|
New Symphony Orchestra (London)
The New Symphony Orchestra (NSO) was founded in London in 1905 by the clarinettist Charles Draper and the flautist Eli Hudson. After ten years it became the orchestra of the Royal Albert Hall, and continued under that name until 1928, after which it resumed its original name, giving concerts during the 1930s. Thomas Beecham was succeeded as the orchestra's principal conductor by Landon Ronald. With Ronald the orchestra played for the Gramophone Company (HMV) in what were later recognised as the first extensive experiments in symphonic recording, beginning in the days of acoustic recording and continuing into the electrical era. History In the early years of the 20th century there was only one permanent orchestra in London – the London Symphony Orchestra (LSO). The orchestras of Covent Garden, the Philharmonic Society and the Queen's Hall were ad hoc ensembles, with players engaged individually for each concert or for a season. Vacancies occurred in the LSO's ranks only rarely, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen's Hall
The Queen's Hall was a concert hall in Langham Place, London, Langham Place, London, opened in 1893. Designed by the architect Thomas Knightley, it had room for an audience of about 2,500 people. It became London's principal concert venue. From 1895 until 1941, it was the home of the The Proms, promenade concerts ("The Proms") founded by Robert Newman (impresario), Robert Newman together with Henry Wood. The hall had drab decor and cramped seating but superb acoustics. It became known as the "musical centre of the [British] British Empire, Empire", and several of the leading musicians and composers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries performed there, including Claude Debussy, Edward Elgar, Maurice Ravel and Richard Strauss. In the 1930s, the hall became the main London base of two new orchestras, the BBC Symphony Orchestra and the London Philharmonic Orchestra. These two ensembles raised the standards of orchestral playing in London to new heights, and the hall's resident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm Sargent
Sir Harold Malcolm Watts Sargent (29 April 1895 – 3 October 1967) was an English conductor, organist and composer widely regarded as Britain's leading conductor of choral works. The musical ensembles with which he was associated included the Ballets Russes, the Huddersfield Choral Society, the Royal Choral Society, the D'Oyly Carte Opera Company, and the London Philharmonic Orchestra, London Philharmonic, The Hallé, Hallé, Royal Liverpool Philharmonic, Liverpool Philharmonic, BBC Symphony Orchestra, BBC Symphony and Royal Philharmonic Orchestra, Royal Philharmonic orchestras. Sargent was held in high esteem by choirs and instrumental soloists, but because of his high standards and a statement that he made in a 1936 interview disputing musicians' rights to tenure, his relationship with orchestral players was often uneasy. Despite this, he was co-founder of the London Philharmonic, was the first conductor of the Liverpool Philharmonic as a full-time ensemble, and played a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov. At the time, his name was spelled , which he romanized as Nicolas Rimsky-Korsakow; the BGN/PCGN transliteration of Russian is used for his name here; ALA-LC system: , ISO 9 system: .. (18 March 1844 – 21 June 1908) was a Russian composer, a member of the group of composers known as The Five. He was a master of orchestration. His best-known orchestral compositions—'' Capriccio Espagnol'', the '' Russian Easter Festival Overture'', and the symphonic suite '' Scheherazade''—are staples of the classical music repertoire, along with suites and excerpts from some of his fifteen operas. ''Scheherazade'' is an example of his frequent use of fairy-tale and folk subjects. Rimsky-Korsakov believed in developing a nationalistic style of classical music, as did his fellow composer Mily Balakirev and the critic Vladimir Stasov. This style employed Russian folk song and lore along with exotic harmonic, melodic and rhythmic elements in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Midsummer Night's Dream (Mendelssohn)
On two occasions, Felix Mendelssohn composed music for William Shakespeare's play ''A Midsummer Night's Dream'' (in German ''Ein Sommernachtstraum''). First in 1826, near the start of his career, he wrote a concert overture ( Op. 21). Later, in 1842, five years before his death, he wrote incidental music (Op. 61) for a production of the play, into which he incorporated the existing overture. The incidental music includes the famous " Wedding March". Overture The overture in E major, Op. 21, was written by Mendelssohn at 17 years and 6 months old (it was finished on 6 August 1826).'' Grove's Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', 5th ed., 1954 The near-contemporary music scholar George Grove called it "the greatest marvel of early maturity that the world has ever seen in music". It was written as a concert overture, not associated with any performance of the play. The overture was written after Mendelssohn had read a German translation of the play in 1826. The translation was by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
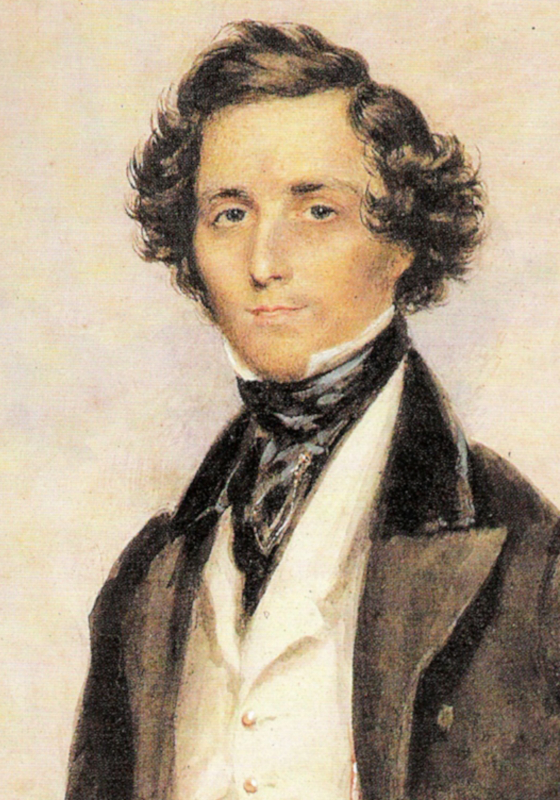
Mendelssohn
Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy (3 February 18094 November 1847), widely known as Felix Mendelssohn, was a German composer, pianist, organist and conductor of the early Romantic period. Mendelssohn's compositions include symphonies, concertos, piano music, organ music and chamber music. His best-known works include the overture and incidental music for ''A Midsummer Night's Dream'' (which includes his " Wedding March"), the '' Italian'' and '' Scottish'' Symphonies, the oratorios '' St. Paul'' and '' Elijah'', the ''Hebrides'' Overture, the mature Violin Concerto, the String Octet, and the melody used in the Christmas carol "Hark! The Herald Angels Sing". Mendelssohn's '' Songs Without Words'' are his most famous solo piano compositions. Mendelssohn's grandfather was the Jewish philosopher Moses Mendelssohn, but Felix was initially raised without religion until he was baptised aged seven into the Reformed Christian church. He was recognised early as a musical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer Gynt
''Peer Gynt'' (, ) is a five-Act (drama), act play in verse written in 1867 by the Norwegian dramatist Henrik Ibsen. It is one of Ibsen's best known and most widely performed plays. ''Peer Gynt'' chronicles the journey of its title character from the Norwegian mountains to the North African desert and back. According to Klaus Van Den Berg, "its origins are Romanticism, Romantic, but the play also anticipates the fragmentations of emerging modernism" and the "cinematic script blends poetry with social satire and realistic scenes with Surrealism, surreal ones."Klaus Van Den Berg, "Peer Gynt" (review), ''Theatre Journal'' 58.4 (2006) 684–687 ''Peer Gynt'' has also been described as the story of a life based on procrastination and avoidance. Ibsen wrote ''Peer Gynt'' in deliberate disregard of the limitations that the conventional stagecraft of the Nineteenth-century theatre, 19th century imposed on drama. Its forty scenes move uninhibitedly in time and space and between conscious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edvard Grieg
Edvard Hagerup Grieg ( , ; 15 June 18434 September 1907) was a Norwegian composer and pianist. He is widely considered one of the leading Romantic music, Romantic era composers, and his music is part of the standard classical repertoire worldwide. His use of Music of Norway, Norwegian folk music in his own compositions brought the music of Norway to fame, as well as helping to develop a Norwegian romantic nationalism, national identity, much as Jean Sibelius did in Finland and Bedřich Smetana in Bohemia. Grieg is the most celebrated person from the city of Bergen, with numerous statues that depict his image and many cultural entities named after him: the city's largest concert building (Grieg Hall), its most advanced music school (Grieg Academy) and its professional choir (Edvard Grieg Kor). The Edvard Grieg Museum at Grieg's former home, Troldhaugen, is dedicated to his legacy. Background Edvard Hagerup Grieg was born in Bergen, Norway. His parents were Alexander Grieg (1806 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylvia (ballet)
''Sylvia'', originally ''Sylvia, ou La nymphe de Diane'', is a full-length classical ballet in two or three act (theatre), acts, first choreography, choreographed by Louis Mérante to music by Léo Delibes. The ballet's premiere took place on 14 June 1876 at the Palais Garnier, but was largely unnoticed by the critics. The first seven productions were commercially unsuccessful, but the 1952 revival, choreographed by Frederick Ashton, popularized the work. Productions in 1997, 2004, 2005, and 2009 productions were all based on Ashton's choreography. History Preparations The origins of the ballet ''Sylvia'' are in the Italian poet Torquato Tasso, Tasso's play ''Aminta'' (1573), which provided the basic plot for the French composer Leo Delibes to set to music. Jules Barbier and Jacques de Reinach, Baron de Reinach adapted this for the Paris Opera Ballet, Paris Opera. The piano arrangement was composed in 1876 and the Suite (music), orchestral suite was done in 1880. In 1875, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coppélia
''Coppélia'' (sometimes subtitled: ''La Fille aux Yeux d'Émail'' (The Girl with the Enamel Eyes)) is a comic ballet from 1870 originally choreographed by Arthur Saint-Léon to the music of Léo Delibes, with libretto by Charles-Louis-Étienne Nuitter. Nuitter's libretto and mise-en-scène was based upon E. T. A. Hoffmann's short story ''Der Sandmann'' (''The Sandman''). In Greek, ''κοπέλα'' (or ''κοπελιά'' in some dialects) means ''young woman''. ''Coppélia'' premiered on 25 May 1870 at the Théâtre Impérial de l'Opéra, with the 16-year-old Giuseppina Bozzacchi in the principal role of Swanhilda and ballerina Eugénie Fiocre playing the part of Frantz '' en travesti''. The costumes were designed by Paul Lormier and Alfred Albert, the scenery by Charles-Antoine Cambon (Act I, scene 1; Act II, scene 1), and Édouard Desplechin and Jean-Baptiste Lavastre (Act I, scene 2). The ballet's first flush of success was interrupted by the Franco-Prussian War and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prélude à L'après-midi D'un Faune
''Prélude à l'Après-midi d'un faune'' ( L. 86), known in English as ''Prelude to the Afternoon of a Faun'', is a symphonic poem for orchestra by Claude Debussy, approximately 10 minutes in duration. It was composed in 1894 and first performed in Paris on 22 December 1894, conducted by Gustave Doret. The flute solo was played by Georges Barrère. The composition was inspired by the poem '' L'après-midi d'un faune'' by Stéphane Mallarmé. It is one of Debussy's most famous works and is considered a turning point in the history of Western art music, as well as a masterpiece of Impressionist composition. Pierre Boulez considered the score to be the beginning of modern music, observing that "the flute of the faun brought new breath to the art of music." The work is dedicated to the composer Raymond Bonheur, son of the painter Auguste Bonheur. Debussy's work later provided the basis for the ballet '' Afternoon of a Faun'' choreographed by Vaslav Nijinsky and a later versio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
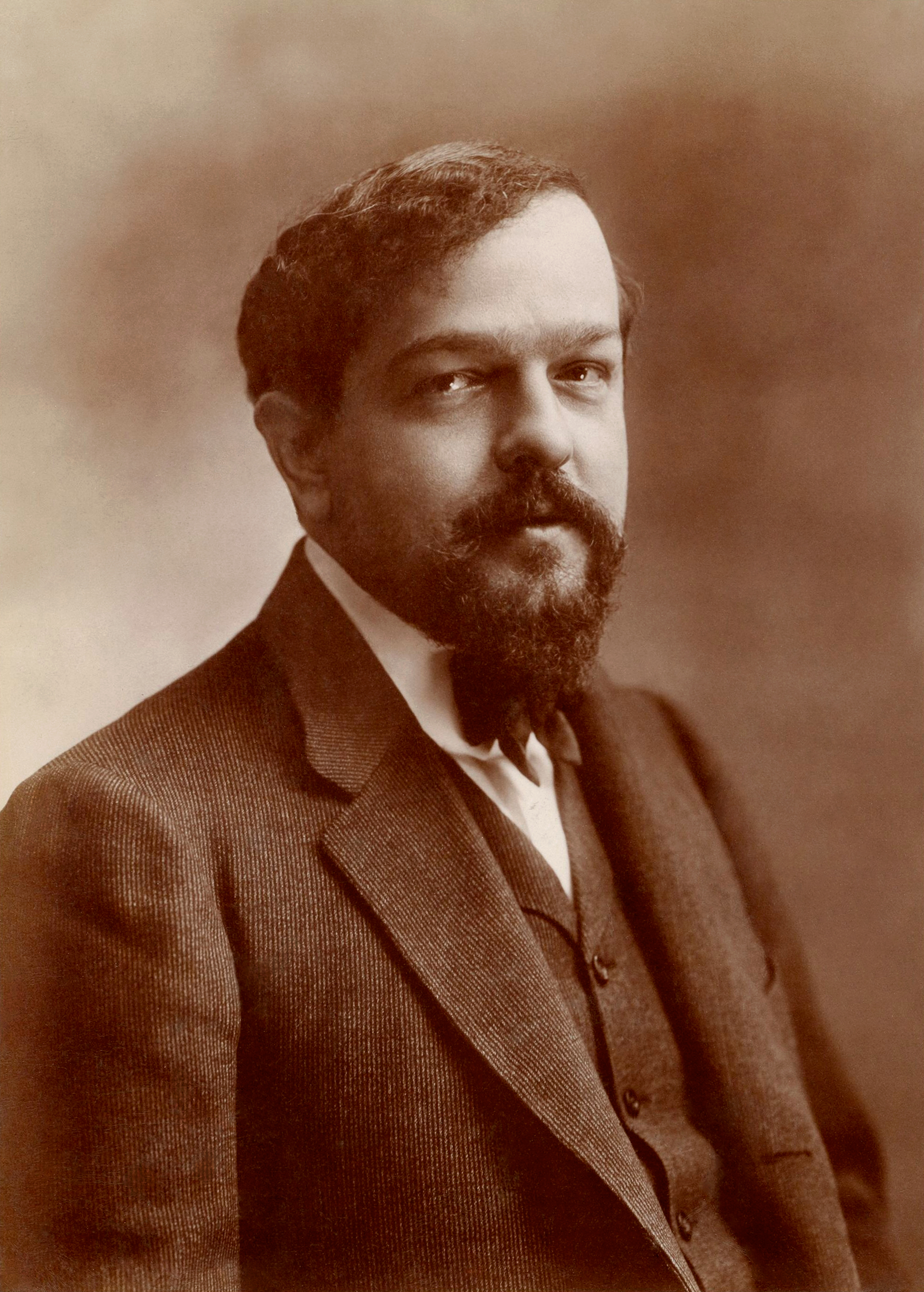
Debussy
Achille Claude Debussy (; 22 August 1862 – 25 March 1918) was a French composer. He is sometimes seen as the first Impressionism in music, Impressionist composer, although he vigorously rejected the term. He was among the most influential composers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Born to a family of modest means and little cultural involvement, Debussy showed enough musical talent to be admitted at the age of ten to France's leading music college, the Conservatoire de Paris. He originally studied the piano, but found his vocation in innovative composition, despite the disapproval of the Conservatoire's conservative professors. He took many years to develop his mature style, and was nearly 40 when he achieved international fame in 1902 with the only opera he completed, ''Pelléas et Mélisande (opera), Pelléas et Mélisande''. Debussy's orchestral works include ''Prélude à l'après-midi d'un faune'' (1894), ''Nocturnes (Debussy), Nocturnes'' (1897–1899 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |