|
Nuclear Safety And Security
Nuclear safety is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The achievement of proper operating conditions, prevention of accidents or mitigation of accident consequences, resulting in protection of workers, the public and the environment from undue radiation hazards". The IAEA defines nuclear security as "The prevention and detection of and response to, theft, sabotage, unauthorized access, illegal transfer or other malicious acts involving nuclear materials, other radioactive substances or their associated facilities". This covers nuclear power plants and all other nuclear facilities, the transportation of nuclear materials, and the use and storage of nuclear materials for medical, power, industry, and military uses. The nuclear power industry has improved the safety and performance of reactors, and has proposed new and safer reactor designs. However, a perfect safety cannot be guaranteed. Potential sources of problems include human errors and external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TMI Cleanup-2
TMI may refer to: Organizations * TMI Associates, a Japanese law firm * TMI Episcopal, formerly Texas Military Institute, a preparatory school affiliated with the Episcopal Church * Taiwan Music Institute, a musical institute in Taiwan * Teen Missions International, an interdenominational mission organization based in Florida * Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station, a nuclear power station in Pennsylvania, USA * Time Module (TMI), a member of the Seiko Group is a corporate group composed of Seiko, Seiko Group Corporation and its subsidiaries and affiliates. It used to be recognized as a corporate group consisting of three core companies Seiko, Seiko Holdings Corp. (Seiko; f/k/a K. Hattori & Co., Ha ..., manufacturer of watch movements * Toastmasters International, an international public speaking organization * Tolani Maritime Institute, a Merchant Navy training institute * The Monroe Institute, a nonprofit education and research organization * Thomas More Inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Power Weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). Yields in the low kilotons can devastate cities. A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than 1.2 megatons of TNT (5.0 PJ). Apart from the blast, effects of nuclear weapons include firestorms, extreme heat and ionizing radiation, radioactive nuclear fallout, an electromagnetic pulse, and a radar blackout. The first nuclear weapons were developed by the Allied Manhattan Project during World War II. Their production continues to require a large scientific and industrial complex, prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committed Dose
The committed dose in radiological protection is a measure of the stochastic health risk due to an intake of radioactive material into the human body. Stochastic in this context is defined as the ''probability'' of cancer induction and genetic damage, due to low levels of radiation. The SI unit of measure is the sievert. A committed dose from an internal source represents the same effective risk as the same amount of effective dose applied uniformly to the whole body from an external source, or the same amount of equivalent dose applied to part of the body. The committed dose is not intended as a measure for deterministic effects, such as radiation sickness, which are defined as the ''severity'' of a health effect which is certain to happen. The radiation risk proposed by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) predicts that an effective dose of one sievert carries a 5.5% chance of developing cancer. Such a risk is the sum of both internal and external ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fusion Experiments
Experiments directed toward developing fusion power are invariably done with dedicated machines which can be classified according to the principles they use to confine the plasma (physics), plasma fuel and keep it hot. The major division is between Magnetic confinement fusion, magnetic confinement and Inertial confinement fusion, inertial confinement. In magnetic confinement, the tendency of the hot plasma to expand is counteracted by the Lorentz force between currents in the plasma and magnetic fields produced by external coils. The particle densities tend to be in the range of to and the linear dimensions in the range of . The particle and energy confinement times may range from under a millisecond to over a second, but the configuration itself is often maintained through input of particles, energy, and current for times that are hundreds or thousands of times longer. Some concepts are capable of maintaining a plasma indefinitely. In contrast, with inertial confinement, ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermonuclear Weapon
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H-bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lower mass, or a combination of these benefits. Characteristics of nuclear fusion reactions make possible the use of non-fissile depleted uranium as the weapon's main fuel, thus allowing more efficient use of scarce fissile material. Its multi-stage design is distinct from the usage of fusion in simpler Boosted fission weapon, boosted fission weapons. The first full-scale thermonuclear test (Ivy Mike) was carried out by the United States in 1952, and the concept has since been employed by at least the five recognized List of states with nuclear weapons#Recognized nuclear-weapon states, nuclear-weapon states and United Nations Security Council, UNSC Permanent members of the United Nations Security Council, permanent members: the Nuclear weapons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
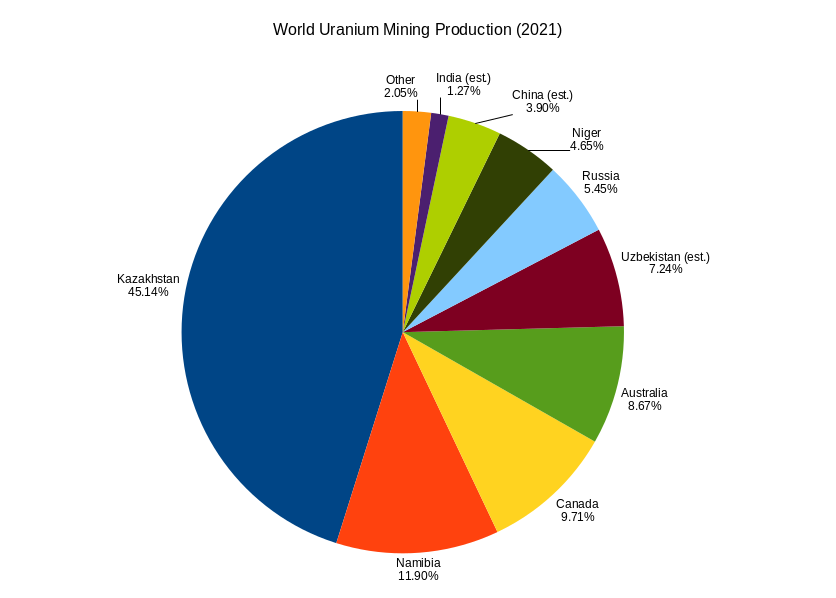
Uranium Mining
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the earth. Over 50,000 tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account for 68% of world production. Other countries producing more than 1,000 tons per year included Namibia, Niger, Russia, Uzbekistan and China. Nearly all of the world's mined uranium is used to power nuclear power plants. Historically uranium was also used in applications such as uranium glass or ferrouranium but those applications have declined due to the radioactivity and toxicity of uranium and are nowadays mostly supplied with a plentiful cheap supply of depleted uranium which is also used in Armour-piercing ammunition, uranium ammunition. In addition to being cheaper, depleted uranium is also less radioactive due to a lower content of short-lived and than natural uranium. Uranium is mined by in-situ leaching (57% of world production) or by convent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as earthworms and woodlice), or decomposer (such as fungi or bacteria). It is not the same as a food web. A food chain depicts relations between species based on what they consume for energy in trophic levels, and they are most commonly quantified in length: the number of links between a trophic consumer and the base of the chain. Food chain studies play an important role in many biological studies. Food chain stability is very important for the survival of most species. When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction or immense decreases of survival of a species. Many food chains and food webs contain a keystone species, a species that has a large impact on the surrounding environment and that can directly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to matter,"Biosphere" in ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 6th ed. (2004) Columbia University Press. with minimal inputs and outputs. Regarding , it is an open system, with capturing |
Nuclear Fusion Power
Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2025, no device has reached net power. Fusion processes require fuel, in a state of plasma, and a confined environment with sufficient temperature, pressure, and confinement time. The combination of these parameters that results in a power-producing system is known as the Lawson criterion. In stellar cores the most common fuel is the lightest isotope of hydrogen ( protium), and gravity provides the conditions needed for fusion energy production. Proposed fusion reactors would use the heavy hydrogen isotopes of deuterium and tritium for DT fusion, for which the Lawson criterion is the easiest to achieve. This produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. It is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, nuclear decommissioning, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapons reprocessing. The storage and disposal of radioactive waste is regulated by government agencies in order to protect human health and the environment. Radioactive waste is broadly classified into 3 categories: low-level waste (LLW), such as paper, rags, tools, clothing, which contain small amounts of mostly short-lived radioactivity; intermediate-level waste (ILW), which contains higher amounts of radioactivity and requires some shielding; and high-level waste (HLW), which is highly radioactive and hot due to decay heat, thus requiring cooling and shielding. Spent nuclear fuel can be processed in nuclear reprocessing plants. One third of the total amount have already been reprocessed. With nuclear reprocessing 96% of the spent fue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of Space Programs
A space program is an organized effort by a government or a company with a goal related to outer space. Lists of space programs include: * List of government space agencies * List of private spaceflight companies * List of human spaceflight programs A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ... * List of space programs of the United States * List of uncrewed spacecraft by program {{DEFAULTSORT:Space programs Space programs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered ''radioactive''. Three of the most common types of decay are Alpha decay, alpha, Beta decay, beta, and Gamma ray, gamma decay. The weak force is the Fundamental interactions, mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetic force, electromagnetic and nuclear forces. Radioactive decay is a randomness, random process at the level of single atoms. According to quantum mechanics, quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the atom has existed. However, for a significant number of identical atoms, the overall decay rate can be expressed as a decay constant or as a half-life. The half-lives of radioactive atoms have a huge range: f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |