|
Norbornene
Norbornene or norbornylene or norcamphene is a highly strained bridged cyclic hydrocarbon. It is a white solid with a pungent sour odor. The molecule consists of a cyclohexene ring with a methylene bridge between carbons 1 and 4. The molecule carries a double bond which induces significant ring strain and significant reactivity. Production Norbornene is made by a Diels–Alder reaction of cyclopentadiene and ethylene. Many substituted norbornenes can be prepared similarly. Related bicyclic compounds are norbornadiene, which has the same carbon skeleton but with two double bonds, and norbornane which is prepared by hydrogenation of norbornene. Reactions Norbornene undergoes an acid-catalyzed hydration reaction to form norborneol. This reaction was of great interest in the elucidation of the non-classical carbocation controversy. Norbornene is used in the Catellani reaction and in norbornene-mediated ''meta''-C−H activation. Certain substituted norbornenes undergo unusual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
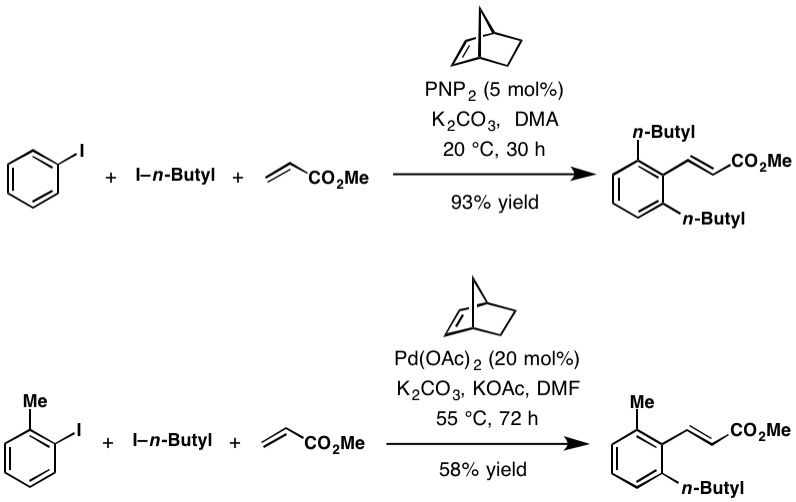
Catellani Reaction
The Catellani reaction was discovered by Marta Catellani (University of Parma, Università degli Studi di Parma, Italy) and co-workers in 1997. The reaction uses aryl iodides to perform bi- or tri-functionalization, including Carbon–hydrogen bond activation, C-H functionalization of the unsubstituted ''Arene substitution pattern, ortho'' Arene substitution pattern, position(s), followed a terminating cross-coupling reaction at the ''Arene substitution pattern, ipso'' Arene substitution pattern, position. This Cross-coupling reaction, cross-coupling cascade reaction depends on the ''Arene substitution pattern, ortho''-directing transient mediator, norbornene. Reaction mechanism The Catellani reaction is catalyzed by palladium and norbornene, although in most cases Stoichiometry, superstoichiometric amounts of norbornene are used to allow the reaction to proceed at a reasonable rate. The generally accepted reaction mechanism, as outlined below, is intricate and believed to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nadic Anhydride
Nadic anhydride, also known as 5-norbornene-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride, is an organic acid anhydride derivative of norbornene. Stereochemistry Nadic anhydride exhibits Endo-exo isomerism, ''endo''-''exo'' isomerism. In the ''exo'' isomer, the acid anhydride group points in the same direction towards the bridging carbon of the norbornene, while in the ''endo'' isomer the acid anhydride group points in the opposite direction. These isomers are respectively named ''cis''-5-norbornene-''exo''-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride (also known as himic anhydride) and ''cis''-5-norbornene-''endo''-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride (also known as carbic anhydride). Commercially available nadic anhydride is mainly the ''endo'' isomer, as this is the isomer predominantly made in the Diels-Alder reaction in its synthesis. Preparation In the patent for the Diels-Alder reaction, nadic anhydride was given as an example of the reaction, made by the addition of maleic anhydride to cyclopentadiene, which gives mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Strain
In organic chemistry, ring strain is a type of instability that exists when bonds in a molecule form angles that are abnormal. Strain is most commonly discussed for small rings such as cyclopropanes and cyclobutanes, whose internal angles are substantially smaller than the idealized value of approximately 109°. Because of their high strain, the heat of combustion for these small rings is elevated. Ring strain results from a combination of angle strain, conformational strain or Pitzer strain (torsional eclipsing interactions), and transannular strain, also known as van der Waals strain or Prelog strain. The simplest examples of angle strain are small cycloalkanes such as cyclopropane and cyclobutane. Ring strain energy can be attributed to the energy required for the distortion of bond and bond angles in order to close a ring. Ring strain energy is believed to be the cause of accelerated rates in altering ring reactions. Its interactions with traditional bond energi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbornadiene
Norbornadiene is an organic compound and a bicyclic hydrocarbon. Norbornadiene is of interest as a metal-binding ligand, whose complexes are useful for homogeneous catalysis. It has been intensively studied owing to its high reactivity and distinctive structural property of being a diene that cannot isomerize (isomers would be anti-Bredt alkenes). Norbornadiene is also a useful dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions. Synthesis Norbornadiene can be formed by a Diels-Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and acetylene : Reactions Quadricyclane, a valence isomer, can be obtained from norbornadiene by a photochemical reaction when assisted by a sensitizer such as acetophenone: : The norbornadiene-quadricyclane couple is of potential interest for solar energy storage when controlled release of the strain energy stored in quadricyclane back to norbornadiene is made possible. Norbornadiene is reactive in cycloaddition reactions. Norbornadiene is also the starting materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbornane
Norbornane (also known as bicyclo .2.1eptane) is an organic compound and a saturated hydrocarbon with chemical formula C7H12. It is a crystalline compound with a melting point of 88 °C. The carbon skeleton is derived from cyclohexane ring with a methylene bridge in the 1,4- position, and is a bridged bicyclic compound. The compound is a prototype of a class of strained bicyclic hydrocarbons. The compound was originally synthesized by reduction of norcamphor. The name norbornane is derived from bornane, which is 1,7,7-trimethylnorbornane, being a derivative of camphor (bornanone). The prefix ''nor'' refers to the stripping of the methyl groups from the parent molecule bornane. See also * 2-Norbornyl cation * Norbornene * Norbornadiene * Bornane * endo-Norborneol * exo-Norborneol * Norcamphor Norcamphor is an organic compound, classified as a bicyclic ketone. It is an structural analog, analog of camphor, but without the three methyl groups. A colorless solid, it is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butadiene
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CH-CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two vinyl groups. It is the simplest conjugated diene. Although butadiene breaks down quickly in the atmosphere, it is nevertheless found in ambient air in urban and suburban areas as a consequence of its constant emission from motor vehicles. The name butadiene can also refer to the isomer, 1,2-butadiene, which is a cumulated diene with structure H2C=C=CH−CH3. This allene has no industrial significance. History In 1863, French chemist E. Caventou isolated butadiene from the pyrolysis of amyl alcohol. This hydrocarbon was identified as butadiene in 1886, after Henry Edward Armstrong isolated it from among the pyrolysis products of petroleum. In 1910, the Russian chemist Sergei Lebedev polymerized butadiene and obtained a material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylidene Norbornene
Ethylidene norbornene (ENB) is an organic compound that consists of an ethylidene (CH3C(H)=) group attached to norbornene. It is a colorless liquid. The molecule consists of two sites of unsaturation. The compound consists of (''E'')- and (''Z'')-stereoisomers, but the mixtures are typically not separated. Preparation and use It is prepared by isomerization of vinyl norbornene, which in turn is obtained by the Diels-Alder reaction of butadiene and cyclopentadiene. : It is a monomer that used in the production of the commercial polymer EPDM. Only the ring alkene participates in the copolymerization. The exocyclic double bond (the ethylidene group) undergoes sulfur vulcanization Sulfur vulcanization is a chemical process for converting natural rubber or related polymers into materials of varying hardness, elasticity, and mechanical durability by heating them with sulfur or sulfur-containing compounds. Sulfur forms cros .... Safety Its (intravenous, rabbit) ranges f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Olefin Copolymer
Cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) is an amorphous polymer made by several polymer manufacturers. COC is a relatively new class of polymers as compared to commodities such as polypropylene and polyethylene. This newer material is used in a wide variety of applications including packaging films, lenses, vials, displays, and medical devices. Various types In 2005 there were "several types of commercial cyclic olefin copolymers based on different types of cyclic monomers and polymerization methods. Cyclic olefin copolymers are produced by chain copolymerization of cyclic monomers such as 8,9,10-trinorborn-2-ene (norbornene) or 1,2,3,4,4a,5,8,8a-octahydro-1,4:5,8-dimethanonaphthalene (tetracyclododecene) with ethene (such as Polyplastics subsidiary TOPAS Advanced Polymers' TOPAS, Mitsui Chemical's APEL), or by ring-opening metathesis polymerization of various cyclic monomers followed by hydrogenation (Japan Synthetic Rubber's ARTON, Zeon Chemical's Zeonex and Zeonor)." These later materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addition Polymerization
Chain-growth polymerization ( AE) or chain-growth polymerisation ( BE) is a polymerization technique where monomer molecules add onto the active site on a growing polymer chain one at a time. There are a limited number of these active sites at any moment during the polymerization which gives this method its key characteristics. Chain-growth polymerization involves 3 types of reactions : # Initiation: An active species I* is formed by some decomposition of an initiator molecule I # Propagation: The initiator fragment reacts with a monomer M to begin the conversion to the polymer; the center of activity is retained in the adduct. Monomers continue to add in the same way until polymers Pi* are formed with the degree of polymerization i # Termination: By some reaction generally involving two polymers containing active centers, the growth center is deactivated, resulting in dead polymer Introduction In 1953, Paul Flory first classified polymerization as " step-growth polymeriza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Transition Temperature
The glass–liquid transition, or glass transition, is the gradual and reversible transition in amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle "glassy" state into a viscous or rubbery state as the temperature is increased. ISO 11357-2: Plastics – Differential scanning calorimetry – Part 2: Determination of glass transition temperature (1999). An amorphous solid that exhibits a glass transition is called a glass. The reverse transition, achieved by supercooling a viscous liquid into the glass state, is called vitrification. The glass-transition temperature ''T''g of a material characterizes the range of temperatures over which this glass transition occurs (as an experimental definition, typically marked as 100 s of relaxation time). It is always lower than the melting temperature, ''T''m, of the crystalline state of the material, if one exists, because the glass is a higher energy state (or enthalpy at const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring-opening Metathesis Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) is a type of chain-growth polymerization involving olefin metathesis. The reaction is driven by relieving ring strain in cyclic olefins. A variety of heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts have been developed for different polymers and mechanisms. Heterogeneous catalysts are typical in large-scale commercial processes, while homogeneous catalysts are used in finer laboratory chemical syntheses. Organometallic catalysts used in ROMP usually have transition metal centres, such as tungsten, ruthenium, titanium, etc., with organic ligands. Heterogeneous catalysis : Heterogeneous catalysis consists of catalysts and substrates in different physical states. The catalyst is typically in solid phase. The mechanism of heterogeneous ring-opening metathesis polymerization is still under investigation. Ring-opening metathesis polymerization of cyclic olefins has been commercialized since the 1970s. Examples of polymers pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |