|
Non-invasive Ventilation
Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) is the use of breathing support administered through a face mask, nasal mask, or a helmet. Air, usually with added oxygen, is given through the mask under positive pressure; generally the amount of pressure is alternated depending on whether someone is breathing in or out. It is termed "non-invasive" because it is delivered with a mask that is tightly fitted to the face or around the head, but without a need for tracheal intubation (a tube through the mouth into the windpipe). While there are similarities with regard to the interface, NIV is not the same as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), which applies a single level of positive airway pressure throughout the whole respiratory cycle; CPAP does not deliver ventilation but is occasionally used in conditions also treated with NIV. Non-invasive ventilation is used in acute respiratory failure caused by a number of medical conditions, most prominently chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheal Intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic catheter, tube into the vertebrate trachea, trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequently performed in critically injured, ill, or anesthetized patients to facilitate Ventilation (physiology), ventilation of the lungs, including mechanical ventilation, and to prevent the possibility of asphyxiation or airway obstruction. The most widely used route is orotracheal, in which an tracheal tube, endotracheal tube is passed through the mouth and larynx, vocal apparatus into the trachea. In a nasotracheal procedure, an endotracheal tube is passed through the nose and vocal apparatus into the trachea. Other methods of intubation involve surgery and include the cricothyrotomy (used almost exclusively in emergency circumstances) and the tracheotomy, used primarily in situations where a prolonged need for air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheostomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision on the front of the neck to open a direct airway to the trachea. The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheal tube (or tracheostomy tube) to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth. Etymology and terminology The etymology of the word ''tracheotomy'' comes from two Greek words: the root ''tom-'' (from Greek τομή ''tomḗ'') meaning "to cut", and the word ''trachea'' (from Greek τραχεία ''tracheía''). The word ''tracheostomy'', including the root ''stom-'' (from Greek στόμα ''stóma'') meaning "mouth", refers to the making of a semi-permanent or permanent opening and to the opening itself. Some sources offer different definitions of the above terms. Part of the ambiguity is due to the uncertainty of the intended permanence of the stoma (hole) at the time it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Lung
An iron lung is a type of negative pressure ventilator, a medical ventilator, mechanical respirator which encloses most of a person's body and varies the air pressure in the enclosed space to stimulate breathing. It assists breathing when Muscles of respiration, muscle control is lost, or the work of breathing exceeds the person's ability. Need for this treatment may result from diseases including polio and botulism and certain poisons (for example, barbiturates and tubocurarine). The use of iron lungs is largely obsolete in modern medicine as more modern breathing therapies have been developed and due to the Polio eradication, eradication of polio in most of the world. In 2020 however, the COVID-19 pandemic revived some interest in them as a cheap, readily-producible substitute for Modes of mechanical ventilation#Continuous positive airway pressure, positive-pressure ventilators, which were feared to be outnumbered by patients potentially needing temporary artificially assiste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Pressure Ventilator
A negative pressure ventilator (NPV) is a type of mechanical ventilator that stimulates an ill person's breathing by periodically applying negative air pressure to their body to expand and contract the chest cavity.Shneerson, Dr. John M., Newmarket General Hospital, ( Newmarket, Suffolk, U.K.)"Non-invasive and domiciliary ventilation: negative pressure techniques,"#5 of series "Assisted ventilation" in ''Thorax,'' 1991;46: pp.131-135, retrieved April 12, 2020Grum, Cyril M., MD, and Melvin L. Morganroth, MD"Initiating Mechanical Ventilation,"in ''Intensive Care Medicine'' 1988;3:6-20, retrieved April 12, 2020Rockoff, Mark, M.D."The Iron Lung and Polio," video (8 minutes), January 11, 2016, OPENPediatrics and Boston Children's Hospital on YouTube, retrieved April 11, 2020 (historical background and images, explanatory diagrams, and live demonstrations) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
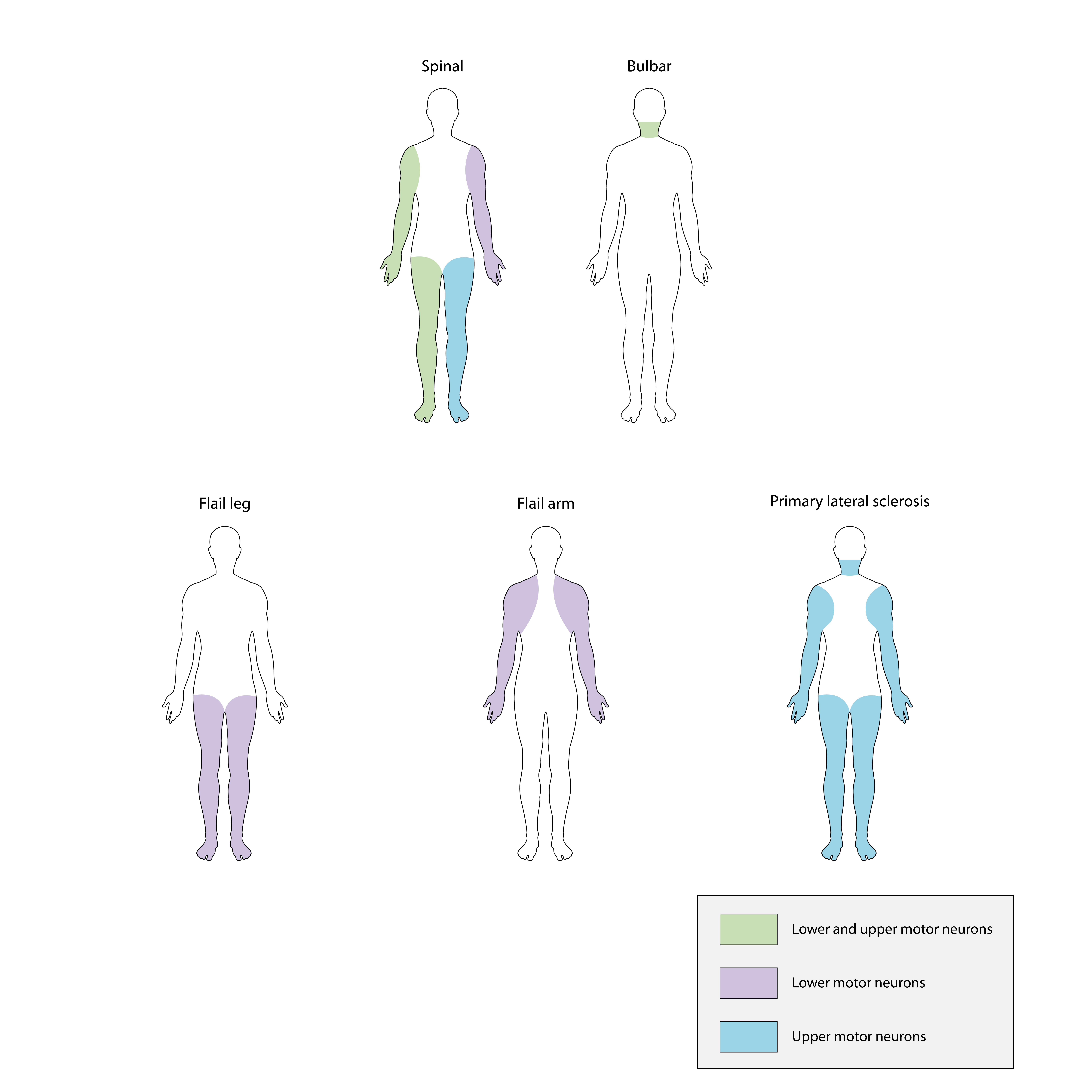
Motor Neuron Disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle stiffness, twitches, weakness, and wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (begins with weakness in the arms or legs) or ''bulbar-onset'' (begins with difficulty in speaking or swallowing). Most cases of ALS (ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway leading to reduced or absent breathing during sleep. These episodes are termed "apneas" with complete or near-complete cessation of breathing, or "hypopneas" when the reduction in breathing is partial. In either case, a fall in oxygen saturation (medicine), blood oxygen saturation, a disruption in sleep, or both, may result. A high frequency of apneas or hypopneas during sleep may interfere with the quality of sleep, whichin combination with disturbances in blood oxygenationis thought to contribute to negative consequences to health and quality of life. The terms obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) or obstructive sleep apnea–hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) may be used to refer to OSA when it is associated with symptoms during the daytime (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Thoracic Society
The American Thoracic Society (ATS) is a nonprofit organization focused on improving care for pulmonary diseases, critical illnesses and sleep-related breathing disorders. It was established in 1905 as the American Sanatorium Association, and changed its name in 1938 to the American Trudeau Society. In 1960, it changed its name again to the American Thoracic Society. Originally the medical section of the American Lung Association, the Society became independently incorporated in 2000 as a 501 (c) (3) organization. Medical and scientific areas of interest Pulmonology, critical care, sleep medicine, infectious disease, pediatrics, allergy/immunology, thoracic surgery, behavioral science, environmental and occupational medicine, physiology, molecular biology, among others. Membership More than 15,000 physicians, research scientists, and nurses and other allied healthcare professionals (32 percent of whom work outside the United States). ATS Assemblies The interests of memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intensive Care Unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine. An intensive care unit (ICU) was defined by the task force of the World Federation of Societies of Intensive and Critical Care Medicine as "an organized system for the provision of care to critically ill patients that provides intensive and specialized medical and nursing care, an enhanced capacity for monitoring, and multiple modalities of physiologic organ support to sustain life during a period of life-threatening organ system insufficiency." Patients may be referred directly from an emergency department or from a ward if they rapidly deteriorate, or immediately after surgery if the surgery is very invasive and the patient is at high risk of complications. History In 1854, Florence Nightingale left for the Crimean War, where triage was used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Severe Asthma
Acute severe asthma, also known as status asthmaticus, is an acute exacerbation of asthma that does not respond to standard treatments of bronchodilators (inhalers) and corticosteroids. Asthma is caused by multiple genes, some having protective effect, with each gene having its own tendency to be influenced by the environment although a genetic link leading to acute severe asthma is still unknown. Symptoms include chest tightness, rapidly progressive dyspnea (shortness of breath), dry cough, use of accessory respiratory muscles, fast and/or labored breathing, and extreme wheezing. It is a life-threatening episode of airway obstruction and is considered a medical emergency. Complications include cardiac and/or respiratory arrest. The increasing prevalence of atopy and asthma remains unexplained but may be due to infection with respiratory viruses. Signs and symptoms An exacerbation (attack) of asthma is experienced as a worsening of asthma symptoms with breathlessness and cough ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergency Medical Services
Emergency medical services (EMS), also known as ambulance services, pre-hospital care or paramedic services, are emergency services that provide urgent pre-hospital treatment and stabilisation for serious illness and injuries and transport to definitive care. They may also be known as a first aid squad, FAST squad, emergency squad, ambulance squad, ambulance corps, life squad or by other acronym, initialisms such as EMAS or EMARS. In most places, EMS can be summoned by members of the public (as well as medical facilities, other emergency services, businesses and authorities) via an emergency telephone number (such as 911 in the United States) which puts them in contact with a dispatching centre, which will then dispatch suitable resources for the call. Ambulances are the primary vehicles for delivering EMS, though Nontransporting EMS vehicle, squad cars, Motorcycle ambulance, motorcycles, Air medical services, aircraft, Water ambulance, boats, Firefighting apparatus, fire appara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a form of positive airway pressure (PAP) ventilation in which a constant level of pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is continuously applied to the upper respiratory tract of a person. The application of positive pressure may be intended to prevent upper airway collapse, as occurs in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), or to reduce the work of breathing in conditions such as acute decompensated heart failure. CPAP therapy is highly effective for managing obstructive sleep apnea. Compliance and acceptance of use of CPAP therapy can be a limiting factor, with 8% of people stopping use after the first night and 50% within the first year. Medical uses Moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea CPAP is the most effective treatment for moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea, in which the mild pressure from the CPAP prevents the airway from collapsing or becoming blocked. CPAP has been shown to be 100% effective at eliminating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Edema
Pulmonary edema (British English: oedema), also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive fluid accumulation in the tissue or air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. This leads to impaired gas exchange, most often leading to shortness of breath ( dyspnea) which can progress to hypoxemia and respiratory failure. Pulmonary edema has multiple causes and is traditionally classified as cardiogenic (caused by the heart) or noncardiogenic (all other types not caused by the heart). Various laboratory tests ( CBC, troponin, BNP, etc.) and imaging studies (chest x-ray, CT scan, ultrasound) are often used to diagnose and classify the cause of pulmonary edema. Treatment is focused on three aspects: * improving respiratory function, * treating the underlying cause, and * preventing further damage and allow full recovery to the lung. Pulmonary edema can cause permanent organ damage, and when sudden (acute), can lead to respiratory failure or cardiac arrest due to hypoxia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |