|
November 1947 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s Lunar node, ascending node of orbit on Friday, November 28, 1947, with an umbral Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of −0.1297. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when part or all of the Moon's near side passes into the Earth's penumbra. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. Occurring about 2.4 days before Apsis, perigee (on November 30, 1947, at 17:45 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. Visibility The eclipse was completely visible over northeast Asia, North America, and northwestern South America, seen rising over much of South America, west Africa, and western Europe and setting over east Asia and Australia. Eclipse details Shown below is a table displaying details about this particular sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Eclipse
A lunar eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to Ecliptic, the plane of the Earth's orbit. This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are exactly or very closely aligned (in syzygy (astronomy), syzygy) with Earth between the other two, which can happen only on the night of a full moon when the Moon is near either lunar node. The type and length of a lunar eclipse depend on the Moon's proximity to the lunar node. When the Moon is totally eclipsed by the Earth (a "deep eclipse"), "What is a deep eclipse? The smaller star is behind the bigger star" it takes on a reddish color that is caused by the planet when it completely blocks direct sunlight from reaching the Moon's surface, as the only light that is diffuse reflection, reflected from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclipse Season
An eclipse season is a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Eclipse seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of the Orbit of the Moon, Moon's orbital plane (orbital inclination, tilted five degrees to the ecliptic, Earth's orbital plane), just as Earth's Season, weather seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's axial tilt, tilted axis as it orbits around the Sun. During the season, the "lunar nodes" – the line where the Moon's orbital plane intersects with the ecliptic, Earth's orbital plane – align with the Sun and Earth, such that a solar eclipse is formed during the new moon phase and a lunar eclipse is formed during the full moon phase. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur during each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later, thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. During the eclipse seaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of December 2, 1956
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Sunday, December 2, 1956, with a magnitude of 0.8047. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. A partial eclipse was visible for parts of Europe, Northeast Africa, and Asia. Eclipse details Shown below are two tables displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. The first table outlines times at which the moon's penumbra or umbra attains the specific parameter, and the second table describes various other parameters pertaining to this eclipse. Eclipse season This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
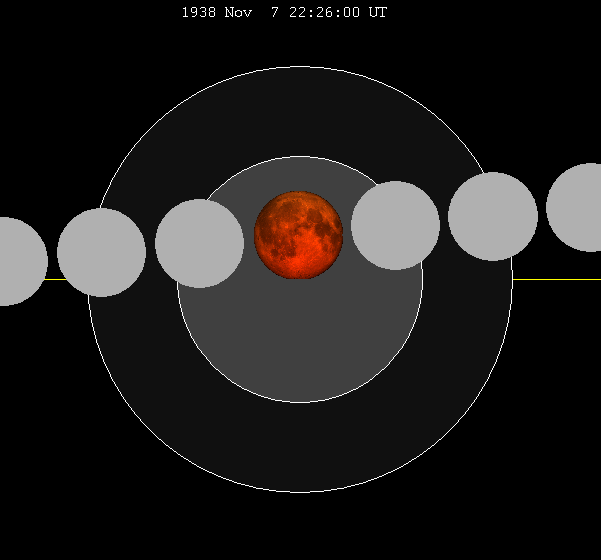
Solar Eclipse Of November 21, 1938
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Monday, November 21 and Tuesday, November 22, 1938, with a magnitude of 0.7781. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. A partial eclipse was visible for parts of Northeast Asia, Hawaii, and western North America. Eclipse details Shown below are two tables displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. The first table outlines times at which the moon's penumbra or umbra attains the specific parameter, and the second table describes various other parameters pertaining to this eclipse. Eclipse season This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
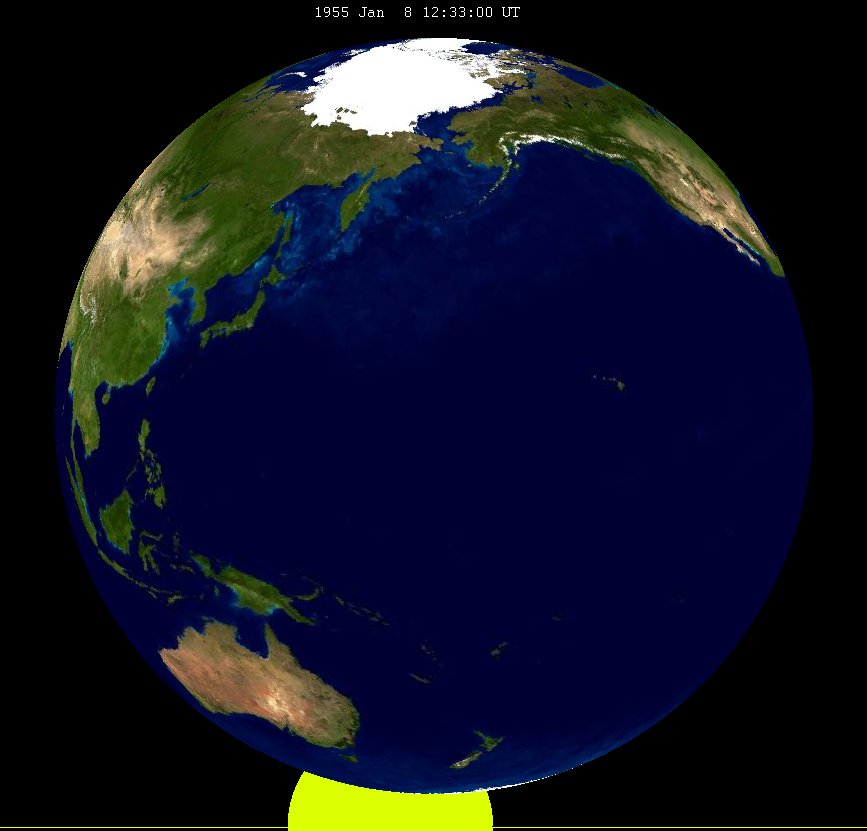
January 1955 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s Lunar node, descending node of orbit on Saturday, January 8, 1955, with an umbral Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of −0.1421. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when part or all of the Moon's near side passes into the Earth's penumbra. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. Occurring about 2.2 days after Apsis, perigee (on January 6, 1955, at 8:55 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. Visibility The eclipse was completely visible over east Asia, east and north Asia, Australia, and northwestern North America, seen rising over much of the western half of Asia and northern Europe and setting over eastern North America and northwestern South America. Eclipse details Shown below is a table displayin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
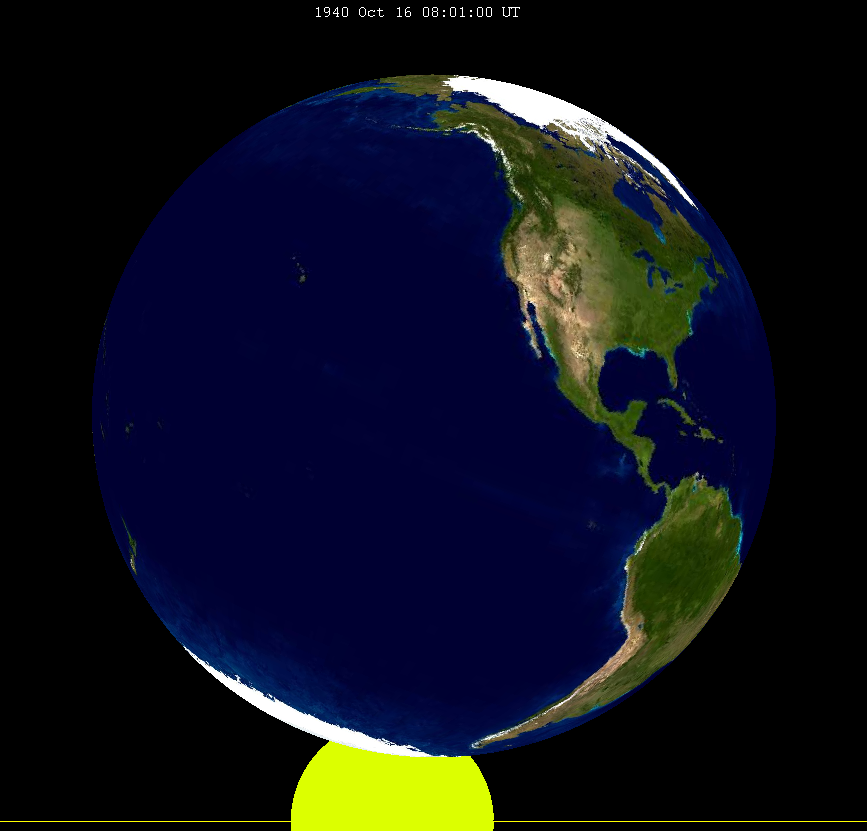
October 1940 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s Lunar node, descending node of orbit on Wednesday, October 16, 1940, with an umbral Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of −0.3749. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when part or all of the Moon's near side passes into the Earth's penumbra. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. Occurring only about 21 hours after Apsis, apogee (on October 15, 1940, at 11:00 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. Visibility The eclipse was completely visible over North America and western South America, seen rising over East Asia and Australia and setting over eastern South America, West Africa, and Western Europe. Eclipse details Shown below is a table displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. It de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
September 1951 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s Lunar node, ascending node of orbit on Saturday, September 15, 1951, with an umbral Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of −0.1927. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when part or all of the Moon's near side passes into the Earth's penumbra. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. Occurring about 3.6 days after Apsis, perigee (on September 11, 1951, at 21:30 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. This eclipse was the last of four penumbral lunar eclipses in 1951, with the others occurring on February 1951 lunar eclipse, February 21, March 1951 lunar eclipse, March 23, and August 1951 lunar eclipse, August 17. Visibility The eclipse was completely visible over east Asia, east and northeast Asia, Australia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
February 1944 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon's Lunar node, ascending node of orbit on Wednesday, February 9, 1944, with an umbral Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of −0.5223. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when part or all of the Moon's near side passes into the Earth's penumbra. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. Occurring about 1.1 days before Apsis, apogee (on February 10, 1944, at 7:45 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. This eclipse was the first of four penumbral lunar eclipses in 1944, with the others occurring on July 1944 lunar eclipse, July 6, August 1944 lunar eclipse, August 4, and December 1944 lunar eclipse, December 29. Visibility The eclipse was completely visible over North America, North and South America, west Africa, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
June 1947 Lunar Eclipse
A partial lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s descending node of orbit on Tuesday, June 3, 1947, with an umbral magnitude of 0.0202. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A partial lunar eclipse occurs when one part of the Moon is in the Earth's umbra, while the other part is in the Earth's penumbra. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. Occurring about 3.2 days before apogee (on June 6, 1947, at 23:00 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. Visibility The eclipse was completely visible over east and southern Africa, west, central, and south Asia, western Australia, and Antarctica, seen rising over Europe, west Africa, and eastern South America and setting over east Asia and eastern Australia. Eclipse details Shown below is a table displaying details about this particular lunar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of May 20, 1947
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Tuesday, May 20, 1947, with a magnitude of 1.0557. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.8 days before perigee (on May 22, 1947, at 9:10 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. Totality was visible from Chile including the capital city Santiago, Argentina, Paraguay, Brazil, Liberia, French West Africa (the parts now belonging to Ivory Coast and Benin), British Gold Coast (today's Ghana) including capital Accra, French Togoland (today's Togo) including capital Lomé, British Nigeria ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Eclipse
A lunar eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to Ecliptic, the plane of the Earth's orbit. This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are exactly or very closely aligned (in syzygy (astronomy), syzygy) with Earth between the other two, which can happen only on the night of a full moon when the Moon is near either lunar node. The type and length of a lunar eclipse depend on the Moon's proximity to the lunar node. When the Moon is totally eclipsed by the Earth (a "deep eclipse"), "What is a deep eclipse? The smaller star is behind the bigger star" it takes on a reddish color that is caused by the planet when it completely blocks direct sunlight from reaching the Moon's surface, as the only light that is diffuse reflection, reflected from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three celestial objects is known as a ''syzygy''. An eclipse is the result of either an '' occultation'' (completely hidden) or a ''transit'' (partially hidden). A "deep eclipse" (or "deep occultation") is when a small astronomical object is behind a bigger one. "What is a deep eclipse? The smaller star is behind the bigger star" The term ''eclipse'' is most often used to describe either a solar eclipse, when the Moon's shadow crosses the Earth's surface, or a lunar eclipse, when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. However, it can also refer to such events beyond the Earth–Moon system: for example, a planet moving into the shadow cast by one of its moons, a moon passing into the shadow cast by its host planet, or a moon passing into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |