|
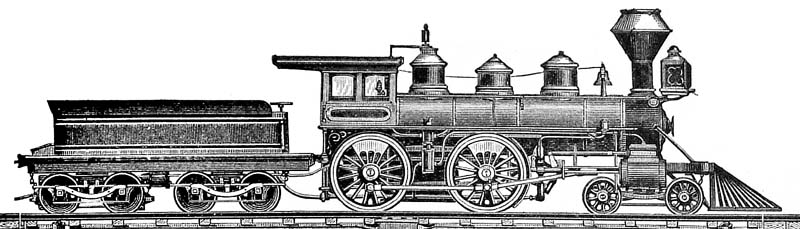
New South Wales Z17 Class Locomotive
The 17 class (formally H.373 class) was a class of steam locomotive built by the Vulcan Foundry for the New South Wales Government Railways of Australia. History Ordered from the Vulcan Foundry, 12 were placed in service in 1887. They had the 4-4-0 wheel arrangement that most locomotives had at the time. Shortly after delivery, the class leader was tested against the Baldwin Locomotive Works built L304 class to see which one could make a faster and better run across the Blue Mountains to Eskbank, with the Baldwin locomotive judged superior. They were also intended to haul passenger service on the steeply graded Sydney to Newcastle and Kiama lines. They proved unpopular with both locomotive crews because of rough riding and track maintenance staff because of their high axle load and were displaced from mainline working and relegated to branch line work following the arrival of the P6 class (C32 class). In 1905/06, new boilers with Belpaire fireboxes were fitted, the smokeboxes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulcan Foundry
The Vulcan Foundry Limited was an English locomotive builder sited at Newton-le-Willows, Lancashire (now Merseyside). History The Vulcan Foundry opened in 1832, as Charles Tayleur and Company to produce girders for bridges, switches, crossings and other ironwork following the opening of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. Due to the distance from the locomotive works in Newcastle-upon-Tyne, it seemed preferable to build and support them locally. In 1832, Robert Stephenson became a partner for a few years. The company had become The Vulcan Foundry Company in 1847 and acquired limited liability in 1864. From the beginning of 1898, the name changed again to The Vulcan Foundry Limited, dropping the word 'company.' Vulcan Halt The site had its own railway station, Vulcan Halt, on the former Warrington and Newton Railway line from to . The wooden-platformed halt was opened on 1 November 1916 by the London and North Western Railway, and closed on 12 June 1965. Steam locom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiama, New South Wales
Kiama () is a coastal town 120 kilometres south of Sydney in the Illawarra. One of the main tourist attractions is the Kiama Blowhole. Kiama features several popular surfing beaches and caravan parks, and numerous alfresco cafes and restaurants. Its proximity to the south of Sydney makes it an attractive destination for many day-trippers and weekenders. History Kiama was the site of two strong volcanic flows, called the Gerringong Volcanics, which came out of Saddleback Mountain, now a collapsed volcanic vent. The Kiama Blowhole is part of an erosion process on the more recent rock, formed into columnar basalt, or latite. Before the cedar-getters (comprising ex-convicts, convicts and runaways, some with cedar licences and many without) arrived in the area around 1810, the local Indigenous Australians, Wodi Wodi of the language group Dharawal, had been using the land for thousands of years, moving every six weeks or so in family groups. This is supported by a midden of sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gauge Locomotives Of Australia
Standard may refer to: Symbols * Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs * Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification Norms, conventions or requirements * Standard (metrology), an object that bears a defined relationship to a unit of measure used for calibration of measuring devices * Standard (timber unit), an obsolete measure of timber used in trade * Breed standard (also called bench standard), in animal fancy and animal husbandry * BioCompute Standard, a standard for next generation sequencing * ''De facto'' standard, product or system with market dominance * Gold standard, a monetary system based on gold; also used metaphorically for the best of several options, against which the others are measured * Internet Standard, a specification ratified as an open standard by the Internet Engineering Task Force * Learning standards, standards applied to education content * Standard displacement, a naval term describing the we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1887
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NSWGR Steam Locomotive Classification
In the first 36 years of its existence, the NSW Railways introduced 42 separate classes of locomotives. The appointment by the Premier of New South Wales, Henry Parkes of Mr E.M.G Eddy as Chief Commissioner in 1888 created an independent railway department and saw the following 36 years with only sixteen new classes produced.New South Wales Department of Railways Archives Classification Steam Locomotive classification on the New South Wales Government Railways The New South Wales Government Railways (NSWGR) was the agency of the Government of New South Wales that administered rail transport in New South Wales, Australia, between 1855 and 1932. Management The agency was managed by a range of diffe ... had three distinct classification systems. From 1855 to 1890 (numerical) The classification was taken from the road number given to the first engine in each class. The engines attached to the then isolated Northern section had the terminal letter "N" added to the road numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirlmere, New South Wales
Thirlmere is a small semi-rural town in the Macarthur Region of New South Wales, Australia, in Wollondilly Shire. Popularly known for its railway origins, the town is located 89 km south west of Sydney (about a 60-minute drive), one third of the distance from Sydney to Canberra. At the , Thirlmere had a population of 4,046. Thirlmere was previously known as ''Village of Thirlmere'' and was originally named after Thirlmere in England. History The Thirlmere area was first explored by the British in 1798, whose attention was focussed more on the Thirlmere Lakes area and finding an alternate route north towards Bathurst. Thirlmere boomed with the creation of the Great Southern Railway in 1863 to 1867, when the area was blanketed in tents to house the many railway workers that came to the area to work. Thirlmere was valued mostly for the proximity of the Thirlmere Lakes (then called Picton Lakes) which were used to provide water for the steam trains. During this period Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Heritage NSW
In 2013, Transport Heritage NSW was established by the Government of New South Wales to manage the State’s rail heritage collection and provide support to the broader transport (bus, tram, rail) heritage sector in NSW following an independent review. History In May 2013, Minister for Transport Gladys Berejiklian acknowledged the importance of steam locomotive 3801, stating it would be a priority of Transport Heritage NSW to return it to service. On 10 December 2013, a majority of the members of the New South Wales Rail Transport Museum voted in support of the creation of Transport Heritage NSW. Other transport heritage groups also expressed concern for their future existence. Peter Lowry was appointed as chairperson of the board and the nominated chief executive of Transport Heritage NSW, Andrew Killingsworth has been seen as a political appointment. In February 2016, Andrew Moritz was appointed as the new chief executive following the resignation of Andrew Killingsworth. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belpaire Firebox
The Belpaire firebox is a type of firebox used on steam locomotives. It was invented by Alfred Belpaire of Belgium in 1864. Today it generally refers to the shape of the outer shell of the firebox which is approximately flat at the top and square in cross-section, indicated by the longitudinal ridges on the top sides. However, it is the similar square cross-section inner firebox which provides the main advantages of this design i.e. it has a greater surface area at the top of the firebox where the heat is greatest, improving heat transfer and steam production, compared with a round-top shape. The flat firebox top would make supporting it against pressure more difficult (e.g. by means of girders, or stays) compared to a round-top. However, the use of a similarly shaped square outer boiler shell allows simpler perpendicular stays to be used between the shells. The Belpaire outer firebox is, nevertheless, more complicated and expensive to manufacture than a round-top version. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales C32 Class Locomotive
The C32 class was a class of steam locomotives built for the New South Wales Government Railways of Australia. History Introduction When the new Chief CommissionerEdward Eddy took office in 1888, he was anxious to have additional locomotives manufactured within the Colony, and the Government sought the formation of a manufacturing company in New South Wales by interested parties. When this failed, designs were prepared prior to inviting tenders in England. Beyer, Peacock and Company was selected to build the new locomotives. The first batch of 50 locomotives were delivered between February 1892 and July 1893. They became known as the ''Manchester Engines''. At the request of the Railway Commissioners, the builders altered the last two engines of the first batch to operate as compounds, but these did not prove satisfactory and during 1901 were converted to 2-cylinders. The particular compound arrangement was never used in another locomotive, before or since. Further orders ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle, New South Wales
Newcastle ( ; Awabakal: ) is a metropolitan area and the second most populated city in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It includes the Newcastle and Lake Macquarie local government areas, and is the hub of the Greater Newcastle area, which includes most parts of the local government areas of City of Newcastle, City of Lake Macquarie, City of Cessnock, City of Maitland and Port Stephens Council. Located at the mouth of the Hunter River, it is the predominant city within the Hunter Region. Famous for its coal, Newcastle is the largest coal exporting harbour in the world, exporting 159.9 million tonnes of coal in 2017. Beyond the city, the Hunter Region possesses large coal deposits. Geologically, the area is located in the central-eastern part of the Sydney Basin. History Aboriginal history Newcastle and the lower Hunter Region were traditionally occupied by the Awabakal and Worimi Aboriginal people, who called the area Malubimba. Based on Aboriginal lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, pp. 46-. Almost every major railroad that operated in North America in the first half of the 19th century owned and operated locomotives of this type. The first use of the name ''American'' to describe locomotives of this wheel arrangement was made by ''Railroad Gazette'' in April 1872. Prior to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)