|
Non-mendelian Inheritance
Non-Mendelian inheritance is any pattern in which traits do not segregate in accordance with Mendelian inheritance#Mendel's laws, Mendel's laws. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus. In Mendelian inheritance, each parent contributes one of two possible alleles for a trait. If the genotypes of both parents in a genetic cross are known, Mendel's laws can be used to determine the distribution of phenotypes expected for the population of offspring. There are several situations in which the proportions of phenotypes observed in the progeny do not match the predicted values. Certain inherited diseases and their presentation display non-Mendelian patterns, complicating making predictions from family history. Types Incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, and polygenic traits follow Mendel's laws, display Mendelian inheritance, and are explained as extensions of Mendel's laws. Incomplete dominance In cases of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. The name gamete was introduced by the German cytologist Eduard Strasburger in 1878. Gametes of both mating individuals can be the same size and shape, a condition known as isogamy. By contrast, in the majority of species, the gametes are of different sizes, a condition known as anisogamy or heterogamy that applies to humans and other mammals. The human ovum has approximately 100,000 times the volume of a single human sperm cell. The type of gamete an organism produces determines its sex and sets the basis for the sexual roles and sexual selection. In humans and other species that produce two Morphology (biology), morphologically distinct types of gametes, and in which Gonochorism, each individual produces only one type, a femal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Carrier
A hereditary carrier (genetic carrier or just carrier), is a person or other organism that has inherited a recessive allele for a genetic trait or mutation but usually does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. Carriers are, however, able to pass the allele onto their offspring, who may then express the genetic trait. Carriers in autosomal inheritances Autosomal dominant-recessive inheritance is made possible by the fact that the individuals of most species (including all higher animals and plants) have two alleles of most hereditary predispositions because the chromosomes in the cell nucleus are usually present in pairs (diploid). Carriers can be female or male as the autosomes are homologous independently from the sex. In carriers the expression of a certain characteristic is recessive. The individual has both a genetic predisposition for the dominant trait and a genetic predisposition for the recessive trait, and the dominant expression prevails in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemophilia
Haemophilia (British English), or hemophilia (American English) (), is a mostly inherited genetic disorder that impairs the body's ability to make blood clots, a process needed to stop bleeding. This results in people bleeding for a longer time after an injury, easy bruising, and an increased risk of bleeding inside joints or the brain. Those with a mild case of the disease may have symptoms only after an accident or during surgery. Bleeding into a joint can result in permanent damage while bleeding in the brain can result in long term headaches, seizures, or an altered level of consciousness. There are two main types of haemophilia: haemophilia A, which occurs due to low amounts of clotting factor VIII, and haemophilia B, which occurs due to low levels of clotting factor IX. They are typically inherited from one's parents through an X chromosome carrying a nonfunctional gene. Most commonly found in men, haemophilia can affect women too, though very rarely. A woman wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Blindness
Color blindness, color vision deficiency (CVD) or color deficiency is the decreased ability to color vision, see color or differences in color. The severity of color blindness ranges from mostly unnoticeable to full absence of color perception. Color blindness is usually a Sex linkage, sex-linked Heredity, inherited problem or variation in the functionality of one or more of the three classes of cone cells in the retina, which mediate color vision. The most common form is caused by a genetic condition called congenital red–green color blindness (including protan and deutan types), which affects ''up to'' 1 in 12 males (8%) and 1 in 200 females (0.5%). The condition is more prevalent in males, because the opsin genes responsible are located on the X chromosome. Rarer genetic conditions causing color blindness include congenital blue–yellow color blindness (tritan type), blue cone monochromacy, and achromatopsia. Color blindness can also result from physical or chemical dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonosome
Sex chromosomes (also referred to as allosomes, heterotypical chromosome, gonosomes, heterochromosomes, or idiochromosomes) are chromosomes that carry the genes that determine the sex of an individual. The human sex chromosomes are a typical pair of mammal allosomes. They differ from autosomes in form, size, and behavior. Whereas autosomes occur in homologous pairs whose members have the same form in a diploid cell, members of an allosome pair may differ from one another. Nettie Stevens and Edmund Beecher Wilson both independently discovered sex chromosomes in 1905. However, Stevens is credited for discovering them earlier than Wilson. Differentiation In humans, each cell nucleus contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, a total of 46 chromosomes. The first 22 pairs are called autosomes. Autosomes are homologous chromosomes i.e. chromosomes which contain the same genes (regions of DNA) in the same order along their chromosomal arms. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are called allosomes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dog Coat Genetics
Dogs have a wide range of coat colors, patterns, textures and lengths. Dog coat qualities are governed by how genes are passed from dogs to their puppies and how those genes are expressed in each dog. Dogs have about 19,000 genes in their genome but only a handful affect the physical variations in their coats. Dogs have two copies of most genes, one from the dog's mother and one from its father. Genes of interest have more than one version, or allele. Usually only one or a small number of alleles exist for each gene. In any one Locus (genetics), gene locus a dog will either be homozygous where the gene is made of two identical alleles (one from its mother and one its father) or heterozygous where the gene is made of two different alleles (one inherited from each parent). To understand genetically why a dog's coat physically looks the way it does requires an understanding of only a handful of canine coat genes and their alleles. For example, to understand how a black and white greyh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
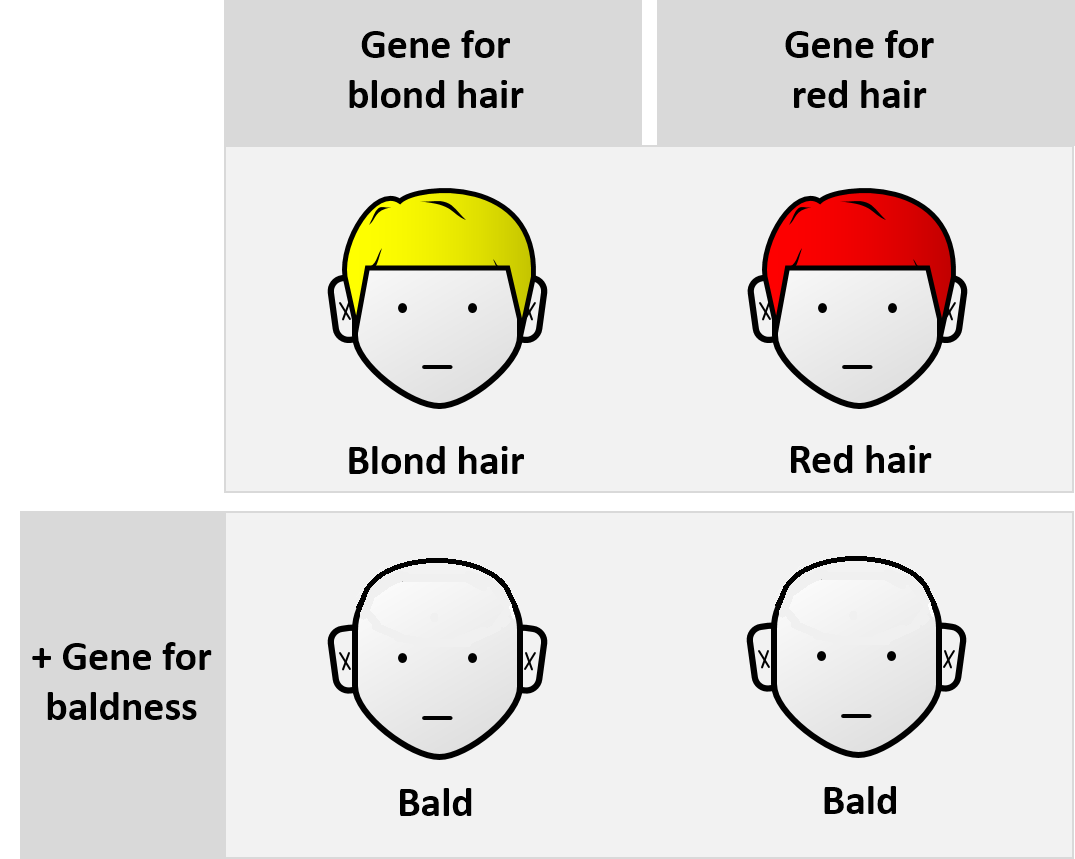
Epistasis
Epistasis is a phenomenon in genetics in which the effect of a gene mutation is dependent on the presence or absence of mutations in one or more other genes, respectively termed modifier genes. In other words, the effect of the mutation is dependent on the genetic background in which it appears. Epistatic mutations therefore have different effects on their own than when they occur together. Originally, the term ''epistasis'' specifically meant that the effect of a gene variant is masked by that of different gene. The concept of ''epistasis'' originated in genetics in 1907 but is now used in biochemistry, computational biology and evolutionary biology. The phenomenon arises due to interactions, either between genes (such as mutations also being needed in regulators of gene expression) or within them (multiple mutations being needed before the gene loses function), leading to non-linear effects. Epistasis has a great influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes, which leads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat (30072497623)
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domesticated feline species. Cat or CAT may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Comics * Cat (comics), a list of several characters * ''Confidential Assassination Troop'', a manhua by Fung Chin Pang from 2003 Film and television * Cat, the title character of the 1965 film ''Cat Ballou'' * Cat (''Red Dwarf''), a character in the sci-fi sitcom * Cat, a character in the animated television series ''CatDog'' * Cat MacKenzie, a character in ''Family Affairs'' * Cat Valentine (''Victorious''), a character in ''Victorious'' and ''Sam & Cat'' * ''Cat'' (TV series), Indian crime thriller streaming television series * Cat, from Peg + Cat Literature * The Fox and the Cat, a pair of fictional characters from the Italian novel ''The Adventures of Pinocchio'' (1881-1883) by Carlo Collodi and several adaptations of the story in other media Music * ''Cat #1'' (album), a 1994 album by Peter Criss * "Cat", a track on the 2011 album ''Minecraft – Volume A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABO Blood Type
The ABO blood group system is used to denote the presence of one, both, or neither of the A and B antigens on erythrocytes (red blood cells). For human blood transfusions, it is the most important of the 47 different blood type (or group) classification systems currently recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusions (ISBT) as of December 2022. A mismatch in this serotype (or in various others) can cause a potentially fatal Blood transfusion#Adverse effects, adverse reaction after a transfusion, or an Organ rejection, unwanted immune response to an organ transplant. Such mismatches are rare in modern medicine. The associated anti-A and anti-B antibodies are usually IgM antibodies, produced in the first years of life by sensitization to environmental substances such as food, bacteria, and viruses. The ABO blood types were discovered by Karl Landsteiner in 1901; he received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1930 for this discovery. ABO blood types are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dog Coat Genetics
Dogs have a wide range of coat colors, patterns, textures and lengths. Dog coat qualities are governed by how genes are passed from dogs to their puppies and how those genes are expressed in each dog. Dogs have about 19,000 genes in their genome but only a handful affect the physical variations in their coats. Dogs have two copies of most genes, one from the dog's mother and one from its father. Genes of interest have more than one version, or allele. Usually only one or a small number of alleles exist for each gene. In any one Locus (genetics), gene locus a dog will either be homozygous where the gene is made of two identical alleles (one from its mother and one its father) or heterozygous where the gene is made of two different alleles (one inherited from each parent). To understand genetically why a dog's coat physically looks the way it does requires an understanding of only a handful of canine coat genes and their alleles. For example, to understand how a black and white greyh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |