|
Objective Test
Objective tests are measures in which responses maximize objectivity, in the sense that response options are structured such that examinees have only a limited set of options (e.g. Likert scale A Likert scale ( ,) is a psychometric scale named after its inventor, American social psychologist Rensis Likert, which is commonly used in research questionnaires. It is the most widely used approach to scaling responses in survey research, s ..., true or false). Structuring a measure in this way is intended to minimize subjectivity or bias on the part of the individual administering the measure so that administering and interpreting the results does not rely on the judgment of the examiner. Although the term ‘objective test’ encompasses a wide range of tests with which most people are somewhat familiar (i.e. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory, Graduate Record Examination, and the Standardized Achievement Test), it is a term that aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objectivity (science)
In science, objectivity refers to attempts to do higher quality research by eliminating personal biases (or prejudices), irrational emotions and false beliefs, while focusing mainly on proven facts and evidence. It is often linked to observation as part of the scientific method. It is thus related to the aim of testability and reproducibility. To be considered objective, the results of measurement must be communicated from person to person, and then for third parties, as an advance in a collective understanding of the world. Such demonstrable knowledge has ordinarily conferred demonstrable powers of prediction or technology. The problem of philosophical objectivity is contrasted with personal subjectivity, sometimes exacerbated by the overgeneralization of a hypothesis to the whole. For example, Newton's law of universal gravitation appears to be the norm for the attraction between celestial bodies, but it was later refined and extended—and philosophically superseded— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Likert Scale
A Likert scale ( ,) is a psychometric scale named after its inventor, American social psychologist Rensis Likert, which is commonly used in research questionnaires. It is the most widely used approach to scaling responses in survey research, such that the term (or more fully the Likert-type scale) is often used interchangeably with '' rating scale'', although there are other types of rating scales. Likert distinguished between a scale proper, which emerges from collective responses to a set of items (usually eight or more), and the format in which responses are scored along a range. Technically speaking, a Likert scale refers only to the former. The difference between these two concepts has to do with the distinction Likert made between the underlying phenomenon being investigated and the means of capturing variation that points to the underlying phenomenon. When responding to a Likert item, respondents specify their level of agreement or disagreement on a symmetric agree-disa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
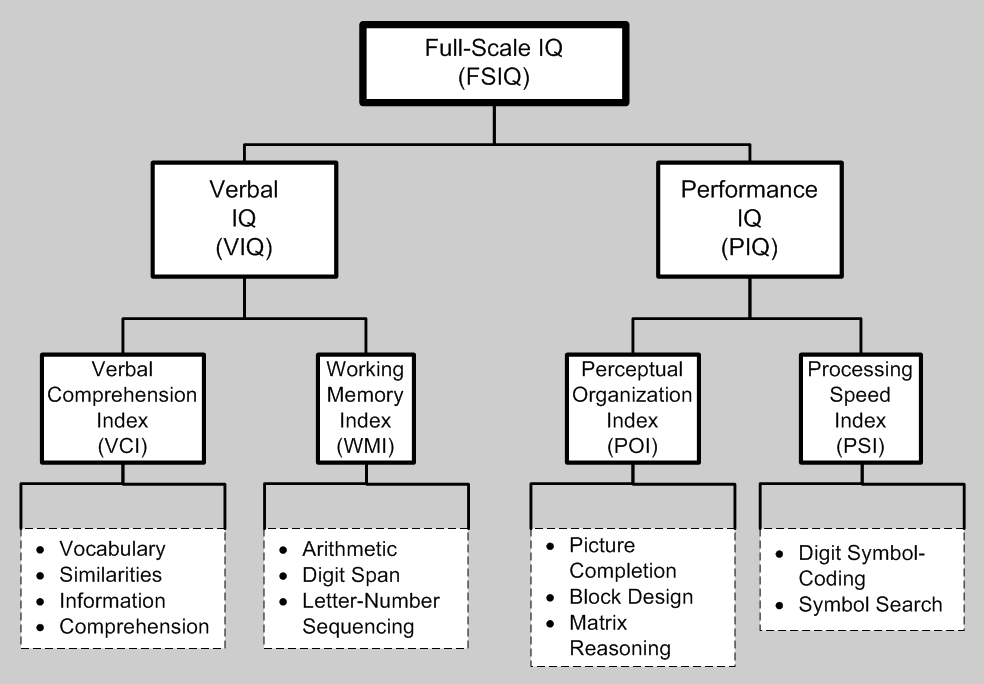
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is an IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability in adults and older adolescents. For children between the ages of 6 and 16, Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) is commonly used. The original WAIS (Form I) was published in February 1955 by David Wechsler, Chief Psychologist at Bellevue Hospital (1932–1967) in NYC, as a revision of the Wechsler–Bellevue Intelligence Scale released in 1939. It is currently in its fifth edition (''WAIS-5''), released in 2024 by Pearson. It is the most widely used IQ test, for both adults and older adolescents, in the world. History The WAIS was founded to get to know Wechsler's patients at Bellevue Hospital and on his definition of intelligence, which he defined as "... the global capacity of a person to act purposefully, to think rationally, and to deal effectively with his environment." He believed that intelligence was made up of specific elements that could b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory
The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) is a standardized psychometric test of adult personality and psychopathology. A version for adolescents also exists, the MMPI-A, and was first published in 1992. Psychologists and other mental health professionals use various versions of the MMPI to help develop treatment plans, assist with differential diagnosis, help answer legal questions (forensic psychology), screen job candidates during the personnel selection process, or as part of a therapeutic assessment procedure. The original MMPI was developed by Starke R. Hathaway and J. C. McKinley, faculty of the University of Minnesota, and first published by the University of Minnesota Press in 1943. It was replaced by an updated version, the MMPI-2, in 1989 (Butcher, Dahlstrom, Graham, Tellegen, and Kaemmer). An alternative version of the test, the MMPI-2 Restructured Form ( MMPI-2-RF), published in 2008, retains some aspects of the traditional MMPI assessment strategy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
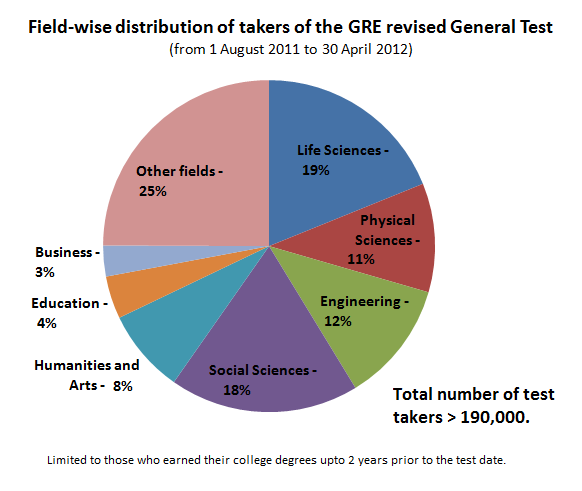
Graduate Record Examinations
The Graduate Record Examinations (GRE) is a standardized test that is part of the admissions process for many graduate schools in the United States and Canada and a few other countries. The GRE is owned and administered by Educational Testing Service (ETS). The test was established in 1936 by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. According to ETS, the GRE aims to measure verbal reasoning, quantitative reasoning, analytical writing, and critical thinking skills that have been acquired over a long period of learning. The content of the GRE consists of certain specific data analysis or interpretation, arguments and reasoning, algebra, geometry, arithmetic, and vocabulary sections. The GRE General Test is offered as a computer-based exam administered at testing centers and institution owned or authorized by Prometric. In the graduate school admissions process, the level of emphasis that is placed upon GRE scores varies widely among schools and departments. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Employment Testing
Employment testing is the practice of administering written, oral, or other tests as a means of determining the suitability or desirability of a job applicant. The premise is that if scores on a test correlate with job performance, then it is economically useful for the employer to select employees based on scores from that test. Legal context (United States) The United States Supreme Court has decided several cases clarifying the place of employment testing in the context of discrimination law. In particular, these cases have addressed the discriminatory use of tests when promoting employees by requiring tests beyond the education required for the job. A central finding in Griggs v. Duke Power Co. was that the employer must demonstrate (or be prepared to demonstrate) that its selection process is related to the job being filled. Test types Different types of assessments may be used for employment testing, including personality tests, intelligence tests, work samples, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology Articles Needing Expert Attention
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both conscious and unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feelings, and motives. Psychology is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the natural and social sciences. Biological psychologists seek an understanding of the emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as behavioral or cognitive scientists. Some psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in individual and social behavior. Others explore the physiological and neurobiological processes that underlie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |