|
Nuzi Ware
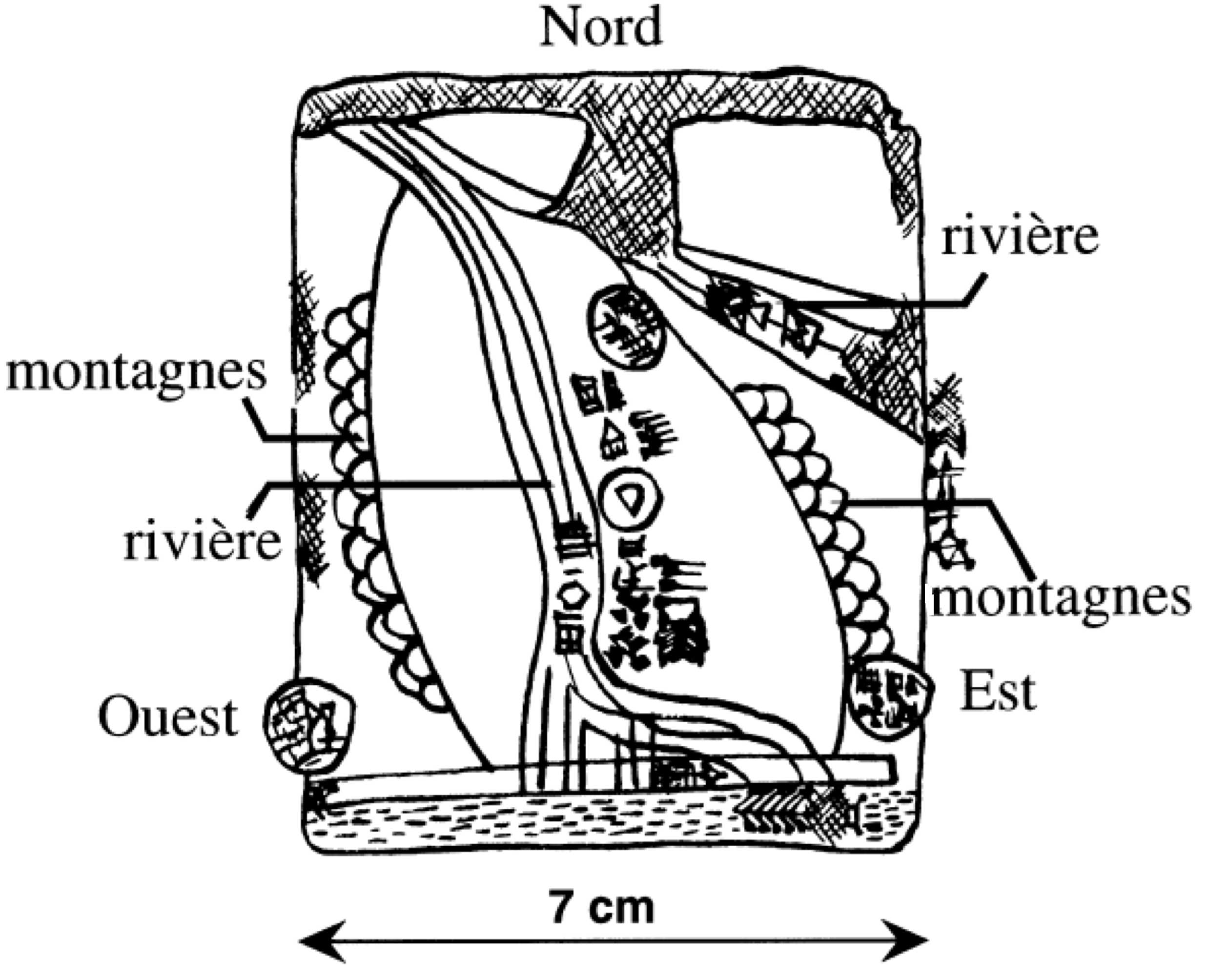
Nuzi ware is the type of a ceramic ware which is especially associated with the Mitanni empire (15th to early 13th century BC). It was first identified at Nuzi, modern Iraq. This is a painted prestige pottery that is mostly found in a socially upscale context. Distribution Nuzi ware is typically found from the Orontes River valley in the west, to as far as Babylon in the east. In the south, specimens were also found in Qatna, a city that lies outside the sphere of influence of the Mitanni empire, which indicates that the Nuzi ceramics was also used as trade goods. Bronze Age pottery in the Middle East is mostly undecorated. The elegantly decorated Nuzi ware, with its delicate vessel shapes thus quickly aroused particular interest among researchers. Development Much older Khabur ware, which is mostly undecorated, or has simple geometrical decorations, precedes Nuzi ware in this general area, and it influenced Nuzi to some extent. The fourth and last phase of Khabur ware (arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuzi Ware Tell Djigan N 3166
Nuzi (Hurrian Nuzi/Nuzu; Akkadian Gasur) at modern Yorghan Tepe (also Yorgan Tepa and Jorgan Tepe), Iraq was an ancient Mesopotamian city 12 kilometers southwest of the city of Arrapha (modern Kirkuk) and 70 kilometers southwest of Sātu Qala, located near the Tigris river. It was occupied from the Ubaid period in the 5th millennium BC until late in the 2nd millennium BC then, after a period of abandonment, in the Parthian era. It reached major importance in the Akkadian Empire period when it was known as Gasur and again in the Mitanni period when its name was Nuzi. History The site has about 15 occupational layers with 12 major strata several of which have subdivisions. The majority of excavation work at the site was on the Late Bronze Age levels with only some soundings to the older strata. Traces of Parthian era occupation were found on the surface.Pfeiffer, Robert H., "The Excavations at Nuzi: Preliminary Report of the Fourth Campaign", Bulletin of the American Schools of O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitanni
Mitanni (–1260 BC), earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, ; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat in Assyrian records, or in Ancient Egypt, Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian language, Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria (region), Syria and southeast Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) with Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan Indo-Aryan superstrate in Mitanni, linguistic and political influences. Since no histories, royal annals or chronicles have yet been found in its excavated sites, knowledge about Mitanni is sparse compared to the other powers in the area, and dependent on what its neighbours commented in their texts. The Hurrians were in the region as of the late 3rd millennium BC. A king of Urkesh with a Hurrian name, Tupkish, was found on a clay sealing dated at Tell Mozan.Salvini, Mirjo. "The earliest evidences of the Hurrians before the formation of the reign of Mittanni." Urkesh and the Hurrians Studies in Honor of Lloyd Cotsen. Urkesh/Mozan Studies Bibliotheca Mesopotamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuzi
Nuzi (Hurrian Nuzi/Nuzu; Akkadian Gasur) at modern Yorghan Tepe (also Yorgan Tepa and Jorgan Tepe), Iraq was an ancient Mesopotamian city 12 kilometers southwest of the city of Arrapha (modern Kirkuk) and 70 kilometers southwest of Sātu Qala, located near the Tigris river. It was occupied from the Ubaid period in the 5th millennium BC until late in the 2nd millennium BC then, after a period of abandonment, in the Parthian era. It reached major importance in the Akkadian Empire period when it was known as Gasur and again in the Mitanni period when its name was Nuzi. History The site has about 15 occupational layers with 12 major strata several of which have subdivisions. The majority of excavation work at the site was on the Late Bronze Age levels with only some soundings to the older strata. Traces of Parthian era occupation were found on the surface.Pfeiffer, Robert H., "The Excavations at Nuzi: Preliminary Report of the Fourth Campaign", Bulletin of the American Schools of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the Iraq–Kuwait border, southeast, Jordan to Iraq–Jordan border, the southwest, and Syria to Iraq–Syria border, the west. The country covers an area of and has Demographics of Iraq, a population of over 46 million, making it the List of countries by area, 58th largest country by area and the List of countries by population, 31st most populous in the world. Baghdad, home to over 8 million people, is the capital city and the List of largest cities of Iraq, largest in the country. Starting in the 6th millennium BC, the fertile plains between Iraq's Tigris and Euphrates rivers, referred to as Mesopotamia, fostered the rise of early cities, civilisations, and empires including Sumer, Akkadian Empire, Akkad, and Assyria. Known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orontes River
The Orontes (; from Ancient Greek , ) or Nahr al-ʿĀṣī, or simply Asi (, ; ) is a long river in Western Asia that begins in Lebanon, flowing northwards through Syria before entering the Mediterranean Sea near Samandağ in Hatay Province, Turkey. As the chief river of the northern Levant, the Orontes has been the site of many major battles including the Battle of Kadesh (13th century BCE), and water distribution remains a controversial issue between the countries in the region. Among the most important cities on the river are Homs, Hama, Jisr al-Shughur, and Antakya (the ancient Antioch, which was also known as "Antioch on the Orontes"). Names In the 9th century BCE, the ancient Assyrian people, Assyrians referred to the river as Arantu, and the nearby Egyptians called it Araunti. The etymology of the name is unknown, yet some sources indicate that it might be derived from ''Arnt'' which means "lioness" in Syriac languages; others called it ''Alimas'', a "water goddess" in Ara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-speaking region of Babylonia. Its rulers established two important empires in antiquity, the 19th–16th century BC Old Babylonian Empire, and the 7th–6th century BC Neo-Babylonian Empire. Babylon was also used as a regional capital of other empires, such as the Achaemenid Empire. Babylon was one of the most important urban centres of the ancient Near East, until its decline during the Hellenistic period. Nearby ancient sites are Kish, Borsippa, Dilbat, and Kutha. The earliest known mention of Babylon as a small town appears on a clay tablet from the reign of Shar-Kali-Sharri (2217–2193 BC), of the Akkadian Empire. Babylon was merely a religious and cultural centre at this point and neither an independent state nor a large city, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qatna
Qatna (modern: , Tell al-Mishrifeh; also Tell Misrife or Tell Mishrifeh) was an ancient city located in Homs Governorate, Syria. Its remains constitute a tell situated about northeast of Homs near the village of al-Mishrifeh. The city was an important center through most of the second millennium BC and in the first half of the first millennium BC. It contained one of the largest royal palaces of Bronze Age Syria and an intact royal tomb that has provided a great amount of archaeological evidence on the funerary habits of that period. First inhabited for a short period in the second half of the fourth millennium BC, it was repopulated around 2800 BC and continued to grow. By 2000 BC, it became the capital of a regional kingdom that spread its authority over large swaths of the central and southern Levant. The kingdom enjoyed good relations with Mari, but was engaged in constant warfare against Yamhad. By the 15th century BC, Qatna lost its hegemony and came under the authorit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khabur Ware
Khabur ware is a specific type of pottery named after the Khabur River region, in northeastern Syria, where large quantities of it were found by the archaeologist Max Mallowan at the site of Chagar Bazar. The pottery's distribution is not confined to the Khabur region, but spreads across northern Iraq and is also found at a few sites in Turkey and Iran. Archaeologists associate the pottery with the cuneiform texts dated to the reign of Shamshi-Adad I, although it is not clear how much earlier it was manufactured. Overview History Four main Khabur ware phases are established, 1–4. While the starting date for phase 1 is inconclusive, a tentative date of ca. 1900 BC is suggested based on evidence from Tell Brak. The beginning of the second, and the main, phase of Khabur ware is dated to the reign of Shamshi-Adad I (ca. 1813 BC), based on evidence from Chagar Bazar, Tell al-Rimah, Tell Taya and Tell Leilan. The third phase of Khabur ware is dated to ca. 1750, and lasts until ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Brak
Tell Brak (Nagar, Nawar) was an ancient city in Syria; it is one the earliest known cities in the world. Its remains constitute a tell located in the Upper Khabur region, near the modern village of Tell Brak, 50 kilometers north-east of Al-Hasaka city, Al-Hasakah Governorate. The city's original name is unknown. During the second half of the third millennium BC, the city was known as Nagar and later on, Nawar. Starting as a small settlement in the seventh millennium BC, Tell Brak's urbanization began in the late 5th millennium BCE and evolved during the fourth millennium BC into one of the biggest cities in Upper Mesopotamia, and interacted with the cultures of southern Mesopotamia. The city shrank in size at the beginning of the third millennium BC with the end of Uruk period, before expanding again around c. 2600 BC, when it became known as Nagar, and was the capital of a regional kingdom that controlled the Khabur river valley. Nagar was destroyed around c. 2300 BC, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alalakh
Alalakh (''Tell Atchana''; Hittite: Alalaḫ) is an ancient archaeological site approximately northeast of Antakya (historic Antioch) in what is now Turkey's Hatay Province. It flourished as an urban settlement in the Middle and Late Bronze Age, c. 2000–1200 BC. The city contained palaces, temples, private houses and fortifications. The remains of Alalakh have formed an extensive mound covering around 22 hectares. In the Late Bronze Age, Alalakh was the capital of the local kingdom of Mukiš. The first palace was built around 2000 BC, and likely destroyed in the 12th century BC. The site was thought to have never been reoccupied after that, but archaeologist Timothy Harrison showed, in a (2022) lecture's graphic, it was inhabited also in Amuq Phases N-O, Iron Age, c. 1200–600 BC.Harrison, Timothy, Lynn Welton, and Stanley Klassen, (13 July 2022)"Highway to Science: The Tayinat and CRANE Projects" ARWA Association, Lecture min. 6:58, n the graphic "Iron Age, Ca. 1200-600 BCE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Mallowan
Sir Max Edgar Lucien Mallowan, (6 May 1904 – 19 August 1978) was a prominent British archaeologist and academic, specializing in the Ancient Near East. Having studied classics at Oxford University, he was trained for archaeology by Leonard Woolley at Ur and Reginald Campbell Thompson at Nineveh. He then directed a number of archaeological expeditions sponsored by the British Museum and the British School of Archaeology in Iraq. He was the second husband of Agatha Christie, having met her during the excavation at Ur in 1930. He served in the Royal Air Force Volunteer Reserve during the Second World War, and then entered academia. He was Professor of Western Asiatic Archaeology at the University of London (1947–1962) and a fellow of All Souls College, Oxford (1962–1971). Early life and education Born Edgar Mallowan on 6 May 1904 in Wandsworth, London, England, to Frederick Mallowan, a businessman who had served with the Austrian horse artillery, and his wife Marguerite ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |