|
Notoliparis Kermadecensis
''Notoliparis kermadecensis'' (from Greek: ''noton'', back, and ''liparos'', fat) is a species of snailfish (Liparidae) that lives in the deep sea. Endemic to the Kermadec Trench in the Southwest Pacific, it is hadobenthic with a depth range between , and can reach a standard length of up to . It is among the deepest living fish; in the Southern Hemisphere only ''Echiodon neotes'' has been recorded deeper, at . A few species from the Northern Hemisphere have been recorded at similar or deeper depths than ''N. kermadecensis'', including the snailfish ''Pseudoliparis amblystomopsis'' from the Kuril–Kamchatka and Japan Trenches. These two species apparently share a common ancestor and occupy similar hadal depth ranges, yet they can only survive at immense pressure and are geographically isolated, and their evolutionary history remains enigmatic. There are indications that the larvae A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jørgen G
Jørgen is a Danish, Norwegian, and Faroese masculine given name cognate to George People with the given name Jørgen * Jørgen Aall (1771–1833), Norwegian ship-owner and politician * Jørgen Andersen (1886–1973), Norwegian gymnast * Jørgen Aukland (born 1975), Norwegian cross-country skier * Jørgen Beck (1914–1991), Danish film actor * Jørgen Bentzon (1897–1951), Danish composer * Jørgen Bjelke (1621–1696), Norwegian officer and nobleman * Jørgen Bjørnstad (1894–1942), Norwegian gymnast * Jørgen Bojsen-Møller (born 1954), Danish sailor and Olympic Champion * Jørgen Thygesen Brahe (1515–1565), Danish nobleman * Jørgen Brønlund (1877–1907), Greenlandic polar explorer, educator, and catechist * Jørgen Bru (1881–1974) was a Norwegian sport shooter * Jørgen Brunchorst (1862–1917), Norwegian natural scientist, politician and diplomat * Jørgen Buckhøj (1935–1994), Danish actor * Jørgen Wright Cappelen (1805–1878), Norwegian bookseller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snailfish
The snailfishes or sea snails (not to be confused with invertebrate sea snails), are a family of marine ray-finned fishes. These fishes make up the Liparidae, a family classified within the order Scorpaeniformes. Widely distributed from the Arctic to Antarctic Oceans, including the oceans in between, the snailfish family contains more than 30 genera and about 410 described species, but there are also many undescribed species. Snailfish are found at depths ranging from shallow coastal waters to more than , including in seven ocean trenches. Taxonomy The snailfish family, Liparidae, was first proposed by the American biologist Theodore Gill in 1861. The 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World'' classifies this family within superfamily Cyclopteroidea, part of the suborder Cottoidei of the order Scorpaeniformes. Other authorities do not recognise this superfamily and classify the two families within it, Cyclopteridae and Liparidae, within the infraorder Cottales alongside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
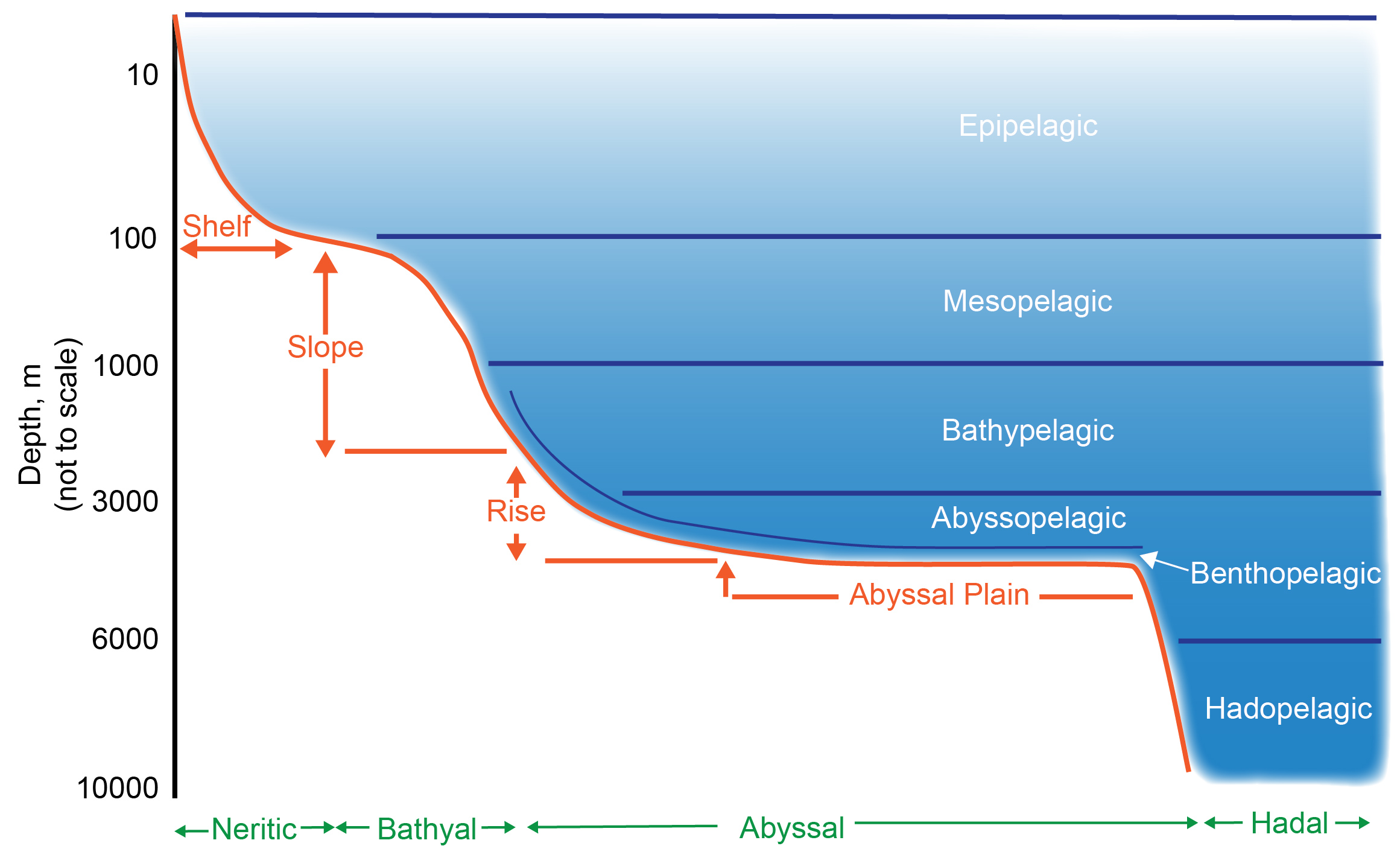
Deep Sea
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combination of low temperatures, darkness, and high pressure. The deep sea is considered the least explored Earth biome as the extreme conditions make the environment difficult to access and explore. Organisms living within the deep sea have a variety of adaptations to survive in these conditions. Organisms can survive in the deep sea through a number of feeding methods including scavenging, predation and filtration, with a number of organisms surviving by feeding on marine snow. Marine snow is organic material that has fallen from upper waters into the deep sea. In 1960, the bathyscaphe ''Trieste'' descended to the bottom of the Mariana Trench near Guam, at , the deepest known spot in any ocean. If Mount Everest () were submerged there, its peak would be more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kermadec Trench
The Kermadec Trench is a linear ocean trench in the south Pacific Ocean. It stretches about from the Louisville Seamount Chain in the north (26°S) to the Hikurangi Plateau in the south (37°S), north-east of New Zealand's North Island. Together with the Tonga Trench to the north, it forms the -long, near-linear Kermadec-Tonga subduction system, which began to evolve in the Eocene when the Pacific plate started to subduct beneath the Australian plate. Convergence rates along this subduction system are among the fastest on Earth, /yr in the north and /yr in the south. Geology The Kermadec Trench is one of Earth's deepest oceanic trenches, reaching a depth of . Formed by the subduction of the Pacific plate under the Indo-Australian plate, it runs parallel with and to the east of the Kermadec Ridge and island arc. The Tonga Trench marks the continuation of subduction to the north. The Kermadec Trench has a southern continuation in the turbidite-filled Hikurangi Trough, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadobenthic
The hadal zone, also known as the hadopelagic zone, is the deepest region of the ocean, lying within oceanic trenches. The hadal zone ranges from around below sea level, and exists in long, narrow, topographic V-shaped depressions. The cumulative area occupied by the 46 individual hadal habitats worldwide is less than 0.25% of the world's seafloor, yet trenches account for over 40% of the ocean's depth range. Most hadal habitat is found in the Pacific Ocean, the deepest of the conventional oceanic divisions. Terminology and definition Historically, the hadal zone was not recognized as distinct from the abyssal zone, although the deepest sections were sometimes called "ultra-abyssal". During the early 1950s, the Danish '' Galathea II'' and Soviet '' Vityaz'' expeditions separately discovered a distinct shift in the life at depths of not recognized by the broad definition of the abyssal zone. The term "hadal" was first proposed in 1956 by Anton Frederik Bruun to describe the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
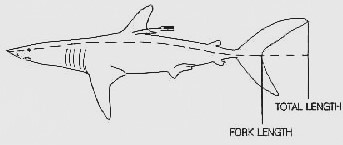
Standard Length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of fish anatomy, their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the Glossary of ichthyology#H, hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal fin, caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most Actinopterygii, bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes (lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echiodon Neotes
''Echiodon neotes'' is a fish species described by Markle and Olney, 1990. ''Echiodon neotes'' is part of the genus '' Echiodon'' and the subfamily Carapinae. References Nielsen, J.G., D.M. Cohen, D.F. Markle and C.R. Robins (1999) FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 18. Ophidiiform fishes of the world (Order Ophidiiformes). An annotated and illustrated catalogue of pearlfishes, cusk-eels, brotulas and other ophidiiform fishes known to date., FAO Fish. Synop. 125(18):178p. Rome: FAO. ''FishBase''. Froese R. & Pauly D. (eds), 2011-06-14 Carapidae {{ophidiiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
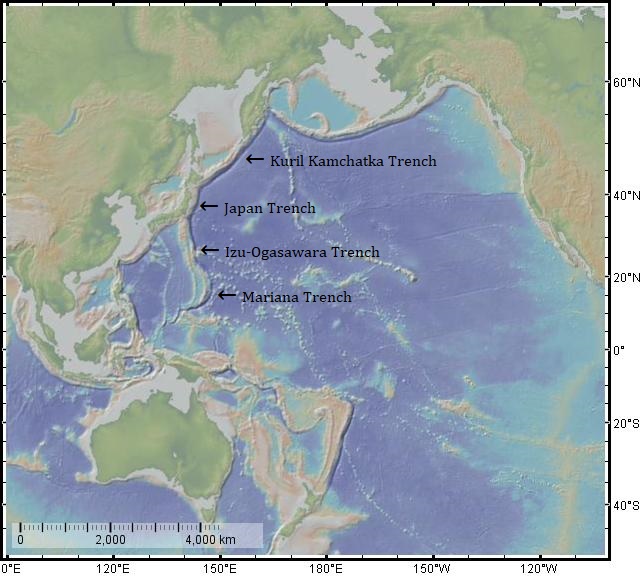
Pseudoliparis Amblystomopsis
''Pseudoliparis amblystomopsis'', or the hadal snailfish, is a species of snailfish from the hadal zone of the Northwest Pacific Ocean, including the Kuril–Kamchatka and Japan Trenches. In October 2008, a team from British and Japanese institutes discovered a shoal of ''Pseudoliparis amblystomopsis'' at a depth of about in the Japan Trench. These were, at the time, the deepest living fish A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ... ever recorded on film. The record was surpassed by a type of snailfish filmed at a depth of in December 2014, and extended in May 2017 when another snailfish was filmed at a depth of . This deepest-water so-called ethereal snailfish remains undescribed, but a close relative found only slightly shallower in the Mariana Trench was described a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuril–Kamchatka Trench
The Kuril–Kamchatka Trench or Kuril Trench (, ''Kurilo-Kamchatskii Zhyolob'') is an oceanic trench in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It lies off the southeast coast of Kamchatka and parallels the Kuril Island chain to meet the Japan Trench east of Hokkaido. It extends from a triple junction with the Ulakhan Fault and the Aleutian Trench near the Commander Islands, Russia, in the northeast, to the intersection with the Japan Trench in the southwest. The trench formed as a result of the subduction zone, which formed in the late Cretaceous, that created the Kuril island arc as well as the Kamchatka volcanic arc. The Pacific plate is being subducted beneath the Okhotsk plate along the trench, resulting in intense volcanism. The maximum depth of the trench is reported in peer-reviewed academic papers as 9,600 meters. Tectonics At the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench, the Pacific plate is subducting beneath the Okhotsk plate, a minor tectonic plate formerly considered to be part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Trench
The Japan Trench is an oceanic trench part of the Pacific Ring of Fire off northeast Japan. It extends from the Kuril Islands to the northern end of the Izu Islands, and is at its deepest. It links the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench to the north and the Izu–Ogasawara Trench to its south with a length of . This trench is created as the oceanic Pacific plate subducts beneath the continental Okhotsk microplate (a microplate formerly a part of the North American plate). The subduction process causes bending of the down going plate, creating a deep trench. Continuing movement on the subduction zone associated with the Japan Trench is one of the main causes of tsunamis and earthquakes in northern Japan, including the megathrust Tōhoku earthquake and resulting tsunami that occurred on 11 March 2011. The rate of subduction associated with the Japan Trench has been recorded at about /yr. Tectonic history During the late Neogene period (23.03–2.58 million years ago), the Japan Tren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadal Zone
The hadal zone, also known as the hadopelagic zone, is the deep sea, deepest region of the ocean, lying within oceanic trenches. The hadal zone ranges from around below sea level, and exists in long, narrow, topographic V-shaped depressions. The cumulative area occupied by the 46 individual hadal marine habitat, habitats worldwide is less than 0.25% of the world's seabed, seafloor, yet trenches account for over 40% of the ocean's depth range. Most hadal habitat is found in the Pacific Ocean, the deepest of the conventional oceanic divisions. Terminology and definition Historically, the hadal zone was not recognized as distinct from the abyssal zone, although the deepest sections were sometimes called "ultra-abyssal". During the early 1950s, the Danish ''Galathea expeditions#Second expedition, Galathea II'' and Soviet ''RV Vityaz (1939), Vityaz'' expeditions separately discovered a distinct shift in the life at depths of not recognized by the broad definition of the abyssal zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Larvae
Ichthyoplankton (from Greek: wikt:ἰχθύς, ἰχθύς, , "fish"; and πλαγκτός, , "drifter") are the Fish eggs, eggs and larvae of fish. They are mostly found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 metres deep, which is sometimes called the epipelagic or photic zone. Ichthyoplankton are planktonic, meaning they cannot swim effectively under their own power, but must drift with the ocean currents. Fish eggs cannot swim at all, and are unambiguously planktonic. Early stage larvae swim poorly, but later stage larvae swim better and cease to be planktonic as they grow into Juvenile fish, juveniles. Fish larvae are part of the zooplankton that eat smaller plankton, while fish eggs carry their own food supply. Both eggs and larvae are themselves eaten by larger animals. Fish can produce high numbers of eggs which are often released into the open water column. Fish eggs typically have a diameter of about . The newly hatched young of oviparous fish are called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |