|
Negative Priming
Negative priming is an implicit memory effect in which prior exposure to a stimulus unfavorably influences the response to the same stimulus. It falls under the category of priming, which refers to the change in the response towards a stimulus due to a subconscious memory effect. Negative priming describes the slow and error-prone reaction to a stimulus that is previously ignored.Mayr, S. & A. Buchner (2007) Negative priming as a memory phenomenon—A review of 20 years of negative priming research. Zeitschrift für Psychologie, 215, 35–51. For example, a subject may be imagined trying to pick a red pen from a pen holder. The red pen becomes the target of attention, so the subject responds by moving their hand towards it. At this time, they mentally block out all other pens as distractors to aid in closing in on just the red pen. After repeatedly picking the red pen over the others, switching to the blue pen results in a momentary delay picking the pen out (however, there is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pens
PEN may refer to: * (National Ecological Party), former name of the Brazilian political party Patriota (PATRI) *PEN International, a worldwide association of writers **English PEN, the founding centre of PEN International **PEN America, located in New York City **PEN Center USA, part of PEN America ** PEN Canada, Toronto **PEN Hong Kong **Sydney PEN, one of three Australian PENs *PEN-International, Postsecondary Education Network International, an international partnership of colleges for those with hearing impairment *Penang International Airport, Malaysia, IATA airport code: PEN *Penarth railway station, Wales, station code: PEN *Peruvian sol, ISO 4217 currency code PEN *, the system of national executive power embodied in the President of Argentina *Polyethylene naphthalate, a polyester *Private Enterprise Number, an organisation identifier *Protective earth neutral in electrical earthing system An earthing system (UK and IEC) or grounding system (US) connects specific parts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
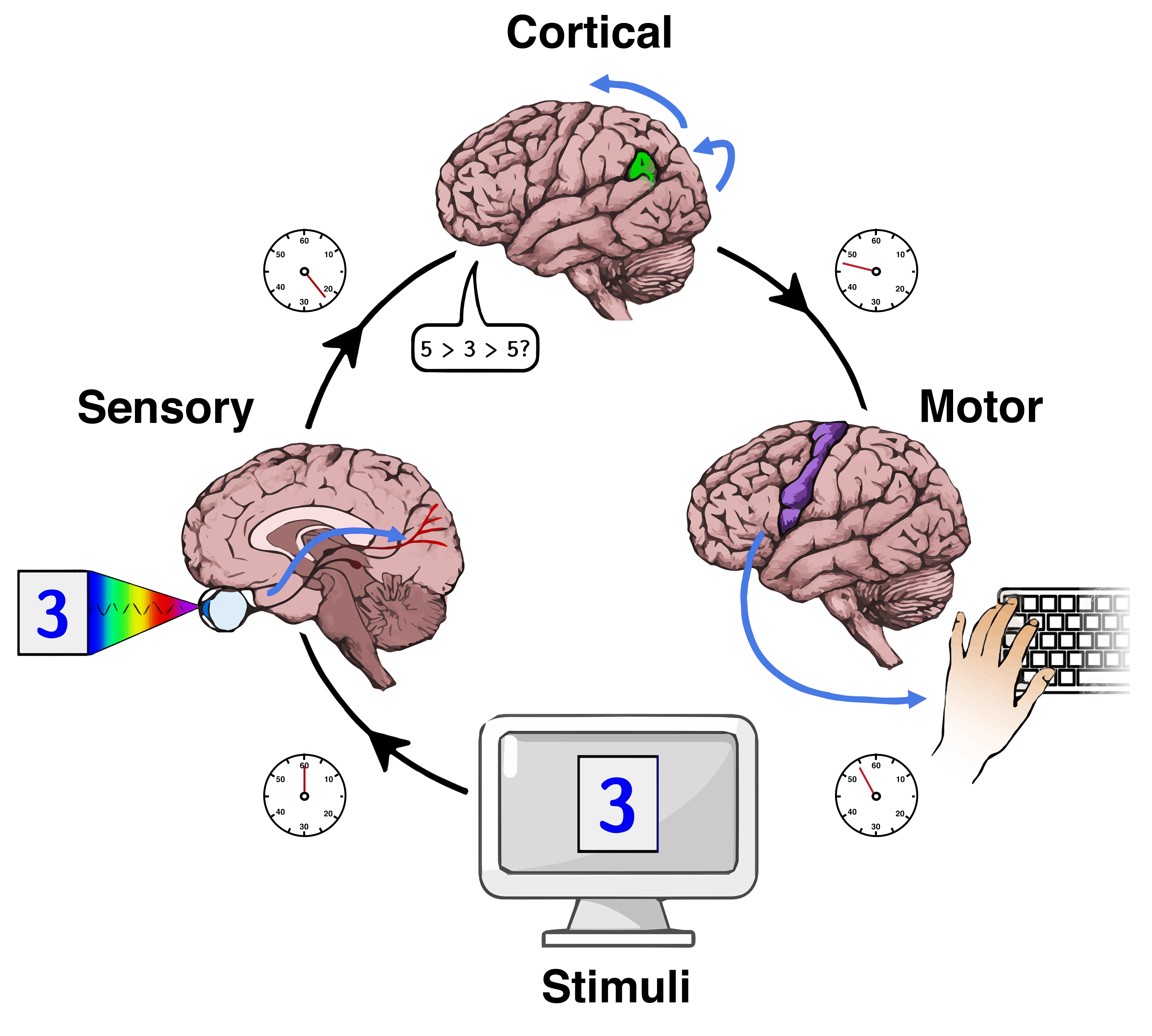
Reaction Time
Mental chronometry is the scientific study of processing speed or reaction time on cognitive tasks to infer the content, duration, and temporal sequencing of mental operations. Reaction time (RT; also referred to as "response time") is measured by the elapsed time between stimulus onset and an individual's response on elementary cognitive tasks (ECTs), which are relatively simple perceptual-motor tasks typically administered in a laboratory setting. Mental chronometry is one of the core methodological paradigms of human experimental, cognitive, and differential psychology, but is also commonly analyzed in psychophysiology, cognitive neuroscience, and behavioral neuroscience to help elucidate the biological mechanisms underlying perception, attention, and decision-making in humans and other species. Mental chronometry uses measurements of elapsed time between sensory stimulus onsets and subsequent behavioral responses to study the time course of information processing in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decay Theory
The Decay theory is a theory that proposes that memory fades due to the mere passage of time. Information is therefore less available for later retrieval as time passes and memory, as well as memory strength, wears away. When an individual learns something new, a neurochemical "memory trace" is created. However, over time this trace slowly disintegrates. Actively memory rehearsal, rehearsing information is believed to be a major factor counteracting this temporal decline. It is widely believed that neurons die off gradually as we age, yet some older memories can be stronger than most recent memories. Thus, decay theory mostly affects the short-term memory system, meaning that older memories (in long-term memory) are often more resistant to shocks or physical attacks on the brain. It is also thought that the passage of time alone cannot cause forgetting, and that decay theory must also take into account some processes that occur as more time passes. History The term "decay theory" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction between sense and reference. Sense is given by the ideas and concepts associated with an expression while reference is the object to which an expression points. Semantics contrasts with syntax, which studies the rules that dictate how to create grammatically correct sentences, and pragmatics, which investigates how people use language in communication. Lexical semantics is the branch of semantics that studies word meaning. It examines whether words have one or several meanings and in what lexical relations they stand to one another. Phrasal semantics studies the meaning of sentences by exploring the phenomenon of compositionality or how new meanings can be created by arranging words. Formal semantics (natural language), Formal semantics relies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysemy
Polysemy ( or ; ) is the capacity for a Sign (semiotics), sign (e.g. a symbol, morpheme, word, or phrase) to have multiple related meanings. For example, a word can have several word senses. Polysemy is distinct from ''monosemy'', where a word has a single meaning. Polysemy is distinct from homonymy—or homophone, homophony—which is an Accident (philosophy), accidental similarity between two or more words (such as ''bear'' the animal, and the verb wikt:bear#Etymology 2, ''bear''); whereas homonymy is a mere linguistic coincidence, polysemy is not. In discerning whether a given set of meanings represent polysemy or homonymy, it is often necessary to look at the history of the word to see whether the two meanings are historically related. Lexicography, Dictionary writers often list polysemes (words or phrases with different, but related, senses) in the same entry (that is, under the same headword) and enter homonyms as separate headwords (usually with a numbering convention such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroop Effect
In psychology, the Stroop effect is the delay in reaction time between neutral and incongruent stimuli. The effect has been used to create a psychological test (the Stroop test) that is widely used in clinical practice and investigation. A basic task that demonstrates this effect occurs when there is an incongruent mismatch between the word for a color (e.g., ''blue'', ''green'', or ''red'') and the font color it is printed in (e.g., the word ''red'' printed in a blue font). Typically, when a person is asked to name the font color for each word in a series of words, they take longer and are more prone to errors when words for colors are printed in incongruous font colors (e.g., it generally takes longer to say "blue" in response to the word ''red'' in a blue font, than in response to a neutral word of the same length in a blue font, like ''kid''). The effect is named after John Ridley Stroop, who first published the effect in English in 1935. The effect had previously been publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroop Task1
Stroop is a Dutch surname. Notable people with the name include: * John Ridley Stroop (1897–1973), American psychologist, after whom the Stroop effect In psychology, the Stroop effect is the delay in reaction time between neutral and incongruent stimuli. The effect has been used to create a psychological test (the Stroop test) that is widely used in clinical practice and investigation. A basic ... was named * Jürgen Stroop (1895–1952), German SS commander responsible for the liquidation of the Warsaw Ghetto; executed for war crimes * Paul D. Stroop (1904–1995), officer of the United States Navy and a naval aviator See also * Stroup (other) {{surname, Stroop Dutch-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Processing Theory
Information processing theory is the approach to the study of cognitive development evolved out of the American experimental tradition in psychology. Developmental psychologists who adopt the information processing perspective account for mental development in terms of maturational changes in basic components of a child's mind. The theory is based on the idea that humans process the information they receive, rather than merely responding to stimuli. This perspective uses an analogy to consider how the mind works like a computer. In this way, the mind functions like a biological computer responsible for analyzing information from the environment. According to the standard information-processing model for mental development, the mind's machinery includes attention mechanisms for bringing information in, working memory for actively manipulating information, and long-term memory for passively holding information so that it can be used in the future. This theory addresses how as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, also known as neural plasticity or just plasticity, is the ability of neural networks in the brain to change through neurogenesis, growth and reorganization. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to reorganize and rewire its neural connections, enabling it to adapt and function in ways that differ from its prior state. This process can occur in response to learning new skills, experiencing environmental changes, recovering from injuries, or adapting to sensory or cognitive deficits. Such adaptability highlights the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of the brain, even into adulthood. These changes range from individual neuron pathways making new connections, to systematic adjustments like cortical remapping or neural oscillation. Other forms of neuroplasticity include homologous area adaptation, cross modal reassignment, map expansion, and compensatory masquerade. Examples of neuroplasticity include neural circuit, circuit and network changes that result fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Facilitation
Neural facilitation, also known as paired-pulse facilitation (PPF), is a phenomenon in neuroscience in which postsynaptic potentials (PSPs) ( EPPs, EPSPs or IPSPs) evoked by an impulse are increased when that impulse closely follows a prior impulse. PPF is thus a form of short-term synaptic plasticity. The mechanisms underlying neural facilitation are exclusively pre-synaptic; broadly speaking, PPF arises due to increased presynaptic concentration leading to a greater release of neurotransmitter-containing synaptic vesicles. Neural facilitation may be involved in several neuronal tasks, including simple learning, information processing, and sound-source localization. Mechanisms Overview plays a significant role in transmitting signals at chemical synapses. Voltage-gated channels are located within the presynaptic terminal. When an action potential invades the presynaptic membrane, these channels open and enters. A higher concentration of enables synaptic vesicles to fuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Effect
The Simon effect is the difference in accuracy or reaction time between trials in which stimulus and response are on the same side and trials in which they are on opposite sides, with responses being generally slower and less accurate when the stimulus and response are on opposite sides. The task is similar in concept to the ''Stroop Effect''. The Stroop Color and Word Test (SCWT) can be used to assess the ability to inhibit cognitive interference that occurs when the processing of a specific stimulus feature impedes the simultaneous processing of a second stimulus attribute. The Simon effect is an extension of this effect, but the interference in this task is generated by spatial features rather than features of the stimuli themselves. Original experiment In J. R. Simon's original study, two lights (the stimulus) were placed on a rotating circular panel. This device would be rotated at varying degrees (away from the horizontal plane). Simon wished to see if an alteration of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interference Theory
The interference theory is a theory regarding human memory. Interference occurs in learning. The notion is that memories encoded in long-term memory (LTM) are forgotten and cannot be retrieved into short-term memory (STM) because either memory could interfere with the other.Edwards, W. H. (2010). ''Motor Learning and Control: From Theory to Practice''. Belmont, CA: Cengage Learning. There is an immense number of encoded memories within the storage of LTM. The challenge for memory retrieval is recalling the specific memory and working in the temporary workspace provided in STM. Retaining information regarding the relevant time of encoding memories into LTM influences interference strength. There are two types of interference effects: proactive and retroactive interference. History John A. Bergström is credited with conducting the first study regarding interference in 1892. His experiment was similar to the Stroop task and required subjects to sort two decks of cards with words i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |