|
Oak Ridge Seminary
The Oak Ridge Seminary (Oak Ridge Female Seminary, Oak-Ridge Academy) was an antebellum school for "young ladies" west of the borough of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. One of 2 girls schools used as an American Civil War hospital for Battle of Gettysburg casualties, the female seminary had also been used as a prison, and General Lee's "Headquarters and tents erepitched in the space adjoining Oak Ridge Seminary" (a field was "on the east side of Miss Carrie Sheads' School".) Background The first school in the area that would become Gettysburg was at the Mummasburg Road and Carlisle Street intersection on the south side of Stevens Run and by 1835, Gettysburg had five common schools. Earlier girls' schools in the Gettysburg borough included one for which Deacon James H. Marsden "took charge" after teacher applications were requested on June 23, 1829. Marsden held classes "from Sept. 25th, 1829, to April 1st, 1830, in the room, later occupied by the late Judge Wills' law office" (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eponym
An eponym is a noun after which or for which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. Adjectives derived from the word ''eponym'' include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''. Eponyms are commonly used for time periods, places, innovations, biological nomenclature, astronomical objects, works of art and media, and tribal names. Various orthographic conventions are used for eponyms. Usage of the word The term ''eponym'' functions in multiple related ways, all based on an explicit relationship between two named things. ''Eponym'' may refer to a person or, less commonly, a place or thing for which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. ''Eponym'' may also refer to someone or something named after, or believed to be named after, a person or, less commonly, a place or thing. A person, place, or thing named after a particular person share an eponymous relationship. In this way, Elizabeth I of England is the eponym of the Elizabethan era, but the Elizabethan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Simon Schmucker
Samuel Simon Schmucker (February 28, 1799 – July 26, 1873) was a German-American Lutheran pastor and theologian. He was integral to the founding of the Lutheran church body known as the General Synod, as well as the oldest continuously operating Lutheran seminary ( Gettysburg Seminary) and college in North America ( Gettysburg College). Later in his career, Schmucker became a controversial figure because of his theological positions, in particular his approach to the Lutheran Confessions. Outside of the church, Schmucker was a noted abolitionist. Early life Samuel Simon Schmucker was born in 1799 in Hagerstown, Maryland. His father, Johann Georg Schmucker, was a German immigrant and an ordained pastor in the Pennsylvania Ministerium. Samuel Schmucker showed a promising intellect at a young age, and entered the University of Pennsylvania at age 15. After teaching briefly at the York Academy, Schmucker went on a missionary journey to the western frontier of Kentucky and Ohio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google News
Google News is a news aggregator service developed by Google. It presents a continuous flow of links to articles organized from thousands of publishers and magazines. Google News is available as an app on Android, iOS, and the Web. Google released a beta version in September 2002 and the official app in January 2006. The initial idea was developed by Krishna Bharat. The service has been described as the world's largest news aggregator. In 2020, Google announced they would be spending billion to work with publishers to create Showcases, "a new format for insightful feature stories". History As of 2014, Google News was watching more than 50,000 news sources worldwide. Versions for more than 60 regions in 28 languages were available in March 2012. , service is offered in the following 38 languages: Afrikaans, Arabic, Bengali, Bulgarian, Catalan, Cantonese, Chinese, Czech, Dutch, English, French, German, Greek, Hebrew, Hindi, Hungarian, Italian, Indonesian, Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retreat From Gettysburg
The Confederate Army of Northern Virginia began its Retreat from Gettysburg on July 4, 1863. Following General Robert E. Lee's failure to defeat the Union Army at the Battle of Gettysburg (July 1–3, 1863), he ordered a retreat through Maryland and over the Potomac River to relative safety in Virginia. The Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by Maj. Gen. George G. Meade, was unable to maneuver quickly enough to launch a significant attack on the Confederates, who crossed the river on the night of July 13 into South Mountain through Cashtown in a wagon train that extended for 15–20 miles, enduring harsh weather, treacherous roads, and enemy cavalry raids. The bulk of Lee's infantry departed through Fairfield in Pennsylvania and through the Monterey Pass toward Hagerstown, Maryland. Reaching the Potomac River, they found that rising waters and destroyed pontoon bridges prevented their immediate crossing. Erecting substantial defensive works, they awaited the arri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
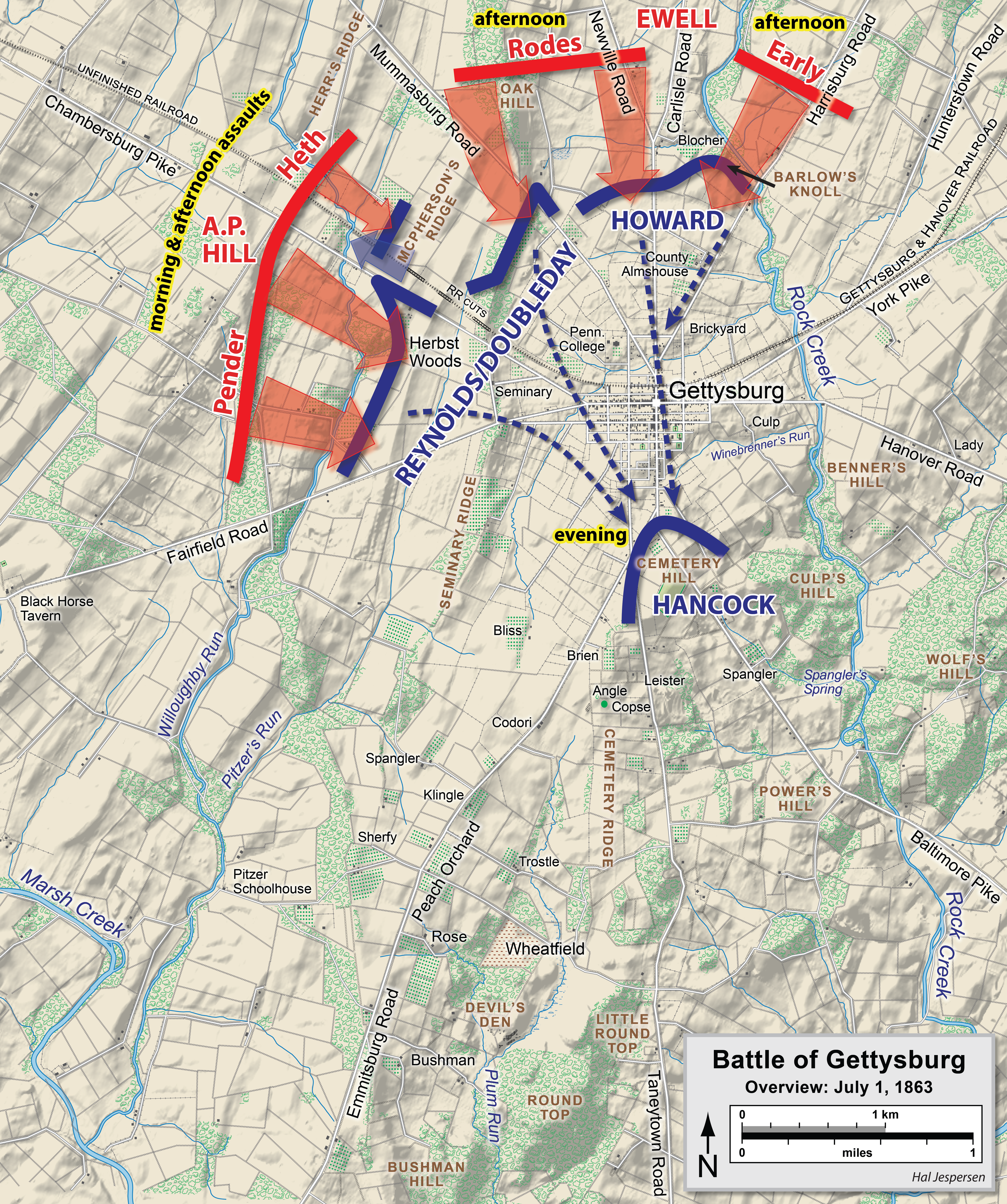
Battle Of Gettysburg, First Day
The first day of the Battle of Gettysburg during the American Civil War took place on July 1, 1863, and began as an engagement between isolated units of the Army of Northern Virginia under Confederate States Army, Confederate Full General (CSA), General Robert E. Lee and the Army of the Potomac under Union Army, Union Major general (United States), Maj. Gen. George G. Meade. It soon escalated into a major battle which culminated in the outnumbered and defeated Union forces retreating to the high ground south of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. The first-day battle proceeded in three phases as combatants continued to arrive at the battlefield. In the morning, two brigades of Confederate Maj. Gen. Henry Heth's division (of Lieutenant General (CSA), Lt. Gen. A.P. Hill's Third Corps, Army of Northern Virginia, Third Corps) were delayed by dismounted Union cavalrymen under Brigadier general (United States), Brig. Gen. John Buford. As infantry reinforcements arrived under Maj. Gen. John F. Rey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early's Raids In Pennsylvania
Early's raids in Pennsylvania were a series of June military actions before the 1863 Battle of Gettysburg in which the Confederate forces of Major General Jubal Early conducted raids and military engagements from Chambersburg through Gettysburg to York York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a Yor .... References {{Reflist Battles of the Gettysburg campaign Battles in Pennsylvania 1863 in Pennsylvania June 1863 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrie Sheads
Carrie Sheads was an American nurse and school principal. She was the principal of an all-girls boarding school near Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. In early July 1863, she wanted to take the girls on a field trip to visit the Union military camp A military camp or bivouac is a semi-permanent military base, for the lodging of an army. Camps are erected when a military force travels away from a major installation or fort during training or operations, and often have the form of large cam ...s. Before she got the chance, everyone at the school awoke one morning to the sound of gunfire. They couldn't get out of Gettysburg in time, so they used the school as a hospital to help wounded soldiers. Carrie Sheads and all the schoolgirls worked as nurses. During a confederate raid “ Colonel Charles Wheelock” ran into her estate and ending up hiding in her cellar. He was later found but Carrie Sheads hid his sword so it would not be stolen. References Female wartime nurses Women in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delaware-Maryland Synod
The Evangelical Lutheran Church in America consists of 65 synods which are configured into nine regional offices. Each of the synods of the ELCA elects one bishop A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ... and three synod council officers at its Synod Assembly to oversee the spiritual and organizational activities of its member congregations. Region 1 (Northwestern United States) Region 2 (Southwestern US and Wyoming) Region 3 (Minnesota and the Dakotas) Region 4 (Central United States) Region 5 (Illinois, Iowa, Wisconsin, Upper Peninsula) Region 6 (Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio, Lower Peninsula) Region 7 (New England, New Jersey, New York, Eastern PA) Region 8 (Delaware, Maryland, West Virginia, Western PA) Region 9 (Southeastern US, the Caribbean) Notes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of Divinity
A Doctor of Divinity (DD or DDiv; ) is the holder of an advanced academic degree in divinity (academic discipline), divinity (i.e., Christian theology and Christian ministry, ministry or other theologies. The term is more common in the English-speaking world than elsewhere. In the United Kingdom and Ireland, the DD is usually a higher doctorate conferred upon a religious scholar of standing and distinction, usually for accomplishments beyond the Doctor of Philosophy, PhD or Doctor of Theology, ThD level. In the United States, the DD is generally an honorary degree. In Catholic higher education, Catholic universities, faculties of Catholic theology, theology usually grant the degree of Doctor of Sacred Theology (STD), but the DD may be awarded as an honorary degree. Doctor of Divinity by country or church Great Britain & Ireland In the United Kingdom and Ireland, the DD is a higher doctorate conferred by universities upon a religious scholar of standing and distinction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapeworm Railroad
The Tapeworm Railroad (Gettysburg Rail Road) was a railway line planned by Congressman Thaddeus Stevens and nicknamed by opponents ridiculing a lengthy serpentine section around the Green Ridge of South Mountain after an orator compared the path to a tapeworm depiction on a product's packaging. Switchbacks were planned on the west slope at Hughs Forge along the E Br Antietam Creek ("Cold Spring Cr" in 1839) and on the east slope at Stevens' 1822 Maria Furnace along Toms Creek (Monocacy River), with three east slope tunnels through spurs of Jacks Mountain. In 1836, Herman Haupt had surveyed the "road from Gettysburg across South Mountain to the Potomac" and in 1838, the rail "bed" was "graded for a number of miles, never got further than Monterey", and included the following (west-to-east): * single-arch ''roadway'' bridge over Toms Creek west of Iron Springs, Pennsylvania * multi-arch bridge * viaduct at Virginia Mills * deep cut near Marsh Creek * elevated railbed on b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
References
A reference is a relationship between Object (philosophy), objects in which one object designates, or acts as a means by which to connect to or link to, another object. The first object in this relation is said to ''refer to'' the second object. It is called a ''name'' for the second object. The next object, the one to which the first object refers, is called the ''referent'' of the first object. A name is usually a phrase or expression, or some other Symbol, symbolic representation. Its referent may be anything – a material object, a person, an event, an activity, or an abstract concept. References can take on many forms, including: a thought, a sensory perception that is Hearing (sense), audible (onomatopoeia), visual perception, visual (text), olfaction, olfactory, or tactile, emotions, emotional state, relationship with other, spacetime coordinates, symbolic system, symbolic or alpha-numeric grid, alpha-numeric, a physical object, or an energy projection. In some cases, meth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gettysburg College
Gettysburg College is a Private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Founded in 1832, the campus is adjacent to the Gettysburg Battlefield. Gettysburg College has about 2,600 students, with roughly equal numbers of men and women. Gettysburg students come from 41 states, Washington, D.C., and 39 countries. The school hosts 24 NCAA Division III men's and women's teams, known as the Bullets, and many club, intramural, and recreational sports programs. History Founding and early roots Gettysburg College was founded in 1832 as a sister institution for the Lutheran Theological Seminary at Gettysburg, Lutheran Theological Seminary; the latter is now a campus of the United Lutheran Seminary. Both owe their inception to Thaddeus Stevens, a Radical Republicans, Radical Republican and Abolitionism in the United States, abolitionist from Gettysburg. The college's original name was Pennsylvania College; it was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |