in Germany. The group's dialect or speech is known as Bavarian language, Bavarian, native to Altbayern ("Old Bavaria"), roughly the territory of the historic Electorate of Bavaria in the 17th century. Like the neighboring Austrians, Bavarians are traditionally Roman Catholicism in Germany, Catholic. In much of ''Altbayern'', membership in the Catholic Church remains above 70%, and the center-right Christian Social Union in Bavaria (successor of the Bavarian People's Party of Weimar Republic, 1919–1933) has traditionally been the strongest party in the Landtag of Bavaria, Landtag, and also the party of all List of minister-presidents of Bavaria, minister-presidents of Bavaria since 1946, with the single exception of Wilhelm Hoegner, 1954–1957. Areal and dialectal subdivision There is no linguistic distinction between Bavarians and Austrians. The territory of Bavaria has changed significantly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
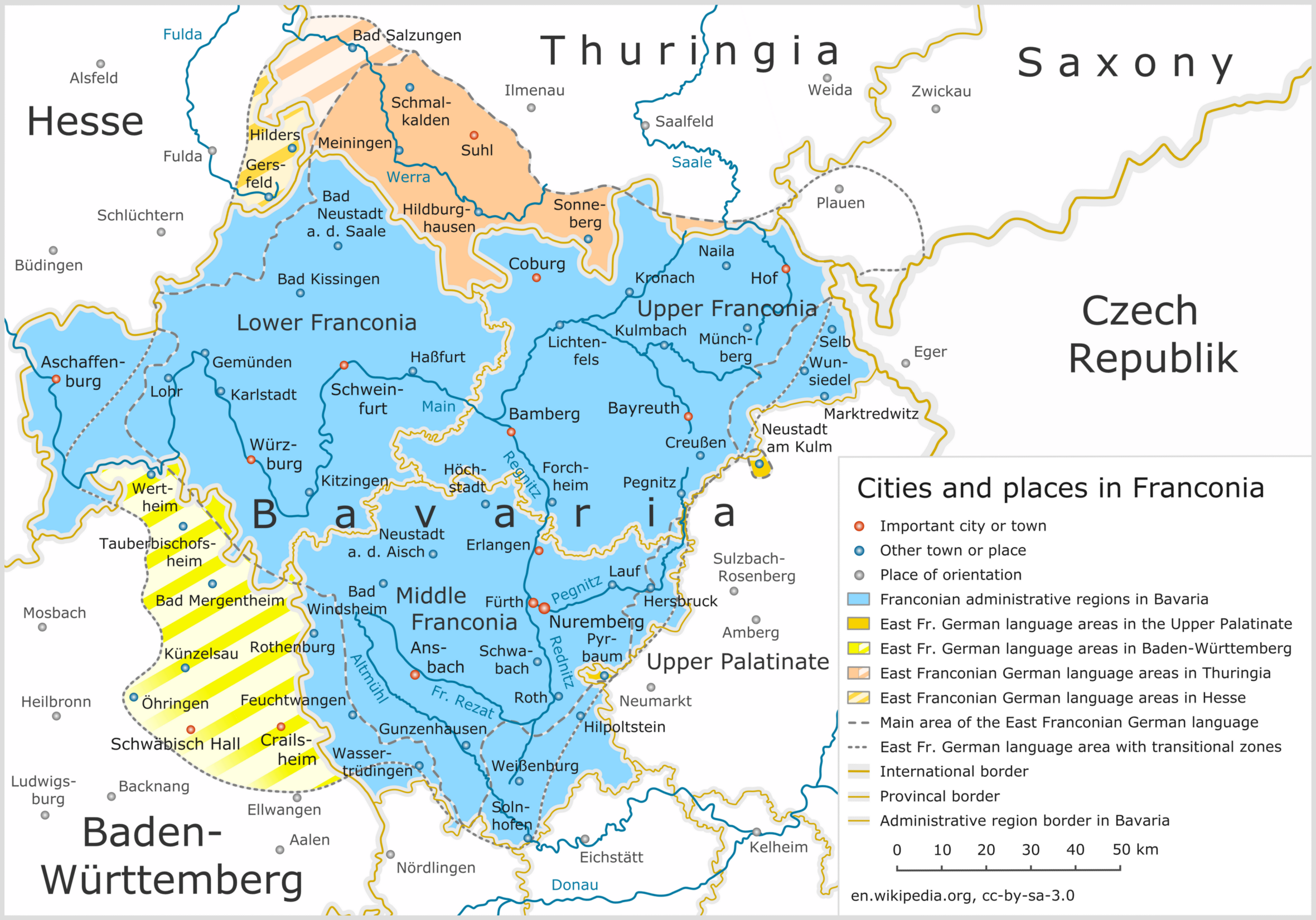
Franconians
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franconia in Bavaria, the adjacent, East Franconian, Franconian-speaking South Thuringia, south of the Thuringian Forest—which constitutes the language boundary between Franconian and Thuringian—and the eastern parts of Heilbronn-Franconia in Baden-Württemberg. Those parts of the Vogtland lying in Saxony (largest city: Plauen) are sometimes regarded as Franconian as well, because the Vogtlandian dialects are mostly East Franconian. The inhabitants of Saxon Vogtland, however, mostly do not consider themselves Franconian. On the other hand, the inhabitants of the Hessian dialect, Hessian-speaking parts of Lower Franconia west of the Spessart (largest city: Aschaffenburg) do consider themselves Franconian, although not speaking the dialect. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Saxon
Old Saxon (), also known as Old Low German (), was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Europe). It is a West Germanic language, closely related to the Anglo-Frisian languages. It is documented from the 8th century until the 12th century, when it gradually evolved into Middle Low German. It was spoken throughout modern northwestern Germany, primarily in the coastal regions and in the eastern Netherlands by Saxons, a Germanic tribe that inhabited the region of Saxony. It partially shares Anglo-Frisian's ( Old Frisian, Old English) Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law which sets it apart from Low Franconian and Irminonic languages, such as Dutch, Luxembourgish and German. The grammar of Old Saxon was fully inflected with five grammatical cases ( nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, and instrumental), three grammati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringii
The Thuringii, or Thuringians were a Germanic people who lived in the kingdom of the Thuringians that appeared during the late Migration Period south of the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. The Thuringian kingdom came into conflict with the Merovingian Franks, and it later came under their influence and Frankish control as a stem duchy. The name is still used for one of modern Germany's federal states ('' Bundesländer''). First appearances The Thuringians do not appear in classical Roman texts under that name, but some have suggested that they were the remnants of the Suebic Hermanduri, the last part of whose name (''-duri'') could represent the same sound as (''-thuri'') and the Germanic suffix ''-ing'', suggests a meaning of "descendants of (the ermanuri)". This people were living near the Marcomanni. Tacitus, in his ''Germania'', describes their homeland as being where the Elbe starts, but also having colonies at the Danube, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onomastics
Onomastics (or onomatology in older texts) is the study of proper names, including their etymology, history, and use. An ''alethonym'' ('true name') or an ''orthonym'' ('real name') is the proper name of the object in question, the object of onomastic study. Scholars studying onomastics are called ''onomasticians''. Onomastics has applications in data mining, with applications such as named-entity recognition, or recognition of the origin of names. It is a popular approach in historical research, where it can be used to identify ethnic minorities within populations and for the purpose of prosopography. Etymology ''Onomastics'' originates from the Greek (), itself derived from (). Branches * Toponymy Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage, and types. ''Toponym'' is the general term for a proper na ... (or more precisely to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |