|
Night Ferry
The ''Night Ferry'' was an international boat train from London Victoria railway station, London Victoria to Gare du Nord, Paris Gare du Nord that crossed the English Channel on a train ferry. It ran from 1936 until 1939 when it ceased due to the onset of World War II. It resumed in 1947, ceasing in 1980. It was operated by Compagnie Internationale des Wagons-Lits until 1977 and then British Rail. History The ''Night Ferry'' was introduced on the night of 14 October 1936. The train was operated by Compagnie Internationale des Wagons-Lits (CIWL) until 1 January 1977, when it was taken over by British Rail. Motive power was provided by the Southern Railway (UK), Southern Railway and later British Railways in England, SNCF in France and from 1957, by National Railway Company of Belgium, SNCB in Belgium. When loaded onto the train ferry the train was split into sections and loaded equally on tracks on the port and starboard sides of the ship, to maintain its balance. It norm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boat Train
A boat train is a passenger train operating to a port for the specific purpose of making connection with a passenger ship, such as a ferry, ocean liner, or cruise ship. Through ticketing is normally available. __NOTOC__ Notable named boat trains *'' Admiraal de Ruijter'', – (1987–2006) *'' Benjamin Britten'', London Liverpool Street – Amsterdam Centraal (1987–?) *'' La Flèche d'Or'' (''Golden Arrow''), Paris Gare du Nord – Calais-Maritime (1929–1972) *''The Golden Arrow'', London Victoria – Dover Marine (1929–1972) *'' The Cunarder'' ** London Waterloo – Southampton Docks (Ocean Terminal) ** London Euston – Liverpool Riverside ** Glasgow Central – Greenock Prince’s Pier *'' Night Ferry'', – Paris Nord / Brussels Midi/Zuid (1936–1980) *''The Statesman'', London Waterloo – Southampton Docks (Ocean Terminal) *'' The Steam Boat'', Toronto – Port McNicoll See also *Train ferry A train ferr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Railway Company Of Belgium
The National Railway Company of Belgium (, NMBS; , SNCB; ) is the national railway company of Belgium. The company formally styles itself using the Dutch and French abbreviations NMBS/SNCB. The corporate logo designed in 1936 by Henry van de Velde consists of the linguistically neutral letter B in a horizontal oval. History NMBS/SNCB is an autonomous government company, formed in 1926 as successor to the Belgian State Railways. From 1942 to 1944, amid Nazi Germany's occupation of Belgium, the company was paid 51 million Belgian francs by the Nazi Germany to send 28 trains carrying 25,843 Jews and Roma people to Auschwitz where only 1,195 survived. The company also sent 16,000 political prisoners to concentration camps. In 2005, the company was split up into three parts: Infrabel, which manages the railway infrastructure, network operations, and network access, the public railway operator NMBS/SNCB itself to manage the freight (B-Cargo) and passenger services, and NMBS/SNCB-Hold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover (locomotive), power source is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving wheels. The most common are diesel–electric locomotives and diesel–hydraulic. Early internal combustion engine, internal combustion locomotives and railcars used kerosene and gasoline as their fuel. Rudolf Diesel patented his first compression-ignition engine in 1898, and steady improvements to the design of diesel engines reduced their physical size and improved their power-to-weight ratios to a point where one could be mounted in a locomotive. Internal combustion engines only operate efficiently within a limited power band, and while low-power gasoline engines could be coupled to mechanical transmission (mechanics), transmissions, the more powerful diesel engines required the development of new forms of transmiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Railways
''Modern Railways'' is a monthly British magazine covering the rail transport industry, which was published by Ian Allan until March 2012 and Key Publishing since then. It has been published since 1962. The magazine was based originally in Shepperton, Surrey, and Tunbridge Wells subsequently. The magazine has always been targeted at both railway professionals and serious amateurs, an aim which derives from its origins as an amalgamation of the enthusiast magazine '' Trains Illustrated'' and the industry journal ''The Locomotive'' in the hands of its first editor Geoffrey Freeman Allen. It is currently edited by Richard Clinnick. Regular contributors include Roger Ford, Ian Walmsley, Alan Williams and Tony Miles. ''Informed Sources'' is a large section written regularly by Roger Ford and ''Pan Up'' is written by Ian Walmsley. Trains Illustrated The first edition of '' Trains Illustrated'' was published at the beginning of 1946. Due to post-war paper shortages, issues 1 to 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basel
Basel ( ; ), also known as Basle ( ), ; ; ; . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine (at the transition from the High Rhine, High to the Upper Rhine). Basel is Switzerland's List of cities in Switzerland, third-most-populous city (after Zurich and Geneva), with 177,595 inhabitants within the city municipality limits. The official language of Basel is Swiss Standard German and the main spoken language is the local Basel German dialect. Basel is commonly considered to be the cultural capital of Switzerland and the city is famous for its many Museums in Basel, museums, including the Kunstmuseum Basel, Kunstmuseum, which is the first collection of art accessible to the public in the world (1661) and the largest museum of Swiss art, art in Switzerland, the Fondation Beyeler (located in Riehen), the Museum Tinguely and the Museum of Contemporary Art (Basel), Museum of Contemporary Art, which is the first public museum of contemporary art in Europe. Forty museums ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gare De Lille Flandres
Lille-Flandres station (, ) is the main railway station of Lille, capital of French Flanders. It is a terminus for SNCF Intercity and regional trains. It opened in 1842 as the ''Gare de Lille'', but was renamed in 1993 when Lille Europe station opened. There is a walking distance between the two stations, which are also adjacent stops on one of the lines of the Lille Metro. Construction The station was built by Léonce Reynaud and Sydney Dunnett for the CF du Nord. Construction began in 1869 and ended in 1892. The station front is the old front from Paris' Gare du Nord and was dismantled then reassembled in Lille at the end of the 19th century; an extra storey, as well as a large clock, were added to the original design. Dunnett added the Hôtel des Voyageurs in 1887, and the rooftop in 1892. Services The station is served by the following services: *High speed services (''TGV'') Paris - Lille *High speed services (''TGV'') Paris - Lille - Tourcoing *Intercity services ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brussels-South Railway Station
Brussels-South railway station, also known as Brussels-Midi railway station (; ), is a major railway station in Brussels, Belgium. Geographically, it is located in Saint-Gilles, Belgium, Saint-Gilles/Sint-Gillis on the border with the adjacent municipality of Anderlecht and just south of the City of Brussels. Brussels-South is one of over a dozen railway stations in Brussels, and one of the three principal rail stations in the heart of the city, the two others being Brussels Central Station, Brussels-Central and Brussels-North railway station, Brussels-North. The station, which was a terminus when it was inaugurated in 1869, became a transit station with the opening of the North–South connection in 1952. Nowadays, it is the List of railway stations in Belgium, busiest station in Belgium, and is the only Brussels stop for international high-speed rail services Eurostar (including the former Thalys) and TGV. It is operated by the National Railway Company of Belgium (SNCB/NMBS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Through Coach
In rail terminology, a through coach is a passenger car (coach) that is re-marshalled during the course of its journey. It begins the journey attached to one train, and arrives at its destination attached to another train. Through coaches save their transit passengers the need to change trains themselves. They also increase the number of direct links offered by the train operator(s). Most frequently in the form of sleeping or couchette cars, through coaches have commonly been used for long-distance journeys, especially in continental Europe, although they are much less common now than they were in the early 1970s. Example In 2010 and 2011, the Basel – Moscow sleeping car ( in 37 hours and 11 minutes) was attached successively to the following trains: * from Basel SBB to Hannover Hbf: ''CNL 472'' Basel SBB – Copenhagen; * from Hannover Hbf to Warszawa Wschodnia: ''EN 447'' Amsterdam – Warszawa Wschodnia; * from Warszawa Wschodnia to Brest: ''405'' Bohumin – Brest; w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham Railway Carriage & Wagon Company
The Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company (BRC&W) was a railway locomotive and carriage builder, founded in Birmingham, England and, for most of its existence, located at nearby Smethwick, with the factory divided by the boundary between the two places. The company was established in 1854. Production BRC&W made not only carriages and wagons, but a range of vehicles, from aeroplanes and military gliders to buses, trolleybuses and tanks. Nevertheless, it is as a builder of railway rolling stock that the company is best remembered, exporting to most parts of the new and old worlds. It supplied vehicles to all four of the pre-nationalisation "big four" railway companies ( LMS, SR, LNER and GWR), British Rail, Pullman (some of which are still in use) and Wagons-Lits, plus overseas railways with diverse requirement including Egypt, India, Iraq, Malaya, Mandate Palestine, South Africa and Nigeria. The company even built, in 1910, Argentina's presidential coach, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
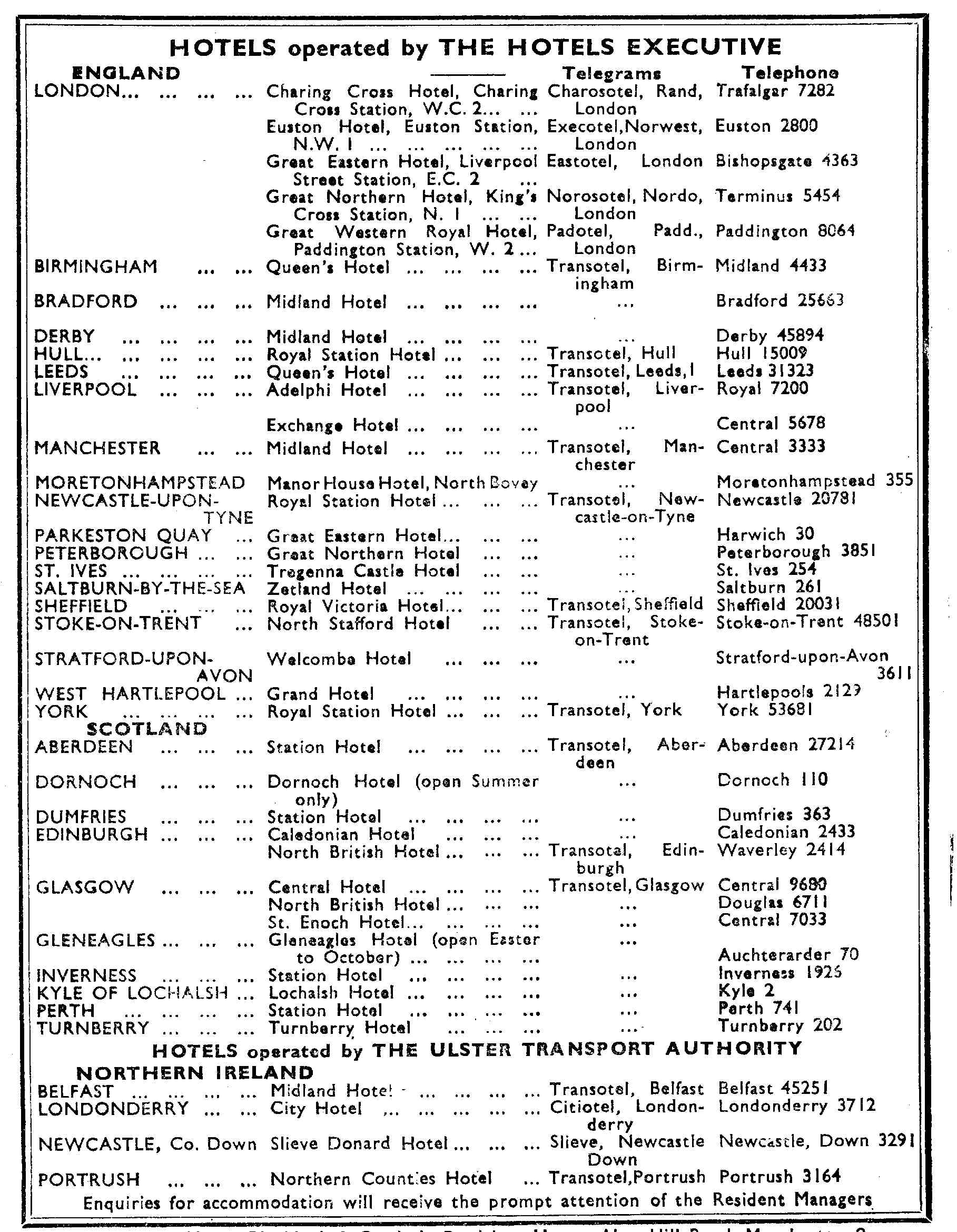
British Transport Hotels
British Transport Hotels (BTH) was the hotels and catering business of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain. Origins of the company Britain's private railway companies pioneered the concept of the railway hotel, initially at locations such as London Euston and Birmingham Curzon Street where hotels were opened at the start of trunk railway operation in 1839. Most of the railway companies followed suit, and by 1913 there were 93 railway owned hotels. The policies of the 'big four' railway companies differed considerably, with the LMS and LNER railways being the most enthusiastic. The Hotels Executive (1948–53) At the nationalisation of transport in Great Britain on 1 January 1948, and the establishment of the British Transport Commission, hotels and catering came under the control of BTC's Railway Executive. However, on 1 July 1948 they were separated from direct railway control and placed under British Transport Commission's Hotels Executive, chaired b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pullman Train (UK)
Pullman trains in Great Britain were mainline luxury railway services that operated with first-class coaches and a steward service, provided by the British Pullman Car Company (PCC) from 1874 until 1962, and then by British Railways from 1962 until 1972. Many named mainline service trains have subsequently used the word 'Pullman' in their titles, but most of these have been normal trains with increased first-class accommodation. Since 1982 however, some railtours have been operated by companies using Pullman (car or coach), Pullman coaches dating from the 1920s to 1950s to recreate the ambience of the heyday of Pullman travel. Origins The first Pullman Railway Coach to enter service in the UK was in 1874 from Bradford Forster Square railway station, Bradford Forster Square to St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras after an assembly of imports from the United States, in an operation pioneered by the Midland Railway, working with the Pullman Company in Chicago. The coach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Railways Mark 1
British Rail Mark 1 is the family designation for the first standardised designs of railway carriages built by British Railways (BR) from 1951 until 1974, now used only for charter services on the main lines or on preserved railways. Following nationalisation in 1948, BR had continued to build carriages to the designs of the "Big Four" companies (the Great Western, Southern, London, Midland and Scottish and London and North Eastern railways), and the Mark 1 was intended to be the standard carriage design for use across all lines, incorporating the best features of each of the former companies' designs. It was also designed to be much stronger than previous designs, to provide better protection for passengers in the event of a collision or derailment. The Mark 1 coaches were built in two distinct tranches: the early vehicles (1951–1960) and, from 1961 onwards, the "Commonwealth" stock – so named on account of their bogies, which were a variant of the bogie designed by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |