|
Newar Caste System
Newar caste system is the system by which Newārs, the historical inhabitants of Kathmandu Valley, are divided into groups on the basis of Vedic varna model and divided according to their hereditary occupations. First introduced at the time of the Licchavis (A.D. 300 – c. 879), the Newar caste system assumed its present shape during the medieval Malla period (A.D. 1201–1769). The Newar caste structure resembles more closely to North India North India is a geographical region, loosely defined as a cultural region comprising the northern part of India (or historically, the Indian subcontinent) wherein Indo-Aryans (speaking Indo-Aryan languages) form the prominent majority populati ... and Madhesi people, Madheshis than that of the Khas people, Khas 'Parbatiyas' in that all four Varna (Brahmin, Kshatriya, Vaishya and Shudra) and untouchables are represented. The social structure of Newars is unique as it is the last remaining example of a pre-Islamic North History of Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
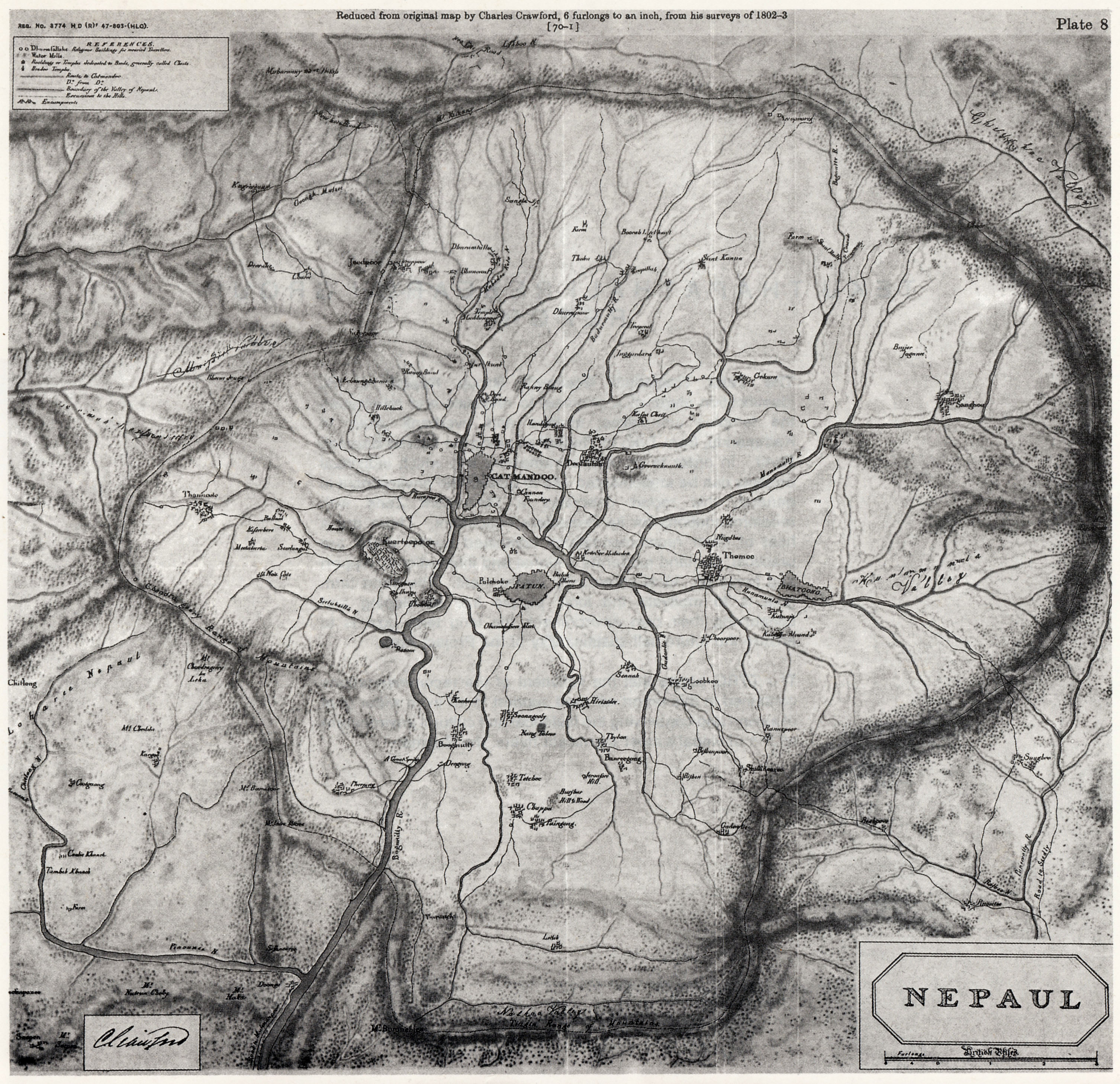
Nepaul Valley Map 1802
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, and India to the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a diverse geography, including fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and its largest city. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious, and multi-cultural state, with Nepali as the official language. The name "Nepal" is first recorded in texts from the Vedic period of the Indian subcontinent, the era in ancient Nepal when Hinduism was founded, the predominant religion of the country. In the middle of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanyakubja Brahmins
Kanyakubja Brahmins are an endogamous Brahmin community mainly found in northern India. They are classified as one of the Pancha Gauda Brahmin communities. Kanyakubja Brahmins emerged as the highest ranking subcaste of Brahmins and are known to have migrated to and colonized many areas outside their northern homeland. In the process, they created a hierarchy of subdivisions and exceedingly complex rank differentiations that correlated their ritual purity and standing with their position within the emerging sacred landscape of early medieval India inversely to the distance separating them from their homeland ~ André Wink. It seems likely that region around Kannauj, was the place of origin of the majority of migrating Brahmans throughout the medieval centuries. Origins The majority of the interviewees assert that the designation of the caste originates from the city of Kannauj, emphasizing that this name signifies a geographical association. The etymology of this caste is so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grihastha
''Gṛhastha'' (Sanskrit: गृहस्थ) literally means "being in and occupied with home, family" or "householder". It refers to the second phase of an individual's life in a four age-based stages of the Hindu asrama system. It follows celibacy (bachelor student) life stage, and embodies a married life, with the duties of maintaining a home, raising a family, educating one's children, and leading a family-centred and a dharmic social life. This stage of ''Asrama'' is conceptually followed by ''Vānaprastha'' (forest dweller, retired) and ''Sannyasa'' (renunciation).RK Sharma (1999), Indian Society, Institutions and Change, , page 28 Combined with other three life stages, Hindu philosophy considers these stages as a facet of Dharma concept, something essential to completing the full development of a human being and fulfilling all the needs of the individual and society. Ancient and medieval era texts of Hinduism consider ''Gṛhastha'' stage as the most important of all st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vajracharya
A vajrācārya (vajra + acharya, Tibetan: རྡོ་རྗེ་སློབ་དཔོན་, ''dorje lopön'', Wyl. ''rdo rje slob dpon,'' Chinese: 金剛阿闍梨, pinyin: ''jīngāng āshélì''; rōmanji: ''kongō ajari'') (alternatively, Chinese: 金剛上師, pinyin'': jīngāng shàngshī'') is a Vajrayana Buddhist master, guru or priest. It is a general term for a tantric master in Vajrayana and Mahayana Buddhist traditions, including Tibetan Buddhism, Chinese Esoteric Buddhism, Chan Buddhism, Shingon, Bhutanese Buddhism, Newar Buddhism. Tibetan Buddhism Dorje Lopön is a title given to high-level religious leaders who preside over Tibetan tantric practice. ''Dorje'' is the Tibetan equivalent of the Sanskrit ''vajra'' and therefore the term appears frequently in Tibetan terminology relating to Vajrayana Buddhism. A Dorje Lopön is usually well educated and trained in tantric practice, and is therefore a well respected figure. They might be the heads of mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Caste System
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic instance of social classification based on castes. It has its origins in ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval, early-modern, and modern India, especially in the aftermath of the collapse of the Mughal Empire and the establishment of the British Raj. Beginning in ancient India, the caste system was originally centered around ''varna'', with ''Brahmins'' (priests) and, to a lesser extent, ''Kshatriyas'' (rulers and warriors) serving as the elite classes, followed by '' Vaishyas'' (traders, merchants, and farmers) and finally '' Shudras'' (labourers). Outside of this system are the oppressed, marginalised, and persecuted ''Dalits'' (also known as " Untouchables") and '' Adivasis'' (tribals). Over time, the system became increasingly rigid, and the emergence of '' jati'' led to further entrenchment, introducing thousands of new castes and sub-castes. With the arrival of Islamic rule, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajkarnikar
Rajkarnikar (Devanagari: राजकर्णिकार) are a newar clan of confectioners and sweet makers situated in Kathmandu Valley, in Nepal. Madhikarmi (मधीकर्मी) from Bhakatpur are equivalent of Rajkarnikar. Etymology The name "Rajkarnikar" means state official. Rajkarnikars in Nepal are found mostly in Yen or Kathmandu Valley, over the regions of Kathmandu, Bhaktapur and Lalitpur (Patan in Nepali; Yela in Newari ); In 2011, their population was 83,000. Around 60,000 still reside in rural areas, and around 20,000 in urban areas. They speak Nepalbhasa. Traditional Occupation Rajkarnikars are sweet makers by tradition. They take on many responsibilities that are considered religiously important. Traditional sweets prepared include various Maris, sweets and confections. Culture Traditionally, in the caste system, they follow Newar Buddhism. Their culture, traditions, religions, beliefs and rooted to Asia, Tibe and Nepal. The worshiping o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapali (Newar Caste)
Kapali is one of the Caste of Newar community in Nepal. It is an ancient caste of Nepal. Kapali caste are found in various parts of Nepal. Newar Kapalis predominantly used to possess high tantric power. The Newar people are the historical inhabitants of the Kathmandu Valley and its surrounding areas in Nepal. Description Generally, Kapalis of Shiva Gotra are widely found in Nepal. They follow mixed Hinduism as well as Buddhism. They mostly follow Hinduism and consider Shiva as the supreme body whereas Guru Gorakhnath is considered as the supreme deity for their welfare. Kapali are taken as kid of Lord Shiva. Although, in different time period, Kapali have developed their own Tantric system. Kapali plays Myali ( a musical instrument like Flute) which has the immense power to call God in the stone idol. The musical instrument is also capable to make the rainfall from the sky as per Sadhak's power. Kapalis had served as nurse, doctor or delivery person during the Malla Dynasty of Nepal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sundhi
Sundhi also known as Sodhi or Sundi or Sudi or Sudhi or Shoundika, is an Indian caste whose traditional occupation has been brewing of alcoholic drinks. The Sundhis are included in the Other Backward Class category in the states of Bihar, Jharkhand and Odisha, though according to Suratha Kumar Malik, Sundhis of Koraput district of Odisha belong to the Dalit community, who are hooch traders and do small businesses. They are considered as Scheduled Caste in West Bengal, where they are also known as Shunri Shunri () is a Bengali Hindu caste whose traditional occupation is the distillation and selling of country wine. Population In the census of 2001, the Shunris numbered 317,543 in West Bengal West Bengal (; Bengali language, Bengali ... (except Saha).Singh, K. S. (1992). People of India: The scheduled castes. India: Anthropological Survey of India. p. 1244 References Indian castes Brewing and distilling castes Social groups of Bihar Social groups of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karnata Dynasty
Karnata was an ancient kingdom, mentioned in the great epic ''Mahabharata'', It gave the name to the South Indian state of Karnataka. References in Mahabharata Sahadeva's Military Campaign to the South of India *Mahabharata, Book 2, Chapter 30 Sahadeva conquered the town of Sanjayanti and the country of the Pashandas and the Karanatakas by means of his messengers alone, and made all of them pay tributes to him. The hero brought under his subjection and exacted tributes from the Paundrayas and the Dravidas along with the Udrakeralas and the Andhras and the Talavanas, the Kalingas and the Ushtrakarnikas, and also the delightful city of Atavi and that of the Yavanas. Nakula's Military Campaign to the West of India *Mahabharata, Book 2, Chapter 32 Nakula subjugated the whole of the desert country and the region known as Sairishaka full of plenty, as also that other one called Mahetta. And the hero had a fierce encounter with the royal sage Akrosa. And the son of Pandu lef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shresthas
The Śreṣṭha () or () is the second largest Newar caste group, occupying around 21% of overall Newar population, or about 1.1% of Nepal’s total population. It is believed that the word ''Srēṣṭha'' is derived from the Newar word ''Śeśyah'', which itself is derivation of a Sanskrit word ''Sista'' meaning 'noble', although literal meaning of the word also translated to 'best or important.' "Shrestha" itself was later adopted as the specific family surname by members of this high-caste Hindu group, although there are over 50 other recognized surnames of Srēṣṭhas. Despite their numerically low national population, their high-status and socio-economic capital puts Śreṣṭhas amongst the most socio-economically privileged and politically over-represented segments of Nepali population. Prior to Nepal’s unification, Srēṣṭha was a collective high-status title given to those Hindu clans referred to as 'Bhāro' (from ''bhārdār''/nobles) who served as the key ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannauj
Kannauj (Hindustani language, Hindustani pronunciation: ) is an ancient city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar palika, Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located 113 km (71 mi) from Etawah, 93 km (58 mi) from Kanpur, 129 km (81 mi) from Lucknow. The city's name is an evolved form of the classical name ''Kanyakubja''. During the ancient Vedic period, it was the capital city of the Pañcāla, Panchala Kingdom during the reign of king Vajrayudha. In the medieval era, it formed the core of the Kingdom of Kannauj and was ruled by multiple successive royal families. It was also known as ''Mahodaya'' during the time of Mihira Bhoja. It is situated 104 kilometres west of the state capital, Lucknow. Kannauj is famous for distilling of scents and perfumes. It is known as "India's perfume capital" and is famous for its traditional Kannauj Perfume, a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




