|
Nine Schools Of Thought
The Nine Schools of Thought were the primary schools during the Hundred Schools of Thought period of China during the Eastern Zhou dynasty. They were: * Confucianism (as interpreted by Mencius and others), * Legalism, * Taoism, * Mohism, * Agriculturalism, * School of Diplomacy, * the Logicians, *Sun Tzu's Militarists * Naturalists Although only the first three of these went on to receive imperial patronage in later dynasties, doctrines from each influenced the others and Chinese society in sometimes unusual ways. The Mohists, for instance, found little interest in their praise of meritocracy but much acceptance for their mastery of defensive siege warfare; much later, however, their arguments against nepotism were used in favor of establishing the imperial examination The imperial examination was a civil service examination system in History of China#Imperial China, Imperial China administered for the purpose of selecting candidates for the Civil service#China, state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical School
List of philosophies, schools of thought and philosophical movements. A Absurdism – Academic skepticism – Accelerationism - Achintya Bheda Abheda – Action, philosophy of – Actual idealism – Actualism – Advaita Vedanta – Aesthetic Realism – Aesthetics – African philosophy – Afrocentrism – Agential realism – Agnosticism – Agnostic theism – Ajātivāda – Ājīvika – Ajñana – Alexandrian school – Alexandrists – Ambedkarism – American philosophy – Analytical Thomism – Analytic philosophy – Anarchism – Ancient philosophy – Animism – Anomalous monism – Anthropocentrism – Antinatalism – Antinomianism – Antipositivism – Anti-psychiatry – Anti-realism – Antireductionism – Applied ethics – Archaeology, philosophy of – Aristotelianism – Arithmetic, philosophy of – Artificial intelligence, philosophy of – Art, philosophy of – Asceticism – Atheism – Atomism – Augustinianism – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Schools Of Thought
The Hundred Schools of Thought () were philosophies and schools that flourished during the late Spring and Autumn period and Warring States period (221 BC). The term was not used to describe these different philosophies until Confucianism, Mohism, and Legalism were created. The era in which they flourished was one of turbulence in China, fraught with chaos and mass militarization, but where Chinese philosophy was developed and patronized by competing bureaucracies. This phenomenon has been called the Contention of a Hundred Schools of Thought. The philosophies that emerged during this period have profoundly influenced East Asian culture and societies. The intellectual landscape of this era was characterized by itinerant scholars, who were often employed by various state rulers as advisers on the way of government, war, and diplomacy. Often, members and traditions of the same school had little in common other than the same influential figure that their beliefs were based on. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
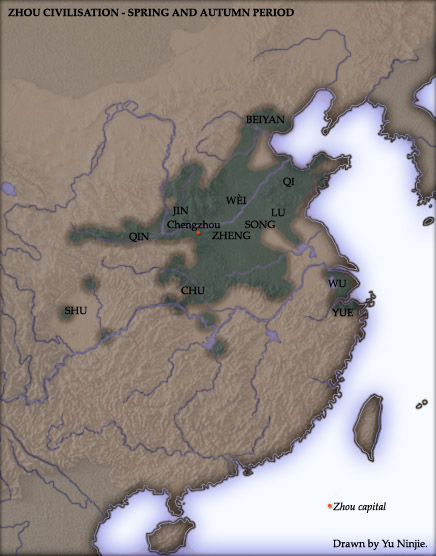
Eastern Zhou Dynasty
The Eastern Zhou (256 BCE) is a period in Chinese history comprising the latter two-thirds of the Zhou dynasty. The period follows the Western Zhou era and is named due to the Zhou royal court relocating the capital eastward from Fenghao (in present-day Xi'an, Shaanxi province) to Chengzhou (near present-day Luoyang, Henan province) after the fall and sacking of the old capital in the hand of Quanrong barbarians. The Eastern Zhou era was characterised by the progressively weakened authority of the Zhou royal house, and correspondingly increasing autonomy and military ambitions of various feudal states. It is subdivided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn period (), during which the ancient aristocracy still held nominal influence in a large number of separate polities; and the Warring States period (221 BCE), which saw the complete decentralization, escalation of interstate warfare and regional administrative sophistication. History According to traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, Religious Confucianism, religion, theory of government, or way of life. Founded by Confucius in the Hundred Schools of Thought era (c. 500 BCE), Confucianism integrates philosophy, ethics, and social governance, with a core focus on virtue, Harmonious Society, social harmony, and Filial piety, familial responsibility. Confucianism emphasizes virtue through self-cultivation and communal effort. Key virtues include ''Ren (philosophy), ren'' (benevolence), ''Yi (philosophy), yi'' (righteousness), ''Li (Confucianism), li'' (propriety), ''Wisdom, zhi'' (wisdom), and ''Xin (virtue), xin'' (sincerity). These values, deeply tied to the notion of ''tian'' (heaven), present a worldview where human relationships and social order are manifestations of sacred moral principles.. While Confucianism does not emphasize an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mencius
Mencius (孟子, ''Mèngzǐ'', ; ) was a Chinese Confucian philosopher, often described as the Second Sage () to reflect his traditional esteem relative to Confucius himself. He was part of Confucius's fourth generation of disciples, inheriting his ideology and developing it further. Living during the Warring States period, he is said to have spent much of his life travelling around the states offering counsel to different rulers. Conversations with these rulers form the basis of the ''Mencius (book), Mencius'', which would later be canonised as a Confucian classic. One primary principle of his work is that human nature is righteous and humane. The responses of citizens to the policies of rulers embodies this principle, and a state with righteous and humane policies will flourish by nature. The citizens, with freedom from good rule, will then allocate time to caring for their wives, brothers, elders, and children, and be educated with rites and naturally become better citizens. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legalism (Chinese Philosophy)
''Fajia'' ( zh, s=法家, p=fǎjiā), or the School of ''fa'' (laws, methods), early translated ''Legalism'' for Shang Yang, is a school of thought representing a broader bibliography, collection of primarily Warring States period classical Chinese philosophy, incorporating more administrative works traditionally said to be rooted in Huang-Lao Daoism. Addressing practical governance challenges of the unstable feudal system, their ideas 'contributed greatly to the formation of the Chinese empire' and bureaucracy, advocating concepts including rule by fa (concept), law, sophisticated administrative fa (concept), technique, and ideas of state power. They are often interpreted in the West along Realism (international relations), realist lines. Though persisting, the Qin to Tang dynasty, Tang were more characterized by the 'centralizing tendencies' of their traditions. The school incorporates the more legalistic ideas of Li Kui (legalist), Li Kui and Shang Yang, and more administrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoism
Taoism or Daoism (, ) is a diverse philosophical and religious tradition indigenous to China, emphasizing harmony with the Tao ( zh, p=dào, w=tao4). With a range of meaning in Chinese philosophy, translations of Tao include 'way', 'road', 'path', or 'technique', generally understood in the Taoist sense as an enigmatic process of transformation Ultimate reality, ultimately underlying reality. Taoist thought has informed the development of various practices within the Taoist tradition and beyond, including forms of Taoist meditation, meditation, Chinese astrology, astrology, qigong, feng shui, and Neidan, internal alchemy. A common goal of Taoist practice is self-cultivation, a deeper appreciation of the Tao, and more harmonious existence. Taoist ethics vary, but generally emphasize such virtues as ''wu wei, effortless action'', ziran, ''naturalness'', ''pu (Taoism), simplicity'', and the Three Treasures (Taoism), three treasures of compassion, frugality, and humility. The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohism
Mohism or Moism (, ) was an ancient Chinese philosophy of ethics and logic, rational thought, and scientific technology developed by the scholars who studied under the ancient Chinese philosopher Mozi (), embodied in an eponymous book: the '' Mozi''. Among its major ethical tenets were altruism and a universal, unbiased respect and concern for all people, stressing the virtues of austerity and utilitarianism. Illuminating its original doctrine, later Mohist logicians were pivotal in the development of Chinese philosophy. Mohism developed at about the same time as Confucianism, Taoism and Legalism, and was one of the four main philosophic schools from around 770–221 BC, during the Spring and Autumn and Warring States period. During that time, Mohism was seen as a major rival to Confucianism. While its influence endured, Mohism almost disappeared as an independent school of thought as it transformed and integrated into sects of Taoism in the wake of the cultural transformat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculturalism
Agriculturalism, also known as the School of Agrarianism, the School of Agronomists, the School of Tillers, and in Chinese as the ''Nongjia'' (), was an early Agrarianism, agrarian Chinese philosophy that advocated peasant utopian communalism and egalitarianism. The Agriculturalists believed that Chinese society should be modeled around that of the early sage king Shennong, a folk hero who was portrayed in Chinese literature as "working in the fields, along with everyone else, and consulting with everyone else when any decision had to be reached." They encouraged farming and agriculture and taught farming and cultivation techniques, as they believed that agricultural development was the key to a stable and prosperous society. Agriculturalism was suppressed during the Qin dynasty and most original texts are now lost. However, concepts originally associated with Agriculturalism have influenced Confucianism and Legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalism, as well as Chinese philosophy as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School Of Diplomacy
The School of Diplomacy ( zh, t=, s=, p=zōng héng jiā), or the School of Vertical and Horizontal Alliances refers to a set of military and diplomatic strategies during the Warring States period of Chinese history (476-220 BCE), aiming for power balance among the strongest Qin State and the other weaker states. According to the ''Book of Han'', the school was one of the Nine Schools of Thought ( zh, t=九流, s=九流, p=Jiǔ Liú). Originated by '' Guiguzi'', the School of Diplomacy's main adherents were , Su Qin, Zhang Yi, , , Yue Yi, , , , Mao Sui, Li Yiji and as detailed in the '' Annals of the Warring States''. By the time of the Warring States period, the major contest was between the powerful State of Qin situated in the west, and the other six mid-power, namely Yan, Zhao, Wei, Qi, Chu, and Han. The seven states engaged in a complex series of pacts and military alliances, commonly referred to as the and , based on two geographic patterns. The Horizontal All ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School Of Names
The School of Names, or School of Forms and Names, is a school of thought in Chinese philosophy that grew out of Mohist logic. Sometimes termed Logicians, "dialecticians" or sophists modernly, Han scholars used it in reference to figures earlier termed Disputers in the Zhuangzi, as a view seemingly dating back to the Warring States period (221 BC). Rather than a unified movement like the Mohists, it represents a ''social category'' of early linguistic debaters. Some arguments in later, more orthodox Mohist texts, with their own logicians, would appear directed at their kind of debates. Figures associated with it include Deng Xi, Yin Wen, Hui Shi, and Gongsun Long. A Three Kingdoms era figure, Xu Gan, is relevant for discussions of names and realities, but was more Confucian and less philosophically relativist. Including figures referenced by the Zhuangzi, some likely served as a bridge between Mohism and the relativism of Zhuangzi Daoism. Hui Shi is noted for relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Tzu
Sun Tzu (; zh, t=孫子, s=孙子, first= t, p=Sūnzǐ) may have been a Chinese General, military general, strategist, philosopher, and writer who lived during the Eastern Zhou period (771–256 BC). Sun Tzu is traditionally credited as the author of ''The Art of War'', a Classical Chinese text on military strategy from the Warring States period, though the earliest parts of the work probably date to at least a century after his purported death. Sun Tzu is revered in Chinese culture, Chinese and East Asian culture as a legendary historical and military figure; however, his historical existence is uncertain. The Han dynasty historian Sima Qian and other traditional Chinese historians placed him as a minister to King Helü of Wu and dated his lifetime to 544–496 BC. The name ''Sun Tzu''by which he is more popularly knownis an Chinese honorifics, honorific which means "Master Sun (surname), Sun". His birth name was said to be Sun Wu ( zh, t=孫武, s=孙武, first=t) and he is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |