|
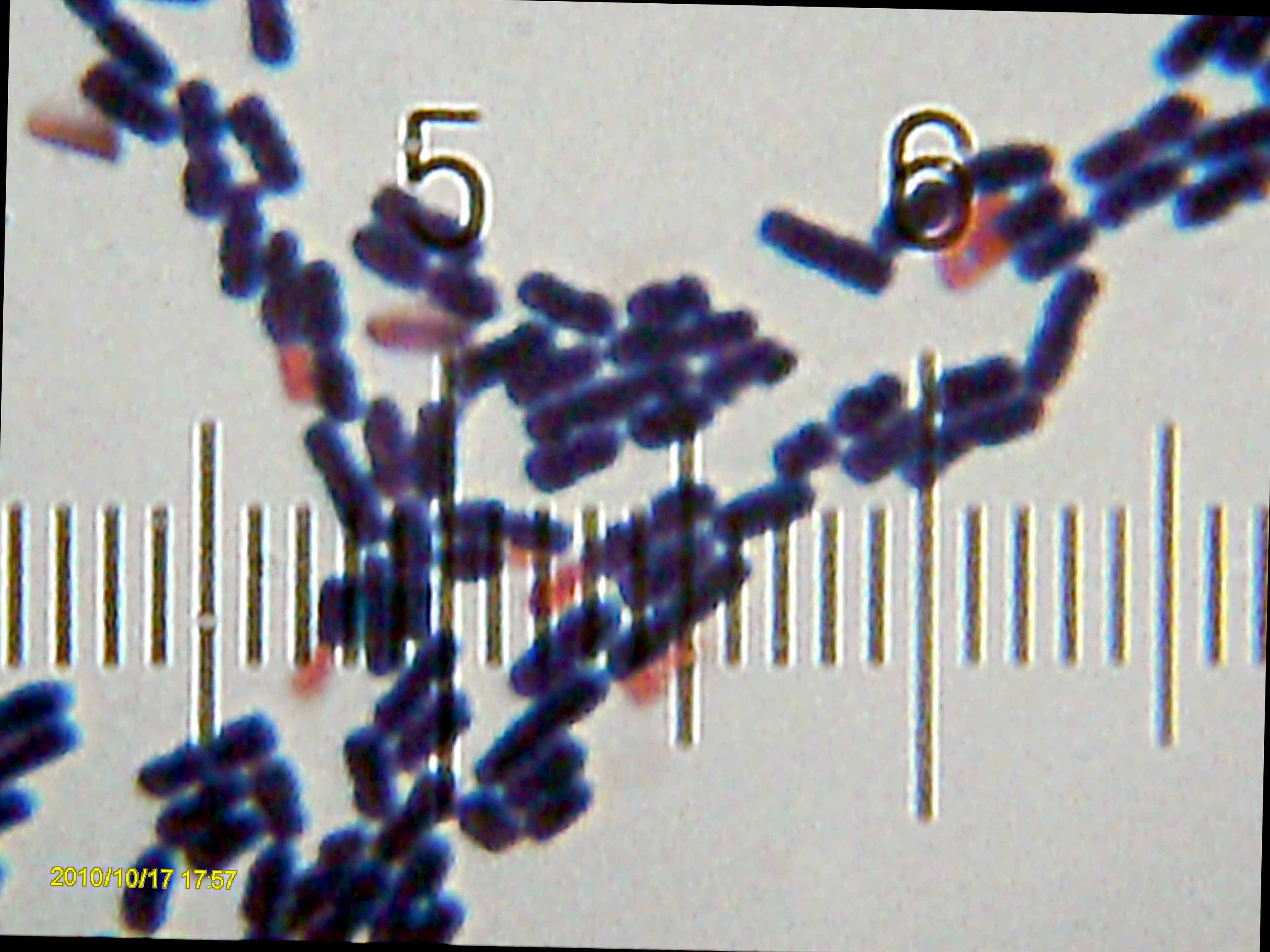
Oceanobacillus Iheyensis
''Oceanobacillus iheyensis'' is a bacterium, the type species of its genus. It is a deep-sea species, having been isolated from a depth of , and is extremely halotolerant and alkaliphilic. Its type strain is HTE831 (JCM 11309T, DSM 14371T). Oceanobacillus iheyensis HTE831 is an alkaliphilic and extremely halotolerant Bacillus-related species isolated from deep-sea sediment. References Further reading * * External links *LPSN Bacillaceae Bacteria describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have gram-positive cell wall structure. The renaming of phyla such as Firmicutes in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The name "Firmicutes" was derived from the Latin words for "tough skin," referring to the thick cell wall typical of bacteria in this phylum. Scientists once classified the Firmicutes to include all gram-positive bacteria, but have recently defined them to be of a core group of related forms called the low- G+C group, in contrast to the Actinomycetota. They have round cells, called cocci (singular coccus), or rod-like forms (bacillus). A few Firmicutes, such as '' Megasphaera'', '' Pectinatus'', '' Selenomonas'' and '' Zymophilus'', have a porous pseudo-outer membrane that causes them to stain gram-negative. Many Bacillota (Firmicutes) produce endospores, which are resistant to desiccatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacilli
Bacilli is a taxonomic class of bacteria that includes two orders, Bacillales and Lactobacillales, which contain several well-known pathogens such as ''Bacillus anthracis'' (the cause of anthrax). ''Bacilli'' are almost exclusively gram-positive bacteria. The name ''Bacillus'', capitalized and italicized, refers to a specific genus of bacteria. The name Bacilli, capitalized but not italicized, can also refer to a less specific taxonomic group of bacteria that includes two orders, one of which contains the genus ''Bacillus''. When the word is formatted with lowercase and not italicized, 'bacillus', it will most likely be referring to shape and not to the genus at all. Ambiguity Several related concepts make use of similar words, and the ambiguity can create considerable confusion. The term "''Bacillus''" (capitalized and italicized) is also the name of a genus (''Bacillus anthracis'') that, among many other genera, falls within the class Bacilli. The word "bacillus" (or its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillales
The Bacillales are an order of Gram-positive bacteria, placed within the Bacillota. Representative genera include ''Bacillus'', '' Listeria'' and ''Staphylococcus ''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultat ...''. See also * List of bacteria genera * List of bacterial orders References Gram-positive bacteria Bacilli {{bacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillaceae
The Bacillaceae are a family of gram-positive, heterotrophic, rod-shaped bacteria that may produce endospores. Motile members of this family are characterized by peritrichous flagella. Some Bacillaceae are aerobic, while others are facultative or strict anaerobes. Most are not pathogenic, but '' Bacillus'' species are known to cause disease in humans. Gram-variable cell wall Some Bacillaceae, such as the genera ''Filobacillus, Lentibacillus,'' and ''Halobacillus ''Halobacillus'' is a bacterial genus from the family of Bacillaceae. ''Halobacillus'' species are gram positive, oxidase positive, catalase negative, rod shaped marine bacteria. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and characterized two species of ' ...'', stain Gram-negative or Gram-variable, but are known to have a Gram-positive cell wall.Lim, J.M., Jeon, C.O., Song, S.M., and C.J. Kim. 2005''Pontibacillus chungwhensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately halophilic Gram-positive bacterium from a solar saltern in Kore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanobacillus
''Oceanobacillus'' is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped and motile bacteria genus from the family of Bacillaceae with a peritrichous flagella. ''Oceanobacillus'' species are commonly found in saline environment. Characteristics of ''Oceanobacillus'' spp. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and characterized four species of the genus ''Oceanobacillus'' from marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island Area of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos .... Colony, morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics of ''Oceanobacillus'' spp. are shown in the Table below. Note: + = Positive, – =Negative, O = Oxidative, F = Fermentative References Further reading * * * * * Bacillaceae Bacteria genera {{Firmicutes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halotolerant
Halotolerance is the adaptation of living organisms to conditions of high salinity. Halotolerant species tend to live in areas such as hypersaline lakes, coastal dunes, saline deserts, salt marshes, and inland salt seas and springs. Halophiles are organisms that live in highly saline environments, and require the salinity to survive, while halotolerant organisms (belonging to different domains of life) can grow under saline conditions, but do not require elevated concentrations of salt for growth. Halophytes are salt-tolerant higher plants. Halotolerant microorganisms are of considerable biotechnological interest. Applications Fields of scientific research relevant to halotolerance include biochemistry, molecular biology, cell biology, physiology, ecology, and genetics. An understanding of halotolerance can be applicable to areas such as arid-zone agriculture, xeriscaping, aquaculture (of fish or algae), bioproduction of desirable compounds (such as phycobiliproteins or caroteno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaliphilic
Alkaliphiles are a class of extremophilic microbes capable of survival in alkaline ( pH roughly 8.5–11) environments, growing optimally around a pH of 10. These bacteria can be further categorized as obligate alkaliphiles (those that require high pH to survive), facultative alkaliphiles (those able to survive in high pH, but also grow under normal conditions) and haloalkaliphiles (those that require high salt content to survive).HORIKOSHI, KOKI. "Alkaliphiles: Some Applications of Their Products for Biotechnology." MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS 63.4 (1999): 735-50. Print. Background information Microbial growth in alkaline conditions presents several complications to normal biochemical activity and reproduction, as high pH is detrimental to normal cellular processes. For example, alkalinity can lead to denaturation of DNA, instability of the plasma membrane and inactivation of cytosolic enzymes, as well as other unfavorable physiological changes.Higashibata, Akir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |