|
Nomorhamphus Ebrardtii
''Nomorhamphus ebrardtii'' is a species of viviparous halfbeak, a ray-finned fish in the family Zenarchopteridae, endemic to brackish and freshwater locations in Sulawesi and the neighbouring island of Kabaena in Indonesia. This species can reach a length of SL. Description ''Nomorhamphus ebrardtii'' grows to a standard length of about . It is an elongate, somewhat compressed fish with the lower mandible considerably longer than the upper mandible. Alongside this there is a fold of skin which projects sideways. The beak contains no teeth but there are small pointed teeth in both jaws. The dorsal fin has ten to twelve soft rays, the anal fin fifteen and the pectoral fins twelve. The dorsal fin is shorter than the anal fin, and its origin is posterior to the origin of the anal fin. The fifth ray of the dorsal fin is the longest but is not as long as the second ray of the anal fin. This is modified in males into an "andropodium", a movable intromittent organ used to deliver milt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canna Maria Louise Popta
Canna Maria Louise Popta (31 May 1860 – 13 June 1929)L.B. Holthuis, Biography i1820-1958, Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie page 82 (in Dutch). was a Dutch biologist. Born in Breda, Popta was one of the first women to enrol as a student at Leiden University where she studied for a degree in geology, zoology and botany, allowing her to teach in high schools. She studied for her doctorate at the University of Berne under the supervision of Eduard Fischer, her thesis was on the Hemiasci, a fungal group which was then thought to be the link between the Phycomycetes and Ascomycota. She lao wrote an 1897 article about fungi on sugar cane. After completing her doctorate she obtained a position at the Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie in Leiden as a Lab Assistant to the curator of reptiles, amphibians and fishes. During her career at the museum she concentrated mainly on ichthyology, eventually retiring in 1928, and dying the following year in Leiden. She wrote over 40 scientifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenarchopteridae
Zenarchopteridae, the viviparous halfbeaks, is a family of ray-finned fishes in the order Beloniformes. The Zenarchopteridae exhibit strong sexual dimorphism, practicing internal fertilisation, and in some cases ovoviviparous or viviparous (the family also includes oviparous species).Berra, T.M. (2001). ''Freshwater Fish Distribution.'' p. 320. Tan, H.H. & Lim, K.K.P. (2013). Three new species of freshwater halfbeaks (Teleostei: Zenarchopteridae: ''Hemirhamphodon'') from Borneo.' The Raffles Bulletin of Zoology 61(2): 735–747. The members in the family are mainly found in fresh and brackish water of tropical Asia and New Guinea, but the genus ''Zenarchopterus'' also includes marine species from the Indo-Pacific. Several, such as the wrestling halfbeak, have become commonly traded aquarium fish. Genera The following genera are classified within the family Zenarchopteridae * '' Dermogenys'' Kuhl & van Hasselt, 1823 * '' Hemirhamphodon'' Bleeker, 1865 * '' Nomorhamphus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class (biology), class of Osteichthyes, bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fish fin, fins made of webbings of skin supported by radially extended thin bony spine (zoology), spines called ''lepidotrichia'', as opposed to the bulkier, fleshy lobed fins of the sister taxon, sister clade Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). Resembling folding fans, the actinopterygian fins can easily change shape and wetted area, providing superior thrust-to-weight ratios per movement compared to sarcopterygian and chondrichthyian fins. The fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the articulation (anatomy), articulation between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). The vast majority of actinopterygians are teleosts. By species count, they domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulawesi
Sulawesi ( ), also known as Celebes ( ), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the List of islands by area, world's 11th-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Archipelago. Within Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and New Guinea, Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra are more populous. The landmass of Sulawesi includes four peninsulas: the northern Minahasa Peninsula, the East Peninsula, Sulawesi, East Peninsula, the South Peninsula, Sulawesi, South Peninsula, and the Southeast Peninsula, Sulawesi, Southeast Peninsula. Three gulfs separate these peninsulas: the Gulf of Tomini between the northern Minahasa and East peninsulas, the Tolo Gulf between the East and Southeast peninsulas, and the Bone Gulf between the South and Southeast peninsulas. The Strait of Makassar runs along the western side of the island and separates the island from Borneo. Etymology The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabaena
Kabaena or Tokotua is an island in the Flores Sea, Indonesia, off the coast of Sulawesi Sulawesi ( ), also known as Celebes ( ), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the List of islands by area, world's 11th-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Min .... Most of it is a part of Bombana Regency within Southeast Sulawesi province, although the southernmost district (Talaga Raya) is administratively part of Central Buton Regency. The island's area is 894.15 km2 and its total population at the 2010 Census was 35,558Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. and at the 2020 Census was 42,877;Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 47,071.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2024. Administrative Districts The island includes six of the 22 districts of Bombana Regency, and one district of Central Buton Regency. These seven districts are tabulated below with their ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea, Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 280 million people, Indonesia is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fourth-most-populous country and the most populous Islam by country, Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's List of islands by population, most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia operates as a Presidential system, presidential republic with an elected People's Consultative Assembly, legislature and consists of Provinces of Indonesia, 38 provinces, nine of which have Autonomous administrative divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
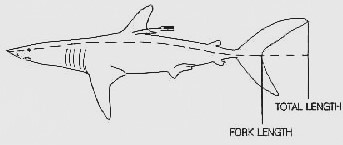
Fish Measurement
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes ( lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viviparity
In animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the mother, with the maternal circulation providing for the metabolic needs of the embryo's development, until the mother gives birth to a fully or partially developed juvenile that is at least metabolically independent. This is opposed to oviparity, where the embryos develop independently outside the mother in eggs until they are developed enough to break out as hatchlings; and ovoviviparity, where the embryos are developed in eggs that remain carried inside the mother's body until the hatchlings emerge from the mother as juveniles, similar to a live birth. Etymology The term "viviparity" and its adjective form "viviparous" both derive from the Latin ''vivus'', meaning "living"; and ''pario'', meaning "give birth to". Reproductive mode Five modes of reproduction have been differentiated in animals based on relations between zygote and parents. The five include two nonviviparous modes: ovulipari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will degenerate in the body. Normally, these are paired structures, but in birds and some cartilaginous fishes, one or the other side fails to develop (together with the corresponding ovary), and only one functional oviduct can be found. Except in teleosts, the oviduct is not directly in contact with the ovary. Instead, the most anterior portion ends in a funnel-shaped structure called the infundibulum, which collects eggs as they are released by the ovary into the body cavity. The only female vertebrates to lack oviducts are the jawless fishes. In these species, the single fused ovary releases eggs directly into the body cavity. The fish eventually extrudes the eggs through a small genital pore towards the rear of the body. Fish and amphibia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oophagy
Oophagy ( ) or ovophagy, literally "egg eating", is the practice of embryos feeding on eggs produced by the ovary while still inside the mother's uterus. The word oophagy is formed from the classical Greek (, "egg") and classical Greek (, "to eat"). In contrast, adelphophagy is the cannibalism of a multi-celled embryo. Oophagy is thought to occur in all sharks in the order Lamniformes and has been recorded in the bigeye thresher (''Alopias superciliosus''), the pelagic thresher (''A. pelagicus''), the shortfin mako (''Isurus oxyrinchus'') and the porbeagle (''Lamna nasus'') among others. It also occurs in the tawny nurse shark (''Nebrius ferrugineus''), and in the family Pseudotriakidae. This practice may lead to larger embryos or prepare the embryo for a predatory lifestyle. There are variations in the extent of oophagy among the different shark species. The grey nurse shark (''Carcharias taurus'') practices intrauterine cannibalism, the first developed embryo consum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |