|
New Mexico Museum Of Space History
The New Mexico Museum of Space History is a museum and planetarium complex in Alamogordo, New Mexico, United States, dedicated to artifacts and displays related to space flight and the Space Age. It includes the International Space Hall of Fame. The Museum of Space History highlights the role that New Mexico has had in the U. S. space program, and is one of eight museums administered by the New Mexico Department of Cultural Affairs. The museum has been accredited by American Alliance of Museums since 1993. The museum is also a Smithsonian Affiliate. The museum is the resting place of Ham, the chimpanzee who, in 1961, became the first great ape to fly into space. Exhibits Main building The museum includes exhibits about the planets of the Solar System, space flight and the primates that were used in early space flight experiments conducted by the United States. The museum holds mock-ups and training units of many important space artifacts such as satellites, the Space Shuttle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alamogordo, New Mexico
Alamogordo () is a city in and the county seat of Otero County, New Mexico, United States. A city in the Tularosa Basin of the Chihuahuan Desert, it is bordered on the east by the Sacramento Mountains and to the west by Holloman Air Force Base. The population was 31,384 as of the 2020 census. Alamogordo is widely known for its connection with the 1945 Trinity test, which was the first ever explosion of an atomic bomb. Humans have lived in the Alamogordo area for at least 11,000 years. The present settlement, established in 1898 to support the construction of the El Paso and Northeastern Railroad, is an early example of a planned community. The city was incorporated in 1912. Tourism became an important economic factor with the creation of White Sands National Monument in 1933, which is still one of the biggest attractions of the city today. During the 1950s and 1960s, Alamogordo was an unofficial center for research on pilot safety and the developing United States' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clyde W
Clyde may refer to: People and fictional characters * Clyde (given name), a list of people and fictional characters * Clyde (surname), including a list of people * Walt Frazier (born 1945), American basketball player nicknamed "Clyde" * Colin Campbell, 1st Baron Clyde (1792–1863), Scottish field marshal * James Avon Clyde, Lord Clyde (1863–1944), Scottish Conservative politician and judge * James Latham Clyde, Lord Clyde (1898–1975), Scottish Unionist politician and judge * James Clyde, Baron Clyde (1932–2009), Scottish judge in the House of Lords Places Australia * Clyde, New South Wales, a suburb of Sydney * Clyde County, New South Wales, a cadastral division * Clyde, Victoria, a suburb of Melbourne * Clyde River, New South Wales * Clyde River (Tasmania) * Electoral district of Clyde, a former electoral district of the Legislative Assembly Canada * Clyde, Alberta, a village * Clyde, Ontario, a town in Waterloo * Clyde Township, a geographic township in the munici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Baseball Hall Of Fame And Museum
The National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum is a history museum and hall of fame in Cooperstown, New York, operated by a private foundation. It serves as the central collection and gathering space for the history of baseball in the United States displaying baseball-related artifacts and exhibits, honoring those who have excelled in baseball positions, playing, manager (baseball), managing, and serving the sport. The Hall's motto is "Preserving History, Honoring Excellence, Connecting Generations". Cooperstown is often used as shorthand (or a Metonymy, metonym) for the National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum. The museum also established and manages the process for honorees into the Hall of Fame. The Hall of Fame was established in 1939 by Stephen Carlton Clark, an heir to the Singer Sewing Machine Company, Singer Sewing Machine fortune. Clark sought to bring tourists to the village hurt by the Great Depression, which reduced the local tourist trade, and Prohibition in the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed X-7
The Lockheed X-7 (dubbed the "Flying Stove Pipe") is an American unmanned test bed of the 1950s for ramjet engines and missile guidance technology. It was the basis for the later Lockheed AQM-60 Kingfisher, a system used to test American air defenses against nuclear missile attack. Early development Development of the Kingfisher was first initiated in December 1946. The X-7 was called into production by the United States Air Force requirement for the development of an unmanned ramjet test plane with a top speed of at least . The X-7 project was developed under the AMC designator MX-883 and was given in the Lockheed in-house designation L-171. The L-171 was initially designated the PTV-A-1 by the USAF but was later designated the X-7 in 1951. Despite its first launch being a failure, after re-development of the original ramjet, following test flights were successful. A total of 130 X-7 flights were conducted from April 1951 to July 1960. Purpose The X-7 laid the foundation for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upham, New Mexico
Upham ( ) is an inhabited, unincorporated community and place in Sierra County, New Mexico, United States. It has gained recognition for being near the site for the Spaceport America facility being developed by the New Mexico Spaceport Authority. This will be Virgin Galactic's world headquarters and mission control location. Upham is located approximately 30 miles east of Truth or Consequences, and 45 miles north of Las Cruces, in the southern part of the state above sea level. Virgin Galactic is the first space tourism Space tourism is human space travel for recreational purposes. There are several different types of space tourism, including orbital, suborbital and lunar space tourism. Tourists are motivated by the possibility of viewing Earth from space, ... company to develop commercial flights into space. Sub-orbital commercial space launches began in 2007. Education Truth or Consequences Municipal Schools is the school district for the entire county. Text l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceport America
Spaceport America, formerly the Southwest Regional Spaceport, is an FAA-licensed spaceport located on of State Trust Land in the Jornada del Muerto desert basin north of Las Cruces, New Mexico, and southeast of Truth or Consequences. With Virgin Galactic's launch of the VSS ''Unity'', with three people aboard, on May 22, 2021, New Mexico became the third US state to launch humans into space after California and Florida. Spaceport America is "the world's first purpose-built commercial spaceport", designed and constructed specifically for commercial users, that had not previously been an airport or federal infrastructure of any kind. The site is built to accommodate both vertical and horizontal launch aerospace vehicles, as well as an array of non-aerospace events and commercial activities. Spaceport America is owned and operated by the State of New Mexico, via a state agency, the New Mexico Spaceport Authority. The first rocket launch at Spaceport America occurred on Sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seat Belt
A seat belt, also known as a safety belt or spelled seatbelt, is a vehicle safety device designed to secure the driver or a passenger of a vehicle against harmful movement that may result during a collision or a sudden stop. A seat belt reduces the likelihood of death or serious injury in a traffic collision by reducing the force of secondary impacts with interior strike hazards, by keeping occupants positioned correctly for maximum effectiveness of the airbag (if equipped), and by preventing occupants being ejected from the vehicle in a crash or if the vehicle rolls over. When in motion, the driver and passengers are traveling at the same speed as the vehicle. If the vehicle suddenly halts or crashes, the occupants continue at the same speed the vehicle was going before it stopped. A seat belt applies an opposing force to the driver and passengers to prevent them from falling out or making contact with the interior of the car (especially preventing contact with, or going ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daisy Outdoor Products
Daisy Outdoor Products (known primarily as Daisy) is an American airgun manufacturer known particularly for their lines of BB guns. It was formed in 1882 initially as the Plymouth Iron Windmill Company in Plymouth, Michigan, to manufacture steel windmills, and from 1888 started bundling BB-caliber air guns with each windmill purchase as a sales promotion. With the unrivaled popularity of their 1888-model Daisy BB Guns, the company changed the name to Daisy Manufacturing Company in 1895 and switched their business to solely producing air guns for sale. Throughout the 20th century, Daisy has been known as a company that makes and sells BB guns and pellet youth rifles. Their Red Ryder BB Gun is perhaps the best known and longest production item, which has been featured in many TV shows and movies since its introduction in the spring of 1940. History The company started in 1882 by watchmaker and inventor Clarence Hamilton in Plymouth, Michigan, as the Plymouth Iron Windmill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Columbia Disaster
On Saturday, February 1, 2003, Space Shuttle Columbia, Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disintegrated as it Atmospheric entry, re-entered the atmosphere over Texas and Louisiana, killing all seven astronauts on board. It was the second List of Space Shuttle missions, Space Shuttle mission to end in disaster, after the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, loss of ''Challenger'' and crew in 1986. The mission, designated STS-107, was the twenty-eighth flight for the orbiter, the 113th flight of the Space Shuttle fleet and the 88th after the ''Challenger'' disaster. It was dedicated to research in various fields, mainly on board the SpaceHab module inside the shuttle's payload bay. During launch, a piece of the Polyurethane foam, insulating foam broke off from the Space Shuttle external tank and struck the Space Shuttle thermal protection system, thermal protection system tiles on the Space Shuttle orbiter, orbiter's left wing. Similar foam shedding had occurred during previous Space Shu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Challenger Disaster
On January 28, 1986, the Space Shuttle Challenger, Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' broke apart 73 seconds into its flight, killing all seven crew members aboard. The spacecraft disintegrated above the Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of Cape Canaveral, Florida, at 16:39:13Coordinated Universal Time, UTC (11:39:13a.m. Eastern Time Zone, EST, local time at the launch site). It was the first fatal accident involving an List of space programs of the United States, American spacecraft while in flight. The mission, designated STS-51-L, was the 10th flight for the Space Shuttle orbiter, orbiter and the 25th flight of the Space Shuttle fleet. The crew was scheduled to deploy a commercial communications satellite and study Halley's Comet while they were in orbit, in addition to taking schoolteacher Christa McAuliffe into space under the Teacher in Space Project. The latter task resulted in a higher-than-usual media interest in and coverage of the mission; the launch and subsequent disaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
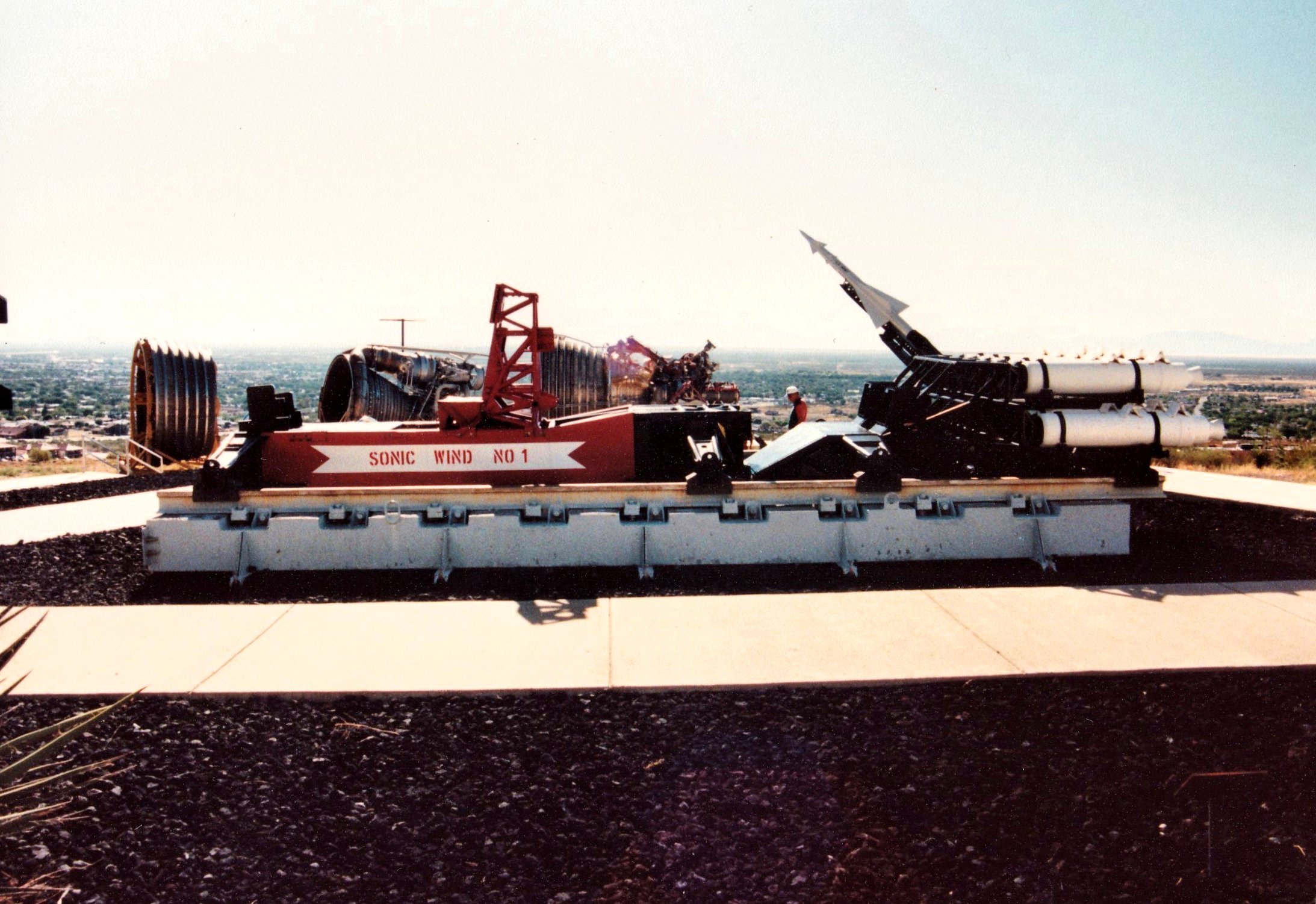
Rocket Sled
A rocket sled is a test platform that slides along a track (e.g. set of rails), propelled by rockets. A rocket sled differs from a rocket car in not using wheels; at high speeds wheels would spin to pieces due to the extreme centrifugal forces. Apart from rare examples running on snow or ice (such as Max Valier's RAK BOBs of the late 1920s and Harry Bull's BR-1 in 1931), most rocket sleds run on a track. Although some rocket sleds ride on single beams or rails, most use a pair of rails. Standard gauge (1.435 m / 56.5 in) is common but sled tracks of narrower or wider gauge also exist. The rail cross-section profile is usually that of a Vignoles rail, commonly used for railroads. Sliding pads, called "slippers", are curved around the head of the rails to prevent the sled from flying off the track. Air cushions and magnetic levitation have also been used as alternatives, with potential benefits including reduced sled vibration. A rocket sled holds the land-based speed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Stapp
John Paul Stapp (July 11, 1910 – November 13, 1999) was an American career U.S. Air Force officer, flight surgeon, physician, biophysicist, and pioneer in studying the effects of acceleration forces on humans. He was a colleague and contemporary of Chuck Yeager, and became known as "the fastest man on earth". His work on Project Manhigh pioneered many developments for the US space program. Early years Born in Salvador de Bahia, Brazil, Stapp was the eldest of four sons of Reverend Charles Franklin Stapp and Mrs. Mary Louise Shannon, Baptist missionaries. He studied in Texas at Brownwood High School in Brownwood and San Marcos Baptist Academy in San Marcos. In 1931, Stapp received a bachelor's degree from Baylor University in Waco, an MA from Baylor in 1932, a PhD in Biophysics from the University of Texas at Austin in 1940, and an MD from the University of Minnesota, Twin Cities, in 1944. He interned for one year at St. Mary's Hospital in Duluth, Minnesota. Stapp w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |